外观
组件的更新
如何触发组件的更新?
我们知道,组件的某些数据发生变化后,对应DOM中的数据也需要发生变化。例如下面这个例子:
当我们点击按钮count加1,同时DOM发生更新。我们并没有取操作DOM,它是如何更新的呢?
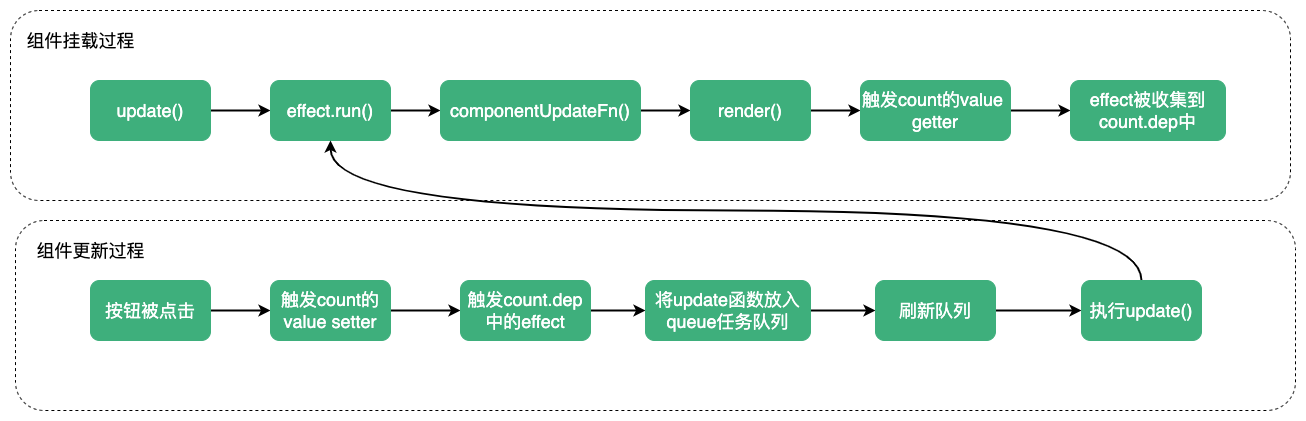
在前文介绍组件的加载过程时,我们知道在组件挂载过程中会创建一个组件更新函数componentUpdateFn,并利用componentUpdateFn创建了一个ReactiveEffect实例。
ts
const setupRenderEffect: SetupRenderEffectFn = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
// ...
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))
// ...
}
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(
componentUpdateFn,
() => queueJob(update),
instance.scope // track it in component's effect scope
))
const update: SchedulerJob = (instance.update = () => effect.run())
// ...
update()
}
在组件挂载过程中,执行了effect.run,而在effect.run中会执行副作用函数componentUpdateFn进行依赖的收集:在componentUpdateFn中会执行组件的渲染函数render,而render的执行过程中,会触发某些响应式数据的get、has等拦截器,进而effect被收集。如果后续数据发生更新(如修改操作触发了响应式数据的set拦截器),则会触发effect,此时组件就会发生更新。
对于上面这个例子,其更新流程可简单用下面流程图进行表示。
现在我们了解了组件时如何被更新的,接下来,我们看下组件实际的更新过程。
组件更新过程
组件的更新会继续执行componentUpdateFn函数,我们继续从componentUpdateFn看:
ts
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// ...
} else { // 组件的更新
let { next, bu, u, parent, vnode } = instance
let originNext = next
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | null | undefined
if (__DEV__) {
pushWarningContext(next || instance.vnode)
}
// 在生命周期前挂钩期间不允许组件effect递归
toggleRecurse(instance, false)
if (next) { // 存在待更新的vnode(来自父组件的更新)
next.el = vnode.el
updateComponentPreRender(instance, next, optimized)
} else {
next = vnode
}
// 执行beforeUpdate钩子
if (bu) {
invokeArrayFns(bu)
}
// 执行onVnodeBeforeUpdate钩子
if ((vnodeHook = next.props && next.props.onVnodeBeforeUpdate)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parent, next, vnode)
}
// 执行hook:beforeUpdate钩子
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
instance.emit('hook:beforeUpdate')
}
// 恢复组件effect递归状态
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
// render
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
// 组件渲染函数渲染的最新vnode
const nextTree = renderComponentRoot(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
const prevTree = instance.subTree
// 更新组件的subTree为最新的vnode
instance.subTree = nextTree
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
// 调用patch更新
patch(
prevTree,
nextTree,
// 旧DOM的父节点
hostParentNode(prevTree.el!)!,
// 锚点
getNextHostNode(prevTree),
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
next.el = nextTree.el
if (originNext === null) {
// self-triggered update. In case of HOC, update parent component
// vnode el. HOC is indicated by parent instance's subTree pointing
// to child component's vnode
updateHOCHostEl(instance, nextTree.el)
}
// 将updated、onVnodeUpdated、hook:updated钩子放到后置任务队列
if (u) {
queuePostRenderEffect(u, parentSuspense)
}
// onVnodeUpdated
if ((vnodeHook = next.props && next.props.onVnodeUpdated)) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook!, parent, next!, vnode),
parentSuspense
)
}
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => instance.emit('hook:updated'),
parentSuspense
)
}
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
devtoolsComponentUpdated(instance)
}
if (__DEV__) {
popWarningContext()
}
}
}
当组件被挂载后,其组件实例的isMounted为true,所以在组件更新过程,就会进入instance.isMount分支。在更新时会先调用组件的一些更新前钩子beforeUpdate等,然后再调用renderComponentRoot方法获取最新的vnode,接着再调用patch,最后将更新后的一些钩子放到后置任务队列中。
对于上面的例子,通过renderComponentRoot执行render后,得到的最新的vnode的type为Fragment,这决定了在patch中进入哪个分支。
进入patch方法,根据n2.type的值,进入Fragment,执行processFragment。
processFragment
ts
const processFragment = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
const fragmentStartAnchor = (n2.el = n1 ? n1.el : hostCreateText(''))!
