外观
vnode中的shapeFlag和patchFlag
shapeFLag
vnode的shapeFLag属性使用二进制的方式描述了组件的类型。shapeFLag的值的类型是个枚举:
ts
export const enum ShapeFlags {
ELEMENT = 1, // 表示一个普通的HTML元素
FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT = 1 << 1, // 函数式组件
STATEFUL_COMPONENT = 1 << 2, // 有状态组件
TEXT_CHILDREN = 1 << 3, // 子节点是文本
ARRAY_CHILDREN = 1 << 4, // 子节点是数组
SLOTS_CHILDREN = 1 << 5, // 子节点是插槽
TELEPORT = 1 << 6, // 表示vnode描述的是个teleport组件
SUSPENSE = 1 << 7, // 表示vnode描述的是个suspense组件
COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE = 1 << 8, // 表示需要被keep-live的有状态组件
COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE = 1 << 9, // 已经被keep-live的有状态组件
COMPONENT = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT | ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT // 组件,有状态组件和函数式组件的统称
}
一个vnode可以是多个不同的的类型,如:
ts
vnode.shapeFlag = ShapeFlags.ELEMENT | ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN
判断某个vnode的类型时可以使用vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT的方式进行判断,或判断vnode是否同时是多种类型vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT | ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN
patchFlag
patchFlag是在编译template模板时,给vnode添加的一个标识信息,这个标识信息反映了vnode的哪些部位绑定了动态值,这样在runtime阶段,可以根据patchFlag判断出哪些内容需要更新,实现靶向更新。
patchFlag的类型和shapeFLag相同,也是个枚举类型:
ts
export const enum PatchFlags {
// 表示vnode具有动态textContent的元素
TEXT = 1,
// 表示vnode具有动态的class
CLASS = 1 << 1,
// 表示具有动态的style
STYLE = 1 << 2,
// 表示具有动态的非class和style的props
PROPS = 1 << 3,
// 表示props具有动态的key,与CLASS、STYLE、PROPS冲突
FULL_PROPS = 1 << 4,
// 表示有监听事件(在同构期间需要添加)
HYDRATE_EVENTS = 1 << 5,
// 表示vnode是个children顺序不会改变的fragment
STABLE_FRAGMENT = 1 << 6,
// 表示children带有key的fragment
KEYED_FRAGMENT = 1 << 7,
// 表示children没有key的fragment
UNKEYED_FRAGMENT = 1 << 8,
// 表示vnode只需要非props的patch。例如只有标签中只有ref或指令
NEED_PATCH = 1 << 9,
// 表示vnode存在动态的插槽。例如动态的插槽名
DYNAMIC_SLOTS = 1 << 10,
// 表示用户在模板的根级别存在注释而创建的片段,这是一个仅用于开发的标志,因为注释在生产中被剥离
DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT = 1 << 11,
// 以下都是一些特殊的flag,它们不能使用位运算进行匹配
// 表示vnode经过静态提升
HOISTED = -1,
// diff算法应该退出优化模式
BAIL = -2
}
以下是针对不同patchFlag的一些示例
PatchFlags.TEXT
vue
<script setup>
import {ref} from 'vue';
const msg = ref('Hello')
</script>
<template>
<h1>{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>
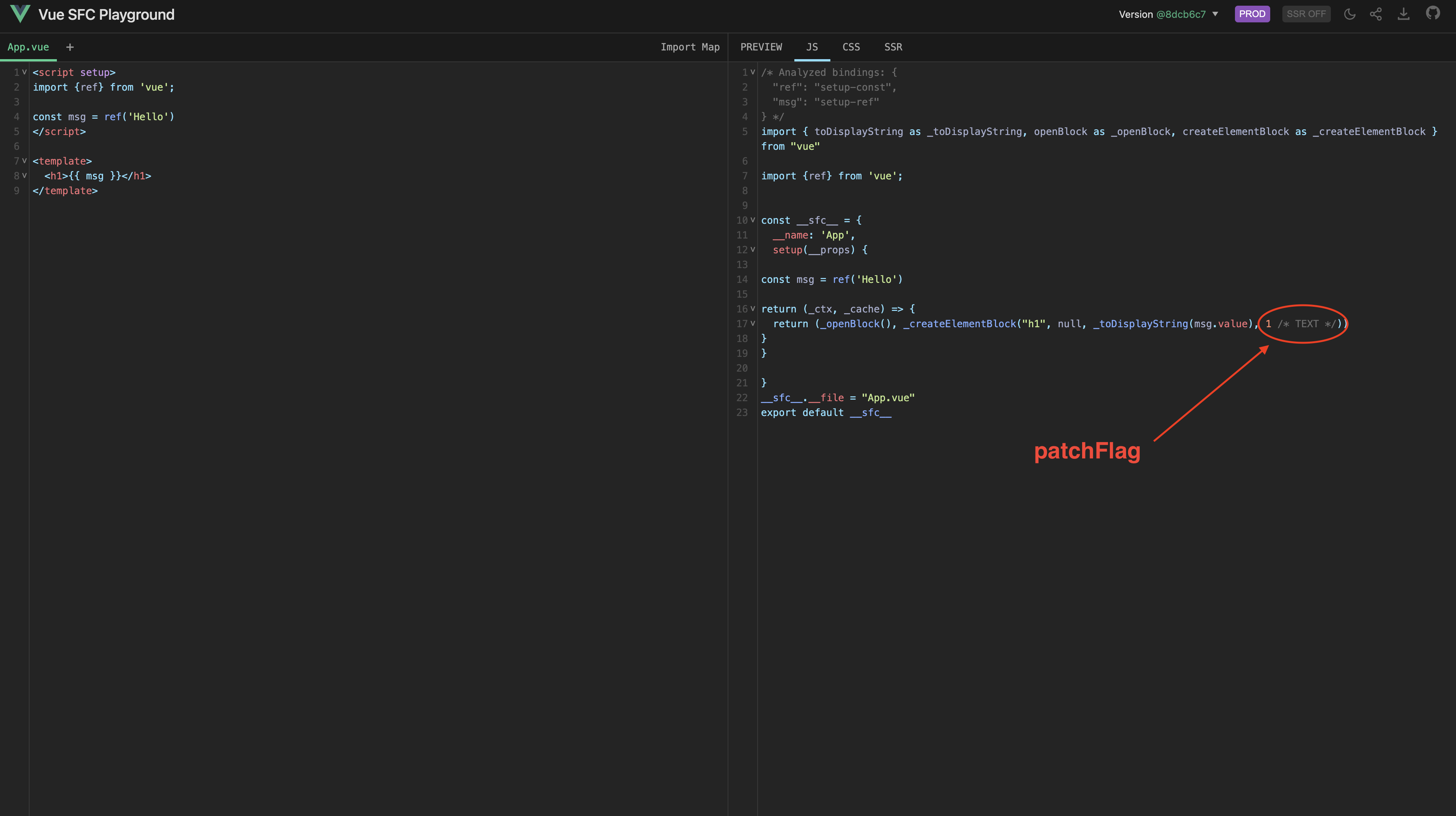
<h1>标签中只绑定了动态的textContext,所以以上模板转为vnode之后,patchFlag为PatchFlags.TEXT。
你可以将代码复制在Vue SFC Playground中进行测试。
PatchFlags.CLASS、PatchFlags.STYLE
vue
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('Hello')
const style = reactive({ fontSize: '24px' })
const classObj = ref('red')
</script>
<template>
<h1 :class="classObj" :style="style">{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>
<style>
.red {
color: red;
}
</style>
<h1>标签绑定了动态的class、style、textContent,所以patchFlag为PatchFlags.TEXT | PatchFlags.CLASS | PatchFlags.STYLE