const fragmentEndAnchor = (n2.anchor = n1 ? n1.anchor : hostCreateText(''))!
let { patchFlag, dynamicChildren, slotScopeIds: fragmentSlotScopeIds } = n2
if (
__DEV__ &&
(isHmrUpdating || patchFlag & PatchFlags.DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT)
) {
patchFlag = 0
optimized = false
dynamicChildren = null
}
if (fragmentSlotScopeIds) {
slotScopeIds = slotScopeIds
? slotScopeIds.concat(fragmentSlotScopeIds)
: fragmentSlotScopeIds
}
if (n1 == null) {
// ...
} else {
if (
patchFlag > 0 &&
patchFlag & PatchFlags.STABLE_FRAGMENT &&
dynamicChildren &&
n1.dynamicChildren
) { // patch block,由模板转成的render函数会生成block
patchBlockChildren(
n1.dynamicChildren,
dynamicChildren,
container,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds
)
if (__DEV__ && parentComponent && parentComponent.type.__hmrId) {
traverseStaticChildren(n1, n2)
} else if (
n2.key != null ||
(parentComponent && n2 === parentComponent.subTree)
) {
traverseStaticChildren(n1, n2, true /* shallow */)
}
} else { // 普通patch
patchChildren(
n1,
n2,
container,
fragmentEndAnchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
}
}
在processFragment中进入更新分支后,又分为两个分支:block分支及普通patch。其中block是用来处理Block节点的(被编译器编译后的render函数的返回值)。
此处由于我们使用h渲染函数进行的渲染,所以此处会进入patchChildren。
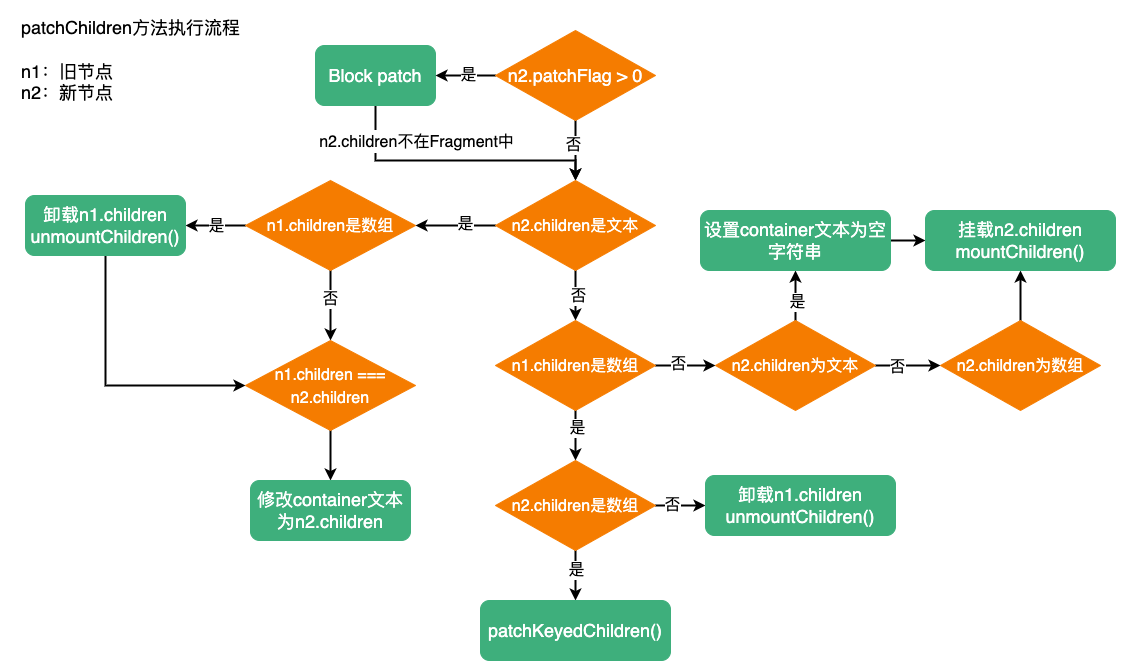
patchChildren
patchChildren:
ts
const patchChildren: PatchChildrenFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized = false
) => {
const c1 = n1 && n1.children
const prevShapeFlag = n1 ? n1.shapeFlag : 0
const c2 = n2.children
const { patchFlag, shapeFlag } = n2
// 此分支用来处理Block
// 对于渲染函数返回的vnode,patchFlag为0
if (patchFlag > 0) {
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.KEYED_FRAGMENT) {
patchKeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
return
} else if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.UNKEYED_FRAGMENT) {
// unkeyed
patchUnkeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
return
}
}
// children有三种可能:文本、数组或没有children
// 新节点的children是文本
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
// 如果旧节点的children是数组,会卸载旧节点的children
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
unmountChildren(c1 as VNode[], parentComponent, parentSuspense)
}
// 新旧子节点不一致,直接修改container的文本
if (c2 !== c1) {
hostSetElementText(container, c2 as string)
}
} else {
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) { // 如果旧节点的children是数组
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) { // 新节点的children也是数组
// two arrays, cannot assume anything, do full diff
patchKeyedChildren(
c1 as VNode[],
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else { // 没有新的children,卸载旧vnode的children
unmountChildren(c1 as VNode[], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
}
} else {
// prev children was text OR null
// new children is array OR null
if (prevShapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) { // 旧节点的children是文本,直接设置为空字符串
hostSetElementText(container, '')
}
// 挂载新节点children
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(
c2 as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
}
}
}
patchChildren中,首先判断如果新节点的patchFlag > 0并且新节点的children在Fragment中,则会按新旧节点children都为数组处理。
如果新节点children为文本,旧节点children为数组时,则需要卸载旧节点的chidlren,否则直接更新container的文本为新节点的children即可。
如果旧节点children是数组,新节点children也是数组,则调用patchKeyedChildren进行全量diff;如果新节点没有children,直接卸载旧节点chidlren即可。
如果旧节点children为空或文本,那么设置container内容为空即可;如果新节点children树数组,则需要挂载新节点的children。
patchChildren流程:
回到上面的例子中,进入patchChildren后,由于n1和n2的children都是数组,所以会调用patchKeyedChildren进行子节点的全量patch。
进入patchKeyedChildren就是核心的Diff过程了,这里对Diff算法单独开启了一篇文章,请参考:vue3 Diff算法。
这里针对该示例,简单描述一下Diff过程。
在patchKeyedChildren中,处理前置节点时,c1与c2中新旧节点进行对位patch,即patch(c1[0], c2[0])、patch(c1[1], c2[1])、patch(c1[2], c2[2])。
patch(c1[0], c2[0])的过程,由于c2[0].shapeFlag = ShapeFlag.ELEMENT | ShapeFlag.TEXT_CHILDREN,所以进入processElement,在processElement由于n1不为空,所以执行patchElement。
patchElement
patchElement处理新旧HTML节点之间的更新。
ts
const patchElement = (
n1: VNode,
n2: VNode,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
// 复用旧节点的DOM
const el = (n2.el = n1.el!)
let { patchFlag, dynamicChildren, dirs } = n2
// #1426 take the old vnode's patch flag into account since user may clone a
// compiler-generated vnode, which de-opts to FULL_PROPS
// n2可能是通过n1克隆来的,cloneVnode的过程,如果传入额外的props,会使patchFlag中添加PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS
// 所以这里判断如果旧节点中存在PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS,则添加PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS
patchFlag |= n1.patchFlag & PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS
const oldProps = n1.props || EMPTY_OBJ
const newProps = n2.props || EMPTY_OBJ
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | undefined | null
// disable recurse in beforeUpdate hooks
parentComponent && toggleRecurse(parentComponent, false)
// 执行新节点的onVnodeBeforeUpdate钩子
if ((vnodeHook = newProps.onVnodeBeforeUpdate)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, n2, n1)
}
// 执行新节点的指令中的beforeUpdate钩子
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(n2, n1, parentComponent, 'beforeUpdate')
}
parentComponent && toggleRecurse(parentComponent, true)
if (__DEV__ && isHmrUpdating) {
patchFlag = 0
optimized = false
dynamicChildren = null
}
const areChildrenSVG = isSVG && n2.type !== 'foreignObject'
// 如果存在dynamicChildren执行patchBlockChildren
// 否则如果optimized为false执行patchChildren
if (dynamicChildren) {
patchBlockChildren(
n1.dynamicChildren!,
dynamicChildren,
el,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
areChildrenSVG,
slotScopeIds
)
if (__DEV__ && parentComponent && parentComponent.type.__hmrId) {
traverseStaticChildren(n1, n2)
}
} else if (!optimized) {
patchChildren(
n1,
n2,
el,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
areChildrenSVG,
slotScopeIds,
false
)
}
// 开始更新props
// 快速路径
if (patchFlag > 0) {
// 节点存在动态的key需要调用patchProps进行全量diff
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS) {
patchProps(
el,
n2,
oldProps,
newProps,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
} else {
// 更新 class
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.CLASS) {
if (oldProps.class !== newProps.class) {
hostPatchProp(el, 'class', null, newProps.class, isSVG)
}
}
// 更新style
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.STYLE) {
hostPatchProp(el, 'style', oldProps.style, newProps.style, isSVG)
}
// 更新除了class、style的其他props,不包括动态key
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.PROPS) {
// dynamicProps中保存着哪些key是动态属性
const propsToUpdate = n2.dynamicProps!