PatchFlags.PROPS
vue
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('Hello')
</script>
<template>
<h1 :title="msg">{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>
<h1>标签绑定了动态的title、textContent,所以patchFlag为PatchFlags.TEXT | PatchFlags.PROPS
PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS
vue
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('Hello')
const dynamicKey = ref('foo')
</script>
<template>
<h1 :[dynamicKey]="msg" >{{ msg }}</h1>
</template>
<h1>标签绑定了动态的textContent和一个动态的dynamicKey属性,所以patchFlag为PatchFlags.TEXT | PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS
PatchFlags.STABLE_FRAGMENT
vue
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('Hello')
function handleClick() {
classObj.red = !classObj.red
}
</script>
<template>
<h1 @click="handleClick" >{{ msg }}</h1>
<span>text</span>
</template>
<template>标签中有多个根标签,会创建一个Fragment类型的vnode,因为<h1>、<span>标签的顺序始终不会发生变化,所以Fragment类型的vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.STABLE_FRAGMENT。
PatchFlags.KEYED_FRAGMENT
vue
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const data = reactive([ 'one', 'two', 'three' ])
</script>
<template>
<span v-for="item in data" :key="item">{{ item }}</span>
</template>
<template>标签中有多个根标签,而且每个标签都有key,所以Fragment类型的vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.KEYED_FRAGMENT
PatchFlags.UNKEYED_FRAGMENT
vue
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
const data = reactive([ 'one', 'two', 'three' ])
</script>
<template>
<span v-for="item in data">{{ item }}</span>
</template>
<template>标签中有多个根标签,但标签都没有key,所以Fragment类型的vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.UNKEYED_FRAGMENT
PatchFlags.NEED_PATCH
vue
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const dom = ref()
const vFocus = {
mounted: (el) => el.focus()
}
</script>
<template>
<input v-focus />
<h1 ref="dom">Hello</h1>
</template>
<input/>和<h1>对应的vnode的patchFlag均为PatchFlags.NEED_PATCH
PatchFlags.DYNAMIC_SLOTS
vue
<template>
<Comp>
<template #one v-if="ok">hello</template>
</Comp>
<Comp>
<template v-for="name in list" #[name]>{{ name }}</template>
</Comp>
</template>
两个<Comp>中的slot都可能发生变化,所以它们对应的vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.DYNAMIC_SLOTS
PatchFlags.DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT
vue
<template>
<!-- title -->
<h1>Hello</h1>
</template>
<template>的根级存在注释,同时有多个标签,便签顺序不会变化,所以根vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.STABLE_FRAGMENT | PatchFlags.DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT
PatchFlags.HOISTED
vue
<template>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<p>test</p>
</template>
<h1>和<p>标签都是两个静态标签,所以它们对应的vnode的patchFlag为PatchFlags.HOISTED
如果只存在一个静态标签,这个静态标签对应的vnode的patchFlag不是PatchFlags.HOISTED,而是默认的0
vue
<template>
<h1>Hello</h1>
</template>