for (let i = 0; i < propsToUpdate.length; i++) {
const key = propsToUpdate[i]
const prev = oldProps[key]
const next = newProps[key]
// 新旧节点props[key]不同或key是value时进行props的更新
if (next !== prev || key === 'value') {
hostPatchProp(
el,
key,
prev,
next,
isSVG,
n1.children as VNode[],
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
unmountChildren
)
}
}
}
}
// 更新text
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.TEXT) {
// 新旧节点children不同才会更新
if (n1.children !== n2.children) {
hostSetElementText(el, n2.children as string)
}
}
} else if (!optimized && dynamicChildren == null) { // 非优化模式,props进行全量diff
patchProps(
el,
n2,
oldProps,
newProps,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
}
// 将一些更新后需要触发的钩子放到
// 注意这里没有组件的update钩子,因为在patchElement中处理的HTML节点,不是组件
if ((vnodeHook = newProps.onVnodeUpdated) || dirs) {
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
vnodeHook && invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, n2, n1)
dirs && invokeDirectiveHook(n2, n1, parentComponent, 'updated')
}, parentSuspense)
}
}
patchElement主要包含四个步骤:
- 触发
onVnodeBeforeUpdate和指令的beforeUpdate钩子函数 patch孩子节点- 更新
props。如果patchFlag > 0,会进入快速路径,根据patchFlag更新对应的props;否则进行props全量diff。 - 将
onVnodeUpdated和指令的updated函数方到后置任务队列
patchProps
patchProps会对新旧节点的props进行全量的diff。
ts
const patchProps = (
el: RendererElement,
vnode: VNode,
oldProps: Data,
newProps: Data,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean
) => {
// 新旧props不相等时才会更新
if (oldProps !== newProps) {
// 遍历新props的key
for (const key in newProps) {
// 空字符串及一些key、ref、onVnodeBeforeMount等内置props跳过更新
if (isReservedProp(key)) continue
const next = newProps[key]
const prev = oldProps[key]
// 新旧props值不同并且key不等于value
// 延迟更新value
if (next !== prev && key !== 'value') {
hostPatchProp(
el,
key,
prev,
next,
isSVG,
vnode.children as VNode[],
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
unmountChildren
)
}
}
if (oldProps !== EMPTY_OBJ) {
// 遍历旧节点,移除不在新props中的属性
for (const key in oldProps) {
if (!isReservedProp(key) && !(key in newProps)) {
hostPatchProp(
el,
key,
oldProps[key],
null,
isSVG,
vnode.children as VNode[],
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
unmountChildren
)
}
}
}
// 更新value
if ('value' in newProps) {
hostPatchProp(el, 'value', oldProps.value, newProps.value)
}
}
}
回到示例中,此时进入patchElement的新旧节点分别为{type:'button', children: 'add count'}、{type:'button', children: 'add count'},新节点中并不存在dynamicChildren属性,所以继续patchChildren,在patchChildren中根据新节点shapeFlags属性,需要更新节点的文本内容,但因为button内容其实未发生变化,所以不会发生更新操作。patch(c1[0], c2[0])中没有发生任何更新。
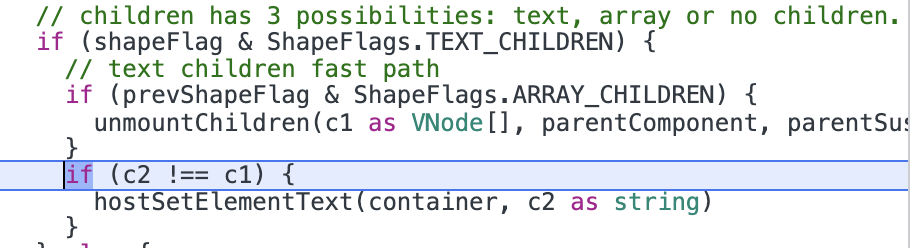
patch(c1[1], c2[1])和patch(c1[0], c2[0])是相同的,只不过这一次新旧节点的children不同了,所以这次会更新div的内容为1。
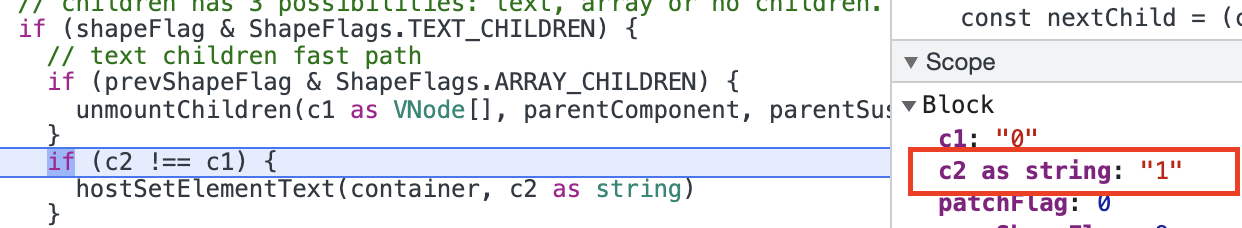
patch(c1[2], c2[2])和patch(c1[0], c2[0])相同,不会发生更新。
至此,DOM的内容更新到最新状态。
使用template模板
前面counter中我们使用setup返回渲染函数来渲染组件,如果我们改用template,更新流程是否和使用渲染函数一致呢?下面我们使用template替换渲染函数,再分析更新流程。
和使用渲染函数一样,在点击按钮后,同样会调用通过编译器生成的渲染函数,生成最新的vnode(这里其实是个Block),然后进行新旧vnode的patch
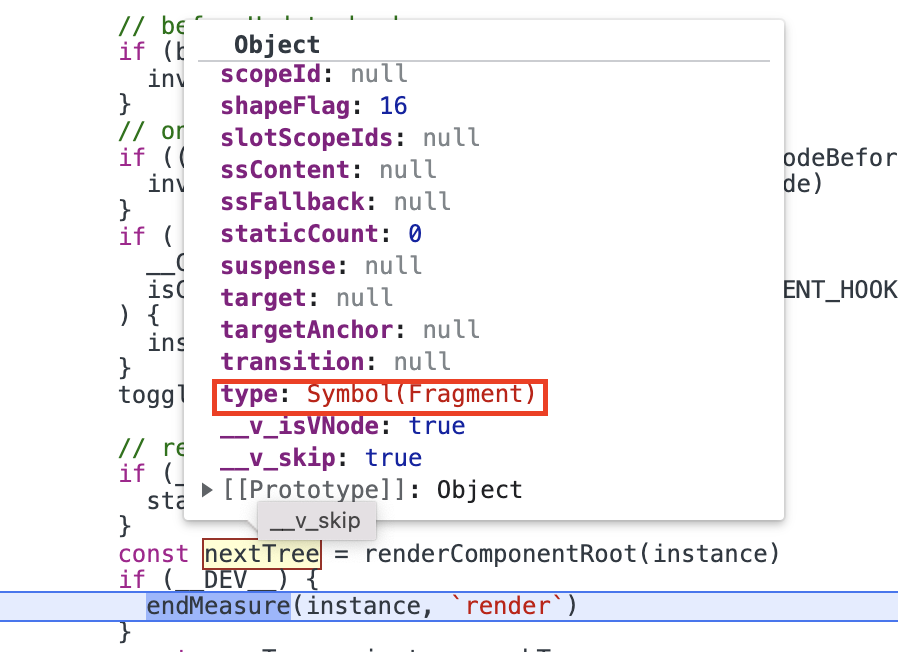
在进入patch后,因为新vnode的type为Fragment,所以进入processFragment。进入processFragment后,由于新节点的patchFlag为PatchFlag.STABLE_FRAGMENT,并且新旧节点都存在dynamicChildren属性,所以会执行patchBlockChildren方法。
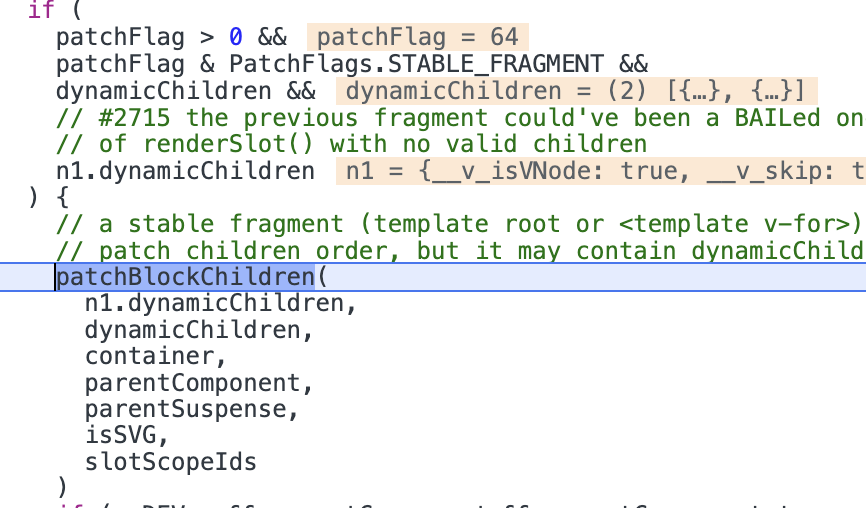
此时n1.dynamicChildren与n2.dynamicChildren中都有两个动态节点(第二个div中没有动态内容,所以不会被收集到dynamicChildren中)。分别为button与第一个div。
patchBlockChildren
ts
const patchBlockChildren: PatchBlockChildrenFn = (
oldChildren,
newChildren,
fallbackContainer,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds
) => {
for (let i = 0; i < newChildren.length; i++) {
const oldVNode = oldChildren[i]
const newVNode = newChildren[i]
// 确定需要打补丁的容器
const container =
// oldVNode may be an errored async setup() component inside Suspense
// which will not have a mounted element
oldVNode.el &&
// - In the case of a Fragment, we need to provide the actual parent
// of the Fragment itself so it can move its children.
(oldVNode.type === Fragment ||
// - In the case of different nodes, there is going to be a replacement
// which also requires the correct parent container
!isSameVNodeType(oldVNode, newVNode) ||
// - In the case of a component, it could contain anything.
oldVNode.shapeFlag & (ShapeFlags.COMPONENT | ShapeFlags.TELEPORT))
? hostParentNode(oldVNode.el)!
: // In other cases, the parent container is not actually used so we
// just pass the block element here to avoid a DOM parentNode call.
fallbackContainer
patch(
oldVNode,
newVNode,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
true
)
}
}
patchBlockChildren中会遍历dynamicChildren,进行对位patch。
patch(oldButton, newButton)、patch(oldDiv, newDiv)的过程和使用h渲染函数时是一致的,这里就不再细述了。
你会发现但当我们改用template替换渲染函数后,第二个div并没有经过patch。这就是vue3编译器优化的效果。template经过编译器编译的渲染函数中,生成的组件的根节点是个Block,Block中的dynamicChildren包含了子代所有的动态节点,在发生更新操作时,直接patch dynamicChildren中的动态节点,避免了静态节点之间的patch。
对于Block的介绍,可以参考:Block
子组件如何触发更新?
下面我们在counter中添加一个子组件ComA,它接收一个count,当点击按钮,子组件也会进行更新,接下来看下子组件是如何触发更新。
ComA对应的vnode在patch阶段会进入shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT分支执行processComponent方法。
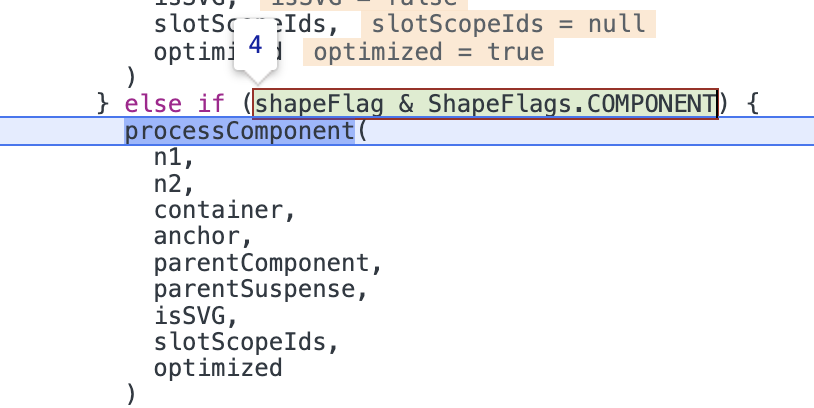
在processComponent中因为新旧节点不为空,所以执行updateComponent。
updateComponent
ts
const updateComponent = (n1: VNode, n2: VNode, optimized: boolean) => {
const instance = (n2.component = n1.component)!
// 组件需要更新
if (shouldUpdateComponent(n1, n2, optimized)) {
if (
__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ &&
instance.asyncDep &&
!instance.asyncResolved
) { // Suspense更新
if (__DEV__) {
pushWarningContext(n2)
}
updateComponentPreRender(instance, n2, optimized)
if (__DEV__) {
popWarningContext()
}
return
} else {
// 使instance.next指向新节点
instance.next = n2
// 如果更新函数已经在队列中了,需要从队列中删除(前提是位置在当前正在执行的任务之后)
invalidateJob(instance.update)
// 执行组件实例的更新函数
instance.update()
}
} else { // 组件不需要更新
// 将旧节点的el复制给新节点
n2.el = n1.el
// 将instance.vnode指向新节点
instance.vnode = n2
}
}
在updateComponent中首先要利用shouldUpdateComponent检查组件是否需要更新。如果组件不需要更新,只需将旧节点的el替换新节点的el,然后将组件实例的vnode指向最新的节点即可。如果组件需要更新,则会分两种情况:Suspense更新、普通组件更新。
对于Suspense组件的更新,会调用updateComponentPreRender方法,普通组件的更新会调用组件实例的update函数,即组件的更新函数。
shouldUpdateComponent源码
ts
export function shouldUpdateComponent(
prevVNode: VNode,
nextVNode: VNode,
optimized?: boolean
): boolean {
const { props: prevProps, children: prevChildren, component } = prevVNode
const { props: nextProps, children: nextChildren, patchFlag } = nextVNode
const emits = component!.emitsOptions
if (__DEV__ && (prevChildren || nextChildren) && isHmrUpdating) {
return true
}
// vnode中存在运行时指令或transition强制刷新
if (nextVNode.dirs || nextVNode.transition) {
return true
}
// 优化模式并且新节点patchFlag大于等于0
if (optimized && patchFlag >= 0) {
// 动态的插槽需要更新
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.DYNAMIC_SLOTS) {
return true
}
// props具有动态的key
if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.FULL_PROPS) {
// 如果旧节点不存在props,是否更新取决于新节点中是否存在props
if (!prevProps) {
return !!nextProps
}
// 新旧节点都存在props,对比props中的每个key
return hasPropsChanged(prevProps, nextProps!, emits)
}
// 具有动态的非style、class props
else if (patchFlag & PatchFlags.PROPS) {
// 遍历dynamicProps,检查是否有属性变化
// dynamicProps中保存了哪些属性是动态的
const dynamicProps = nextVNode.dynamicProps!
for (let i = 0; i < dynamicProps.length; i++) {
const key = dynamicProps[i]
if (
nextProps![key] !== prevProps![key] &&
!isEmitListener(emits, key)
) {
return true
}
}
}
}
// 此分支使用手动渲染函数所产生的vnode
else {
// 如果旧节点存在children或新节点存在children
if (prevChildren || nextChildren) {
// 新节点不存在children或新节点存在children但不是稳定的
if (!nextChildren || !(nextChildren as any).$stable) {
return true
}
}
// 新旧props相同,则不需要更新
if (prevProps === nextProps) {
return false
}
// 如果旧节点不存在props,是否更新取决于新节点中是否存在props
if (!prevProps) {
return !!nextProps
}
// 旧节点存在props,新节点不存在props,需要更新
if (!nextProps) {
return true
}
return hasPropsChanged(prevProps, nextProps, emits)
}
return false
}
回到示例中,在使用shouldUpdateComponent函数检查是否需要更新组件时,因为旧props.key为0,而新props.key为1,所以组件需要更新。
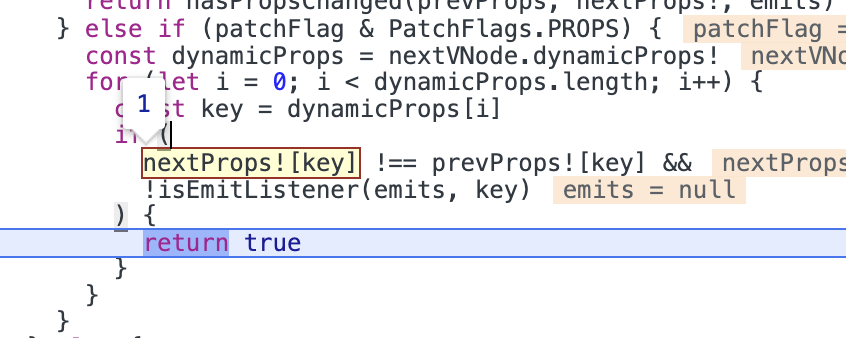
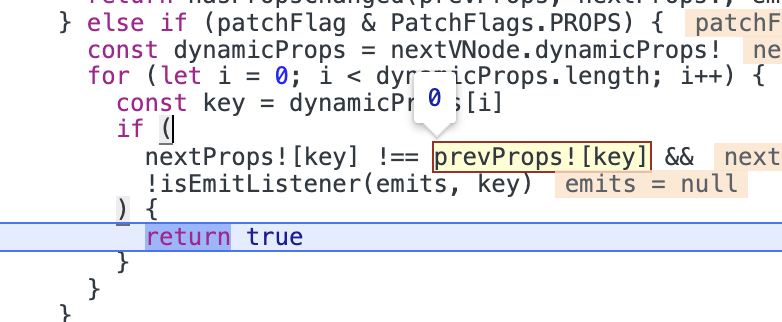
所以在updateComponent中会调用instance.update函数进行更新。
综上可以看出,子组件是否需要更新,取决于子组件中是否存在自定义的指令或transition或子组件中的props是否发生变化。
Teleport的更新
ts
export const TeleportImpl = {
__isTeleport: true,
process(
n1: TeleportVNode | null,
n2: TeleportVNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
internals: RendererInternals
) {
const {
mc: mountChildren,
pc: patchChildren,
pbc: patchBlockChildren,
o: { insert, querySelector, createText, createComment }
} = internals
const disabled = isTeleportDisabled(n2.props)
let { shapeFlag, children, dynamicChildren } = n2
if (__DEV__ && isHmrUpdating) {
optimized = false
dynamicChildren = null
}
if (n1 == null) {
// ...
} else {
// update content
n2.el = n1.el
const mainAnchor = (n2.anchor = n1.anchor)!
const target = (n2.target = n1.target)!
const targetAnchor = (n2.targetAnchor = n1.targetAnchor)!
// 旧节点中是否已经被禁用
const wasDisabled = isTeleportDisabled(n1.props)
const currentContainer = wasDisabled ? container : target
const currentAnchor = wasDisabled ? mainAnchor : targetAnchor
isSVG = isSVG || isTargetSVG(target)
if (dynamicChildren) {
patchBlockChildren(
n1.dynamicChildren!,
dynamicChildren,
currentContainer,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds
)
// 即使在block tree模式下
// 我们也需要确保传送中的所有根级节点都继承以前的 DOM 引用
// 以便它们可以在未来的补丁中移动。
traverseStaticChildren(n1, n2, true)
} else if (!optimized) {
patchChildren(
n1,
n2,
currentContainer,
currentAnchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
false
)
}
// 如果新节点中已经被禁用
if (disabled) {
// 旧节点中未被禁用
if (!wasDisabled) {
// 由启用到禁用
// 移动到container中
moveTeleport(
n2,
container,
mainAnchor,
internals,
TeleportMoveTypes.TOGGLE
)
}
}
// 新节点中启用状态
else {
// target改变
if ((n2.props && n2.props.to) !== (n1.props && n1.props.to)) {
const nextTarget = (n2.target = resolveTarget(
n2.props,
querySelector
))
// 移动到新的target中
if (nextTarget) {
moveTeleport(
n2,
nextTarget,
null,
internals,
TeleportMoveTypes.TARGET_CHANGE
)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
'Invalid Teleport target on update:',
target,
`(${typeof target})`
)
}
}
// target未改变,但旧节点中是禁用状态
else if (wasDisabled) {
// 禁用变为启用
// 移动到target中
moveTeleport(
n2,
target,
targetAnchor,
internals,
TeleportMoveTypes.TOGGLE
)
}
}
}
}
// ...
}
Teleport的更新主要包含两步:
patch孩子节点- 如果
disabled状态改变或to的目标改变,需要移动DOM到目标节点中
Suspense的更新
patchSuspense
ts
function patchSuspense(
n1: VNode,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
{ p: patch, um: unmount, o: { createElement } }: RendererInternals
) {
const suspense = (n2.suspense = n1.suspense)!
suspense.vnode = n2
n2.el = n1.el
const newBranch = n2.ssContent!
const newFallback = n2.ssFallback!
const { activeBranch, pendingBranch, isInFallback, isHydrating } = suspense
// 存在正在等待的分支
if (pendingBranch) {
// 将suspense.pendingBranch设置为新的content
suspense.pendingBranch = newBranch
// 如果新旧pendingBranch类型相同,则进行patch
if (isSameVNodeType(newBranch, pendingBranch)) {
// same root type but content may have changed.
patch(
pendingBranch,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
// 如果异步依赖全部加载完成,则可以直接解析suspense内容
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
suspense.resolve()
} else if (isInFallback) { // 在fallback状态,将activeBranch与新节点的ssFallback进行patch
patch(
activeBranch,
newFallback,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, newFallback)
}
}
// 如果新旧pendingBranch类型不同
else {
// toggled before pending tree is resolved
suspense.pendingId++
if (isHydrating) {
suspense.isHydrating = false
suspense.activeBranch = pendingBranch
} else {
// 卸载旧的pendingBranch
unmount(pendingBranch, parentComponent, suspense)
}
// 重置异步依赖数量为0
suspense.deps = 0
// 丢弃来自pending branch的effects
suspense.effects.length = 0
// 使用一个新的div替换旧的hiddenContainer
suspense.hiddenContainer = createElement('div')
// 已经在fallback状态,挂载新节点的conent到suspense.hiddenContainer
if (isInFallback) {
// already in fallback state
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
// 如果不存在异步依赖,可以直接解析suspense内容
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
suspense.resolve()
} else { // 否则将新节点的fallback与activeBranch进行patch
patch(
activeBranch,
newFallback,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, newFallback)
}
}
// 存在激活分支并且激活分支与新content类型相同,进行patch
else if (activeBranch && isSameVNodeType(newBranch, activeBranch)) {
// toggled "back" to current active branch
patch(
activeBranch,
newBranch,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
// force resolve
suspense.resolve(true)
} else {
// switched to a 3rd branch
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
suspense.resolve()
}
}
}
}
// 不存在正在等待的分支
else {
// 存在激活分支并且新的content和激活分支类型相同,将两者进行patch
if (activeBranch && isSameVNodeType(newBranch, activeBranch)) {
// root did not change, just normal patch
patch(
activeBranch,
newBranch,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, newBranch)
}
else {
// root node toggled
// 触发n2的onPending
triggerEvent(n2, 'onPending')
// mount pending branch in off-dom container
suspense.pendingBranch = newBranch
suspense.pendingId++
// 挂载新的content到suspense.hiddenContainer中
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
// 不存在异步依赖,直接解析suspense
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
// incoming branch has no async deps, resolve now.
suspense.resolve()
} else {
const { timeout, pendingId } = suspense
if (timeout > 0) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (suspense.pendingId === pendingId) {
suspense.fallback(newFallback)
}
}, timeout)
} else if (timeout === 0) {
suspense.fallback(newFallback)
}
}
}
}
}
总结
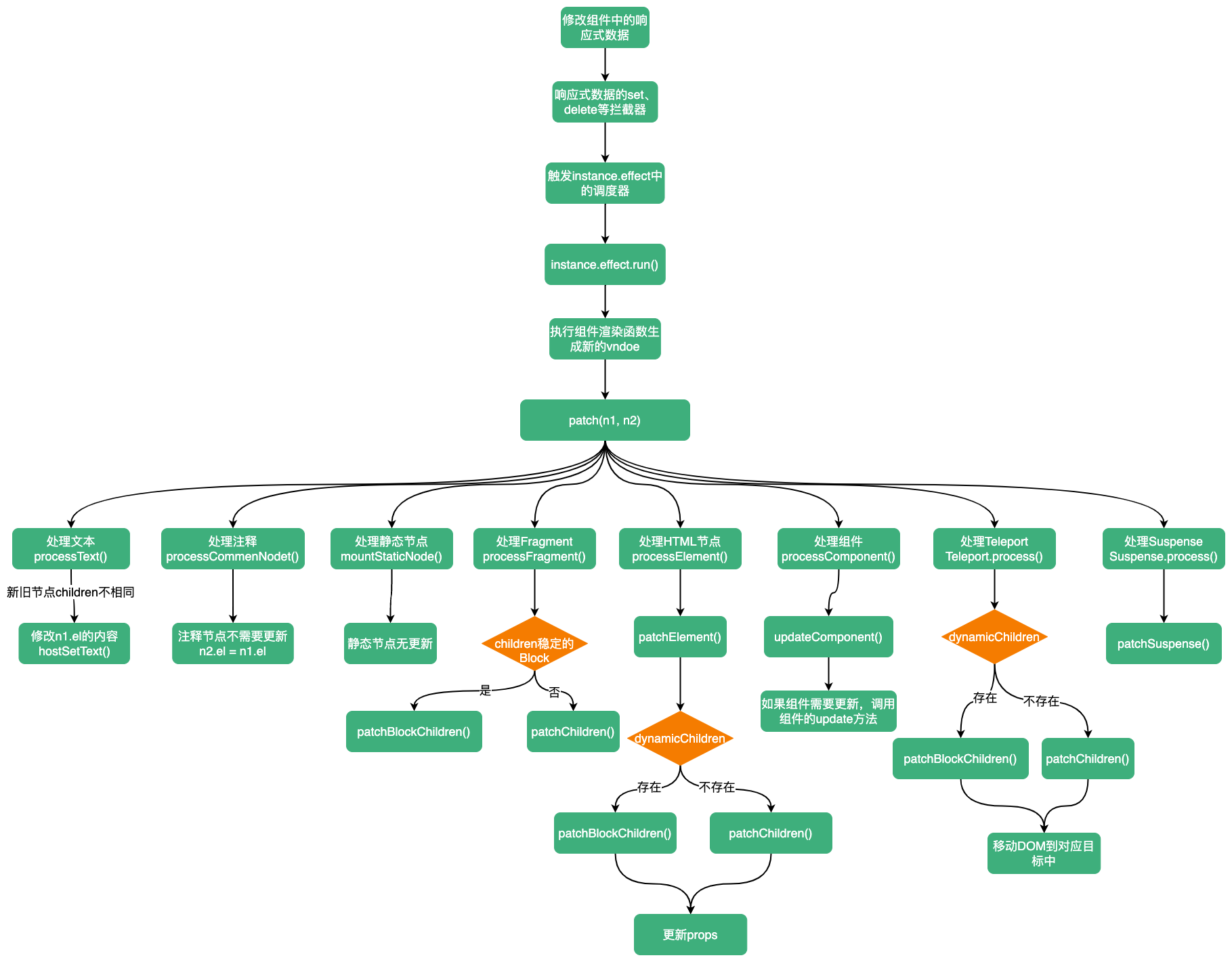
当组件内某些响应式状态发生变化后,会触发instance.update,由渲染函数生成一个最新的vnode。接着调用patch方法对新旧节点进行打补丁。
组件更新流程图: