外观
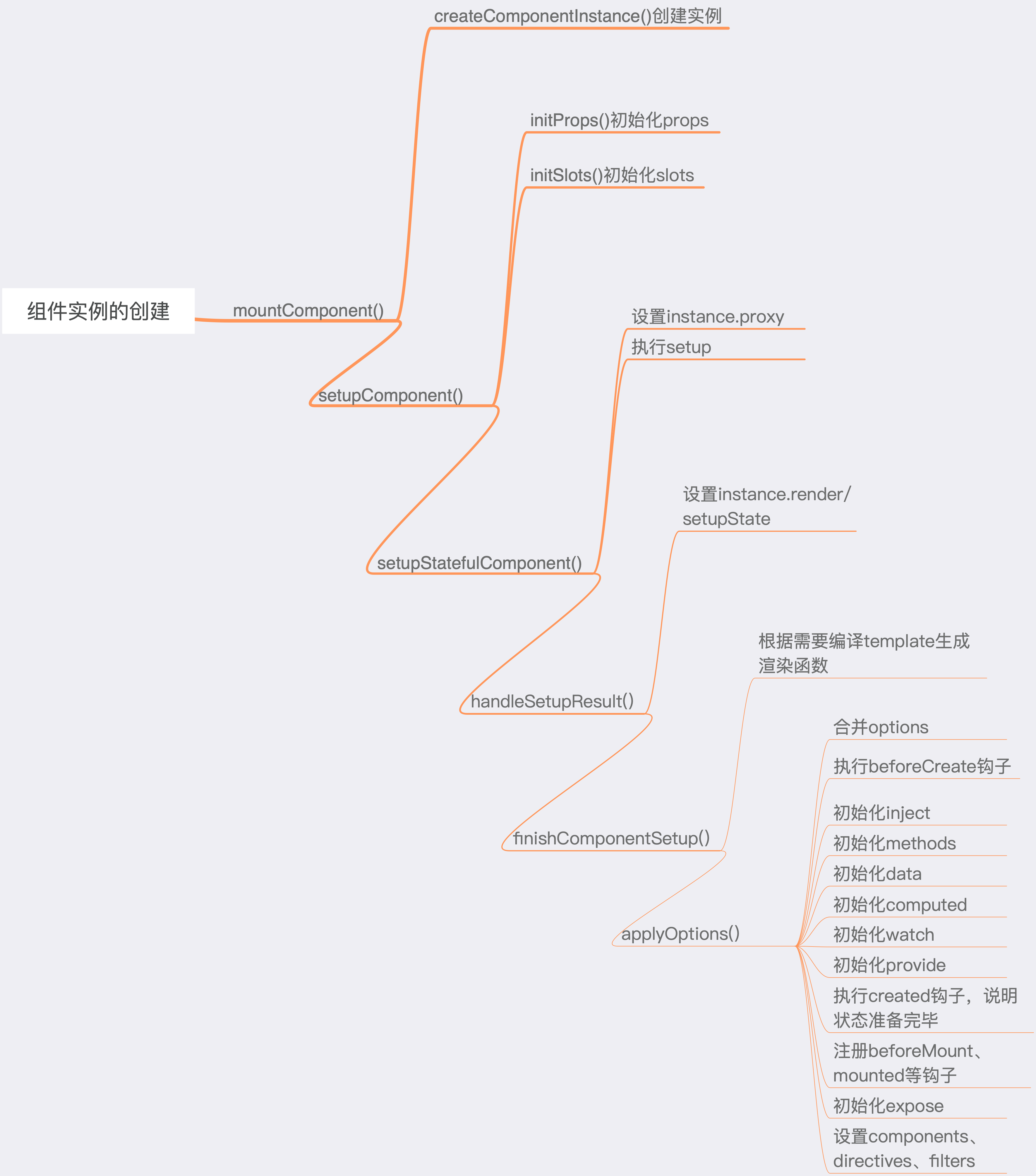
组件实例的创建过程
组件实例的类型说明
ts
export interface ComponentInternalInstance {
// 唯一标识
uid: number
type: ConcreteComponent
// 父组件实例
parent: ComponentInternalInstance | null
// 跟组件实例
root: ComponentInternalInstance
// app实例上下文
appContext: AppContext
// 对应的vnode
vnode: VNode
// 来自父组件更新的待处理的新vnode
next: VNode | null
// 组件本身的vdom树的根vnode
subTree: VNode
// 使用组件更新函数构建的ReactiveEffect对象
effect: ReactiveEffect
// 更新函数,一个包含effect.run()的函数
update: SchedulerJob
// 返回vdom树的渲染函数
render: InternalRenderFunction | null
/**
* SSR render function
* @internal
*/
ssrRender?: Function | null
/**
* Object containing values this component provides for its descendents
* @internal
*/
provides: Data
/**
* Tracking reactive effects (e.g. watchers) associated with this component
* so that they can be automatically stopped on component unmount
* @internal
*/
scope: EffectScope
// 从instance.proxy中获取属性时,缓存key的来源,以减少hasOwnProperty的调用
accessCache: Data | null
/**
* cache for render function values that rely on _ctx but won't need updates
* after initialized (e.g. inline handlers)
* @internal
*/
renderCache: (Function | VNode)[]
// 注册的组件
components: Record<string, ConcreteComponent> | null
// 注册的指令
directives: Record<string, Directive> | null
// 注册的filters,仅在v2兼容模式
filters?: Record<string, Function>
// 标准化的props options
propsOptions: NormalizedPropsOptions
// 标准化的emits options
emitsOptions: ObjectEmitsOptions | null
// 组件的inheritAttrs options
inheritAttrs?: boolean
/**
* is custom element?
*/
isCE?: boolean
/**
* custom element specific HMR method
*/
ceReload?: (newStyles?: string[]) => void
// the rest are only for stateful components ---------------------------------
// 组件中的this指向
proxy: ComponentPublicInstance | null
// 通过expose()暴露的属性
exposed: Record<string, any> | null
exposeProxy: Record<string, any> | null
// 使用with块的运行时编译的渲染函数的上下文代理对象
// 当在线编译模板时,生成的渲染函数使用了with
withProxy: ComponentPublicInstance | null
// 组件实例代理的目标,组件中this的代理目标
ctx: Data
// state
// data options的返回值,会使用reactive处理为响应式数据
data: Data
// 组件已解析的的props对象
props: Data
// 组件所有透传 attributes 的对象
attrs: Data
// 组件的插槽对象
slots: InternalSlots
refs: Data
// emit函数
emit: EmitFn
// 被.once修饰的事件,被调用过一次,会将其事件名保存在emitted,防止之后被调用
emitted: Record<string, boolean> | null
// 缓存props的默认值
propsDefaults: Data
// setup返回值(如果是对象)的代理对象,使用proxyRefs进行代理,可自动脱ref
setupState: Data
/**
* devtools access to additional info
* @internal
*/
devtoolsRawSetupState?: any
// setup上下文
setupContext: SetupContext | null
// suspense边界
suspense: SuspenseBoundary | null
/**
* suspense pending batch id
* @internal
*/
suspenseId: number
// setup的返回值(Promise)
asyncDep: Promise<any> | null
/**
* @internal
*/
asyncResolved: boolean
// lifecycle
isMounted: boolean
isUnmounted: boolean
isDeactivated: boolean
// 以下是一些生命周期钩子函数
[LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_CREATE]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.CREATED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_MOUNT]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.MOUNTED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_UPDATE]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.UPDATED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_UNMOUNT]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.UNMOUNTED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.RENDER_TRACKED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.RENDER_TRIGGERED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.ACTIVATED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.DEACTIVATED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.ERROR_CAPTURED]: LifecycleHook
[LifecycleHooks.SERVER_PREFETCH]: LifecycleHook<() => Promise<unknown>>
/**
* For caching bound $forceUpdate on public proxy access
*/
f?: () => void
/**
* For caching bound $nextTick on public proxy access
*/
n?: () => Promise<void>
}
createComponentInstance
在vue3中通过createComponentInstance方法创建组件实例。createComponentInstance接收三个参数:vnode、parent(父组件实例)、suspense
ts
export function createComponentInstance(
vnode: VNode,
parent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
suspense: SuspenseBoundary | null
) {
const type = vnode.type as ConcreteComponent
// app实例的上下文对象
const appContext =
(parent ? parent.appContext : vnode.appContext) || emptyAppContext
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance = {
uid: uid++,
vnode,
type,
parent,
appContext,
root: null!, // to be immediately set
next: null,
subTree: null!, // will be set synchronously right after creation
effect: null!,
update: null!, // will be set synchronously right after creation
scope: new EffectScope(true /* detached */),
render: null,
proxy: null,
exposed: null,
exposeProxy: null,
withProxy: null,
provides: parent ? parent.provides : Object.create(appContext.provides),
accessCache: null!,
renderCache: [],
components: null,
directives: null,
// 标准化props options及emits options
propsOptions: normalizePropsOptions(type, appContext),
emitsOptions: normalizeEmitsOptions(type, appContext),
emit: null!, // to be set immediately
emitted: null,
propsDefaults: EMPTY_OBJ,
inheritAttrs: type.inheritAttrs,
ctx: EMPTY_OBJ,
data: EMPTY_OBJ,
props: EMPTY_OBJ,
attrs: EMPTY_OBJ,
slots: EMPTY_OBJ,
refs: EMPTY_OBJ,
setupState: EMPTY_OBJ,
setupContext: null,
suspense,
suspenseId: suspense ? suspense.pendingId : 0,
asyncDep: null,
asyncResolved: false,
isMounted: false,
isUnmounted: false,
isDeactivated: false,
// 一些生命周期钩子
bc: null,
c: null,
bm: null,
m: null,
bu: null,
u: null,
um: null,
bum: null,
da: null,
a: null,
rtg: null,
rtc: null,
ec: null,
sp: null
}
// 设置组件实例代理的目标,组件中的this就是instance.ctx的代理对象
// 开发环境下会创建一个包含$、$el、$data、$attrs等属性的对象,以方便调试
// 生产环境下,将通过代理的方式去拦截this.$、this.$el、this.$data操作
if (__DEV__) {
instance.ctx = createDevRenderContext(instance)
} else {
instance.ctx = { _: instance }
}
// 设置组件实例的根实例
instance.root = parent ? parent.root : instance
// 绑定emit函数的第一个参数为组件实例
instance.emit = emit.bind(null, instance)
// 自定义元素的特殊处理
if (vnode.ce) {
vnode.ce(instance)
}
return instance
}
在创建组件实例过程中有步比较重要的操作就是标准化组件实例的props与emits。
标准化props
normalizePropsOptions方法可以接受三个参数:comp(组件或包含options的某些属性的对象)、appContext(app实例的上下文对象)、asMixin(作为mixin处理props, 默认false)
ts
export function normalizePropsOptions(
comp: ConcreteComponent,
appContext: AppContext,
asMixin = false
): NormalizedPropsOptions {
// 从appContext获取缓存的进过处理好的props,如果有,直接返回
const cache = appContext.propsCache
const cached = cache.get(comp)
if (cached) {
return cached
}
const raw = comp.props
const normalized: NormalizedPropsOptions[0] = {}
const needCastKeys: NormalizedPropsOptions[1] = []
// 处理通过mixin/extend注入的props
let hasExtends = false
// 如果支持 options api 并且comp不是function
if (__FEATURE_OPTIONS_API__ && !isFunction(comp)) {
const extendProps = (raw: ComponentOptions) => {
if (__COMPAT__ && isFunction(raw)) {
raw = raw.options
}
hasExtends = true
const [props, keys] = normalizePropsOptions(raw, appContext, true)
extend(normalized, props)
if (keys) needCastKeys.push(...keys)
}
// 处理全局mixin注入的props
if (!asMixin && appContext.mixins.length) {
appContext.mixins.forEach(extendProps)
}
// 处理extent注入的props
if (comp.extends) {
extendProps(comp.extends)
}
// 处理局部mixin注入的props
if (comp.mixins) {
comp.mixins.forEach(extendProps)
}
}
// 如果组件不存在props,也没有通过mixin、extends方式注入的props,则缓存一个空数组
if (!raw && !hasExtends) {
cache.set(comp, EMPTY_ARR as any)
return EMPTY_ARR as any
}
// 如果组件本身的props是数组时,其中的元素必须为字符串
if (isArray(raw)) {
for (let i = 0; i < raw.length; i++) {
if (__DEV__ && !isString(raw[i])) {
warn(`props must be strings when using array syntax.`, raw[i])
}
// 将字符串props转为驼峰模式
const normalizedKey = camelize(raw[i])
// 验证props的命名是否符合要求,不准以$开头的props
if (validatePropName(normalizedKey)) {
normalized[normalizedKey] = EMPTY_OBJ
}
}
} else if (raw) {
if (__DEV__ && !isObject(raw)) {
warn(`invalid props options`, raw)
}
for (const key in raw) {
// 将key转为驼峰式
const normalizedKey = camelize(key)
// 验证props的命名是否符合要求,不准以$开头的props
if (validatePropName(normalizedKey)) {
const opt = raw[key]
// 如果key所对应的opt是数组或方法,则将opt作为type
const prop: NormalizedProp = (normalized[normalizedKey] =
isArray(opt) || isFunction(opt) ? { type: opt } : opt)
if (prop) {
// 获取Boolean在prop.type中的索引,如果返回-1,代表prop.type中不允许Boolean类型
const booleanIndex = getTypeIndex(Boolean, prop.type)
// 获取String在prop.type中的索引
const stringIndex = getTypeIndex(String, prop.type)
prop[BooleanFlags.shouldCast] = booleanIndex > -1
prop[BooleanFlags.shouldCastTrue] =
stringIndex < 0 || booleanIndex < stringIndex
// 如果prop类型中存在Boolean或存在默认值,则将key存入needCastKeys中
if (booleanIndex > -1 || hasOwn(prop, 'default')) {
needCastKeys.push(normalizedKey)
}
}
}
}
}
// 将normalized和needCastKeys构造成一个数组并缓存到app实例的上下文对象中
const res: NormalizedPropsOptions = [normalized, needCastKeys]
cache.set(comp, res)
return res
}
标准化emits
ts
export function normalizeEmitsOptions(
comp: ConcreteComponent,
appContext: AppContext,
asMixin = false
): ObjectEmitsOptions | null {
// 尝试从emits缓存中获取emit
const cache = appContext.emitsCache
const cached = cache.get(comp)
if (cached !== undefined) {
return cached
}
const raw = comp.emits
let normalized: ObjectEmitsOptions = {}
// 处理通过mixin/extend注入的emits
let hasExtends = false
if (__FEATURE_OPTIONS_API__ && !isFunction(comp)) {
const extendEmits = (raw: ComponentOptions) => {
const normalizedFromExtend = normalizeEmitsOptions(raw, appContext, true)
// 只要存在通过mixins、extend方式注入的emits,将hasExtends设置为true
if (normalizedFromExtend) {
hasExtends = true
extend(normalized, normalizedFromExtend)
}
}
// 处理通过全局mixin注入的emits选项
if (!asMixin && appContext.mixins.length) {
appContext.mixins.forEach(extendEmits)
}
// 处理通过extends注入的emits选项
if (comp.extends) {
extendEmits(comp.extends)
}
// 处理通过局部mixins注入的emits选项
if (comp.mixins) {
comp.mixins.forEach(extendEmits)
}
}
// 如果组件本身不存在emits,而且也没有通过mixin、extends等方式注入emits,则缓存一个null
if (!raw && !hasExtends) {
cache.set(comp, null)
return null
}
if (isArray(raw)) {
raw.forEach(key => (normalized[key] = null))
} else {
extend(normalized, raw)
}
// 将规范后的emits缓存至app实例的上下文对象中
cache.set(comp, normalized)
return normalized
}
可以看到如果通过全局mixin、局部mixin、extends及组件自身props同时定义key相同的props或emits,其优先级顺序为:组件自身props或emits > 局部mixin > extends > 全局mixin
setupComponent
在创建完组件实例后,会调用一个setupComponent方法。
ts
export function setupComponent(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
isSSR = false
) {
isInSSRComponentSetup = isSSR
const { props, children } = instance.vnode
const isStateful = isStatefulComponent(instance)
// 初始化props
initProps(instance, props, isStateful, isSSR)
// 初始化slots
initSlots(instance, children)
// 执行setup
const setupResult = isStateful
? setupStatefulComponent(instance, isSSR)
: undefined
isInSSRComponentSetup = false
return setupResult
}
setupComponent函数主要有三个作用:
- 初始化
props,参考:组件props的初始化过程 - 初始化
slots - 执行
setup
setupStatefulComponent
setupStatefulComponent源码
ts
function setupStatefulComponent(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
isSSR: boolean
) {
const Component = instance.type as ComponentOptions
if (__DEV__) {
// 校验组件自身名称
if (Component.name) {
validateComponentName(Component.name, instance.appContext.config)
}
// 校验局部注册的组件名,components的key
if (Component.components) {
const names = Object.keys(Component.components)
for (let i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
validateComponentName(names[i], instance.appContext.config)
}
}
// 校验局部注册的指令
if (Component.directives) {
const names = Object.keys(Component.directives)
for (let i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
validateDirectiveName(names[i])
}
}
// compilerOptions仅在使用了完整的构建版本时才有效
if (Component.compilerOptions && isRuntimeOnly()) {
warn(
`"compilerOptions" is only supported when using a build of Vue that ` +
`includes the runtime compiler. Since you are using a runtime-only ` +
`build, the options should be passed via your build tool config instead.`
)
}
}
// 通过this进行访问属性时记录属性的来源
instance.accessCache = Object.create(null)
// 组件中this的指向
instance.proxy = markRaw(new Proxy(instance.ctx, PublicInstanceProxyHandlers))
if (__DEV__) {
exposePropsOnRenderContext(instance)
}
const { setup } = Component
if (setup) {
// 创建setup中的上下文对象
const setupContext = (instance.setupContext =
setup.length > 1 ? createSetupContext(instance) : null)
setCurrentInstance(instance)
pauseTracking()
const setupResult = callWithErrorHandling(
setup,
instance,
ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION,
[__DEV__ ? shallowReadonly(instance.props) : instance.props, setupContext]
)
resetTracking()
unsetCurrentInstance()
if (isPromise(setupResult)) {
setupResult.then(unsetCurrentInstance, unsetCurrentInstance)
if (isSSR) {
// return the promise so server-renderer can wait on it
return setupResult
.then((resolvedResult: unknown) => {
handleSetupResult(instance, resolvedResult, isSSR)
})
.catch(e => {
handleError(e, instance, ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION)
})
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__) {
// async setup returned Promise.
// bail here and wait for re-entry.
instance.asyncDep = setupResult
if (__DEV__ && !instance.suspense) {
const name = Component.name ?? 'Anonymous'
warn(
`Component <${name}>: setup function returned a promise, but no ` +
`<Suspense> boundary was found in the parent component tree. ` +
`A component with async setup() must be nested in a <Suspense> ` +
`in order to be rendered.`
)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`setup() returned a Promise, but the version of Vue you are using ` +
`does not support it yet.`
)
}
} else {
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult, isSSR)
}
} else {
finishComponentSetup(instance, isSSR)
}
}
在执行setup前,会对组件名、组件中注册的组件名、组件中注册的指令名进行校验,检查是否合法。
ts
if (__DEV__) {
// 校验组件自身名称
if (Component.name) {
validateComponentName(Component.name, instance.appContext.config)
}
// 校验局部注册的组件名,components的key
if (Component.components) {
const names = Object.keys(Component.components)
for (let i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
validateComponentName(names[i], instance.appContext.config)
}
}
// 校验局部注册的指令
if (Component.directives) {
const names = Object.keys(Component.directives)
for (let i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
validateDirectiveName(names[i])
}
}
// compilerOptions仅在使用了完整的构建版本时才有效
if (Component.compilerOptions && isRuntimeOnly()) {
warn(
`"compilerOptions" is only supported when using a build of Vue that ` +
`includes the runtime compiler. Since you are using a runtime-only ` +
`build, the options should be passed via your build tool config instead.`
)
}
}
其中组件名的验证规则是:1.不能是内置tag(slot、component);2. 不能是原生标签。如果不符合条件,则进行警告提示。
ts
export function validateComponentName(name: string, config: AppConfig) {
const appIsNativeTag = config.isNativeTag || NO
if (isBuiltInTag(name) || appIsNativeTag(name)) {
warn(
'Do not use built-in or reserved HTML elements as component id: ' + name
)
}
}
指令的验证规则是:不能是内置指令,包括bind、cloak、else-if、else、for、html、if、model、on、once、pre、show、slot、text、memo
ts
export const isBuiltInDirective = /*#__PURE__*/ makeMap(
'bind,cloak,else-if,else,for,html,if,model,on,once,pre,show,slot,text,memo'
)
export function validateDirectiveName(name: string) {
if (isBuiltInDirective(name)) {
warn('Do not use built-in directive ids as custom directive id: ' + name)
}
}
然后对instance进行了两步操作:1.修改instance.accessCache为一个空对象;2.修改instance.proxy为一个代理对象。
ts
// 通过this进行访问属性时记录属性的来源
instance.accessCache = Object.create(null)
// 组件中this的指向
instance.proxy = markRaw(new Proxy(instance.ctx, PublicInstanceProxyHandlers))
instance.accessCache会用来缓存通过this访问的属性需要从哪里获取。例如:
ts
export default defineComponent({
data() {
const a = ref(0)
return {
a
}
},
setup() {
const b = ref(0)
return {
b
}
}
})
当通过this.a访问a属性时,会先尝试从setup的返回结果中查找,由于setup的返回值中不存在a属性,所以接着从data的返回值中查找,在data的返回结果中存在a属性,返回a属性对应的值,同时会将a属性的查找来源标记为AccessTypes.DATA,保存到instance.accessCache中,当下次要获取this.a时,可以直接从instance.accessCache中获取到a属性的来源,直接到data的返回值中获取a属性。
this.b同this.a相同,只不过在setup中可以找到b属性,所以不会再从data返回值中找着了。同样,在instance.accessCache中会缓存b属性的来源,由于b属性时从setup返回值中找到的,所以会将其来源标记为AccessTypes.SETUP。
关于this属性查找的顺序可参考:详解组件中的this
然后就开始执行setup。在执行setup之前,需要先创建setup的上下文对象。注意这里如果在使用setup函数时,声明参数时,是不会创建上下文的。
ts
const setupContext = (instance.setupContext =
setup.length > 1 ? createSetupContext(instance) : null)
// 设置当前实例
setCurrentInstance(instance)
// 停止依赖收集
pauseTracking()
createSetupContext:
ts
export function createSetupContext(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance
): SetupContext {
// 创建expose函数
const expose: SetupContext['expose'] = exposed => {
// setup中expose应该只能被调用一次
if (__DEV__ && instance.exposed) {
warn(`expose() should be called only once per setup().`)
}
instance.exposed = exposed || {}
}
let attrs: Data
if (__DEV__) {
// We use getters in dev in case libs like test-utils overwrite instance
// properties (overwrites should not be done in prod)
return Object.freeze({
get attrs() {
return attrs || (attrs = createAttrsProxy(instance))
},
get slots() {
return shallowReadonly(instance.slots)
},
get emit() {
return (event: string, ...args: any[]) => instance.emit(event, ...args)
},
expose
})
} else {
return {
get attrs() {
return attrs || (attrs = createAttrsProxy(instance))
},
slots: instance.slots,
emit: instance.emit,
expose
}
}
}
接下来就是执行setup。
ts
const setupResult = callWithErrorHandling(
setup,
instance,
ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION,
[__DEV__ ? shallowReadonly(instance.props) : instance.props, setupContext]
)
// 恢复依赖收集
resetTracking()
// 取消当前实例
unsetCurrentInstance()
执行完setup后,获得setup的返回值setupResult。然后根据setupResult进入不同分支。
ts
// 如果setupResult是Promise
if (isPromise(setupResult)) {
// Promise的setupResult执行前首先清空当前组件实例
setupResult.then(unsetCurrentInstance, unsetCurrentInstance)
if (isSSR) { // 服务端渲染
// return the promise so server-renderer can wait on it
return setupResult
.then((resolvedResult: unknown) => {
handleSetupResult(instance, resolvedResult, isSSR)
})
.catch(e => {
handleError(e, instance, ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION)
})
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__) { // 支持suspense
instance.asyncDep = setupResult
if (__DEV__ && !instance.suspense) {
const name = Component.name ?? 'Anonymous'
warn(
`Component <${name}>: setup function returned a promise, but no ` +
`<Suspense> boundary was found in the parent component tree. ` +
`A component with async setup() must be nested in a <Suspense> ` +
`in order to be rendered.`
)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`setup() returned a Promise, but the version of Vue you are using ` +
`does not support it yet.`
)
}
} else {
handleSetupResult(instance, setupResult, isSSR)
}
如果setupResult不是Promise的话,则会调用一个handleSetupResult方法。
ts
export function handleSetupResult(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
setupResult: unknown,
isSSR: boolean
) {
if (isFunction(setupResult)) { // setupResult是Function,则将其作为渲染函数处理
if (__SSR__ && (instance.type as ComponentOptions).__ssrInlineRender) {
// when the function's name is `ssrRender` (compiled by SFC inline mode),
// set it as ssrRender instead.
instance.ssrRender = setupResult
} else {
instance.render = setupResult as InternalRenderFunction
}
} else if (isObject(setupResult)) { // setupResult是Object,将其结果作为setupState
if (__DEV__ && isVNode(setupResult)) {
warn(
`setup() should not return VNodes directly - ` +
`return a render function instead.`
)
}
// setup returned bindings.
// assuming a render function compiled from template is present.
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
instance.devtoolsRawSetupState = setupResult
}
// 使用proxyRefs自动脱ref
instance.setupState = proxyRefs(setupResult)
if (__DEV__) {
exposeSetupStateOnRenderContext(instance)
}
} else if (__DEV__ && setupResult !== undefined) { // 其它情况,进行提示
warn(
`setup() should return an object. Received: ${
setupResult === null ? 'null' : typeof setupResult
}`
)
}
finishComponentSetup(instance, isSSR)
}
finishComponentSetup中有两步重要的操作:
- 如果组件实例中没有渲染函数,需要根据模板编译出渲染函数
- 执行vue2相关
options
ts
export function finishComponentSetup(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
isSSR: boolean,
skipOptions?: boolean
) {
const Component = instance.type as ComponentOptions
if (__COMPAT__) {
convertLegacyRenderFn(instance)
if (__DEV__ && Component.compatConfig) {
validateCompatConfig(Component.compatConfig)
}
}
// 设置组件的渲染函数,通过setup返回值可能已经设置过了
if (!instance.render) {
// 如果不在SSR环境下,进行即使编译
if (!isSSR && compile && !Component.render) {
const template =
(__COMPAT__ &&
instance.vnode.props &&
instance.vnode.props['inline-template']) ||
Component.template
if (template) {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `compile`)
}
const { isCustomElement, compilerOptions } = instance.appContext.config
const { delimiters, compilerOptions: componentCompilerOptions } =
Component
const finalCompilerOptions: CompilerOptions = extend(
extend(
{
isCustomElement,
delimiters
},
compilerOptions
),
componentCompilerOptions
)
if (__COMPAT__) {
// pass runtime compat config into the compiler
finalCompilerOptions.compatConfig = Object.create(globalCompatConfig)
if (Component.compatConfig) {
extend(finalCompilerOptions.compatConfig, Component.compatConfig)
}
}
// 编译template为渲染函数
Component.render = compile(template, finalCompilerOptions)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `compile`)
}
}
}
// 设置组件的渲染函数
instance.render = (Component.render || NOOP) as InternalRenderFunction
// 对于运行时编译的渲染函数中使用了with,需要对ctx的代理对象做一些特殊处理
if (installWithProxy) {
installWithProxy(instance)
}
}
// 支持 vue2 de options
if (__FEATURE_OPTIONS_API__ && !(__COMPAT__ && skipOptions)) {
setCurrentInstance(instance)
pauseTracking()
applyOptions(instance)
resetTracking()
unsetCurrentInstance()
}
// 如果没有渲染函数进行提示
if (__DEV__ && !Component.render && instance.render === NOOP && !isSSR) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (!compile && Component.template) {
warn(
`Component provided template option but ` +
`runtime compilation is not supported in this build of Vue.` +
(__ESM_BUNDLER__
? ` Configure your bundler to alias "vue" to "vue/dist/vue.esm-bundler.js".`
: __ESM_BROWSER__
? ` Use "vue.esm-browser.js" instead.`
: __GLOBAL__
? ` Use "vue.global.js" instead.`
: ``) /* should not happen */
)
} else {
warn(`Component is missing template or render function.`)
}
}
}
applyOptions
applyOptions用于初始化options。applyOptions函数接收一个参数:instance组件实例。
applyOptions完整代码
ts
export function applyOptions(instance: ComponentInternalInstance) {
// 合并options:将全局mixins、局部mixins、extends及自身options合并到一个新的options对象中
const options = resolveMergedOptions(instance)
const publicThis = instance.proxy! as any
const ctx = instance.ctx
// do not cache property access on public proxy during state initialization
shouldCacheAccess = false
// 执行beforeCreate钩子
if (options.beforeCreate) {
callHook(options.beforeCreate, instance, LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_CREATE)
}
const {
// state
data: dataOptions,
computed: computedOptions,
methods,
watch: watchOptions,
provide: provideOptions,
inject: injectOptions,
// lifecycle
created,
beforeMount,
mounted,
beforeUpdate,
updated,
activated,
deactivated,
beforeDestroy,
beforeUnmount,
destroyed,
unmounted,
render,
renderTracked,
renderTriggered,
errorCaptured,
serverPrefetch,
// public API
expose,
inheritAttrs,
// assets
components,
directives,
filters
} = options
const checkDuplicateProperties = __DEV__ ? createDuplicateChecker() : null
if (__DEV__) {
const [propsOptions] = instance.propsOptions
if (propsOptions) {
for (const key in propsOptions) {
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.PROPS, key)
}
}
}
// options initialization order (to be consistent with Vue 2):
// - props (already done outside of this function)
// - inject
// - methods
// - data (deferred since it relies on `this` access)
// - computed
// - watch (deferred since it relies on `this` access)
if (injectOptions) {
resolveInjections(
injectOptions,
ctx,
checkDuplicateProperties,
instance.appContext.config.unwrapInjectedRef
)
}
if (methods) {
for (const key in methods) {
const methodHandler = (methods as MethodOptions)[key]
if (isFunction(methodHandler)) {
// In dev mode, we use the `createRenderContext` function to define
// methods to the proxy target, and those are read-only but
// reconfigurable, so it needs to be redefined here
if (__DEV__) {
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
value: methodHandler.bind(publicThis),
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
writable: true
})
} else {
ctx[key] = methodHandler.bind(publicThis)
}
if (__DEV__) {
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.METHODS, key)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methodHandler}" in the component definition. ` +
`Did you reference the function correctly?`
)
}
}
}
if (dataOptions) {
if (__DEV__ && !isFunction(dataOptions)) {
warn(
`The data option must be a function. ` +
`Plain object usage is no longer supported.`
)
}
const data = dataOptions.call(publicThis, publicThis)
if (__DEV__ && isPromise(data)) {
warn(
`data() returned a Promise - note data() cannot be async; If you ` +
`intend to perform data fetching before component renders, use ` +
`async setup() + <Suspense>.`
)
}
if (!isObject(data)) {
__DEV__ && warn(`data() should return an object.`)
} else {
instance.data = reactive(data)
if (__DEV__) {
for (const key in data) {
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.DATA, key)
// expose data on ctx during dev
if (!isReservedPrefix(key[0])) {
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get: () => data[key],
set: NOOP
})
}
}
}
}
}
// state initialization complete at this point - start caching access
shouldCacheAccess = true
if (computedOptions) {
for (const key in computedOptions) {
const opt = (computedOptions as ComputedOptions)[key]
const get = isFunction(opt)
? opt.bind(publicThis, publicThis)
: isFunction(opt.get)
? opt.get.bind(publicThis, publicThis)
: NOOP
if (__DEV__ && get === NOOP) {
warn(`Computed property "${key}" has no getter.`)
}
const set =
!isFunction(opt) && isFunction(opt.set)
? opt.set.bind(publicThis)
: __DEV__
? () => {
warn(
`Write operation failed: computed property "${key}" is readonly.`
)
}
: NOOP
const c = computed({
get,
set
})
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => c.value,
set: v => (c.value = v)
})
if (__DEV__) {
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.COMPUTED, key)
}
}
}
if (watchOptions) {
for (const key in watchOptions) {
createWatcher(watchOptions[key], ctx, publicThis, key)
}
}
if (provideOptions) {
const provides = isFunction(provideOptions)
? provideOptions.call(publicThis)
: provideOptions
Reflect.ownKeys(provides).forEach(key => {
provide(key, provides[key])
})
}
if (created) {
callHook(created, instance, LifecycleHooks.CREATED)
}
function registerLifecycleHook(
register: Function,
hook?: Function | Function[]
) {
if (isArray(hook)) {
hook.forEach(_hook => register(_hook.bind(publicThis)))
} else if (hook) {
register((hook as Function).bind(publicThis))
}
}
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeMount, beforeMount)
registerLifecycleHook(onMounted, mounted)
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUpdate, beforeUpdate)
registerLifecycleHook(onUpdated, updated)
registerLifecycleHook(onActivated, activated)
registerLifecycleHook(onDeactivated, deactivated)
registerLifecycleHook(onErrorCaptured, errorCaptured)
registerLifecycleHook(onRenderTracked, renderTracked)
registerLifecycleHook(onRenderTriggered, renderTriggered)
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUnmount, beforeUnmount)
registerLifecycleHook(onUnmounted, unmounted)
registerLifecycleHook(onServerPrefetch, serverPrefetch)
if (__COMPAT__) {
if (
beforeDestroy &&
softAssertCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.OPTIONS_BEFORE_DESTROY, instance)
) {
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUnmount, beforeDestroy)
}
if (
destroyed &&
softAssertCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.OPTIONS_DESTROYED, instance)
) {
registerLifecycleHook(onUnmounted, destroyed)
}
}
if (isArray(expose)) {
if (expose.length) {
const exposed = instance.exposed || (instance.exposed = {})
expose.forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(exposed, key, {
get: () => publicThis[key],
set: val => (publicThis[key] = val)
})
})
} else if (!instance.exposed) {
instance.exposed = {}
}
}
// options that are handled when creating the instance but also need to be
// applied from mixins
if (render && instance.render === NOOP) {
instance.render = render as InternalRenderFunction
}
if (inheritAttrs != null) {
instance.inheritAttrs = inheritAttrs
}
// asset options.
if (components) instance.components = components as any
if (directives) instance.directives = directives
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
filters &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.FILTERS, instance)
) {
instance.filters = filters
}
}
在applyOptions中首先会调用一个resolveMergedOptions方法,该方法会将组件中的options进行合并(将全局mixins或局部mixins注入或extends注入的的options与组件自身的options合并)并缓存到组件实例中。 详细过程参考:vue3中options选项的合并策略
当解析完组件options,会用两个变量publicThis、ctx,同时将一个全局变量shouldCacheAccess改为false。shouldCacheAccess为false的作用是在组件初始化期间,不缓存公共实例上的属性访问来源。
ts
const publicThis = instance.proxy! as any
const ctx = instance.ctx
shouldCacheAccess = false
接下来会按照:beforeCreate -> inject -> methods -> data -> computed -> watch -> provide -> created -> 注册生命周期钩子 -> expose -> render -> components -> directives -> filters的顺序进行初始化
执行beforeCreate钩子
ts
if (options.beforeCreate) {
callHook(options.beforeCreate, instance, LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_CREATE)
}
callHook:
ts
function callHook(
hook: Function,
instance: ComponentInternalInstance,
type: LifecycleHooks
) {
callWithAsyncErrorHandling(
isArray(hook)
? hook.map(h => h.bind(instance.proxy!))
: hook.bind(instance.proxy!),
instance,
type
)
}
在callHook中,我们发现用bind改变了hook的this执行,而这个this就是指向了instance.proxy。这就说明我们在组件中所使用到的this其实指向的就是instance.proxy。
继续观察applyOptions的剩余代码,你会发现methods中的各个函数、data函数等都会将this指向instance.proxy.
初始化inject
ts
if (injectOptions) {
resolveInjections(
injectOptions,
ctx,
checkDuplicateProperties,
instance.appContext.config.unwrapInjectedRef
)
}
这里调用了一个resolveInjections函数,用来获取通过inject注入的值。
resolveInjections函数接收四个参数:injectOptions(组件中的inject options)、ctx(instance.ctx)、checkDuplicateProperties(一个检查inject的key是否重复的函数)、unwrapRef(是否自动脱ref)
ts
export function resolveInjections(
injectOptions: ComponentInjectOptions,
ctx: any,
checkDuplicateProperties = NOOP as any,
unwrapRef = false
) {
// 如果injectOptions是个数组,需要将它标准化为一个对象 { key: key }
if (isArray(injectOptions)) {
injectOptions = normalizeInject(injectOptions)!
}
// 遍历injectOptions的键
for (const key in injectOptions) {
const opt = (injectOptions as ObjectInjectOptions)[key]
let injected: unknown
// 如果opt是个对象,调用inject函数获取对应值,key为opt.from或key
if (isObject(opt)) {
// 存在默认值
if ('default' in opt) {
injected = inject(
opt.from || key,
opt.default,
true /* treat default function as factory */
)
} else {
injected = inject(opt.from || key)
}
} else { // opt不是对象时,使用inject函数获取对应值,此时key取opt
injected = inject(opt)
}
// 如果inject注入的值是ref,如果unwrapRef为true,则会自动脱ref(无论读取还是设置属性,都不需要使用.value)
// inject注入的值会被保存到instance.ctx中
if (isRef(injected)) {
if (unwrapRef) {
// 将数据缓存至instance.ctx中
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => (injected as Ref).value,
set: v => ((injected as Ref).value = v)
})
} else {
if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`injected property "${key}" is a ref and will be auto-unwrapped ` +
`and no longer needs \`.value\` in the next minor release. ` +
`To opt-in to the new behavior now, ` +
`set \`app.config.unwrapInjectedRef = true\` (this config is ` +
`temporary and will not be needed in the future.)`
)
}
// 将数据缓存至instance.ctx中
ctx[key] = injected
}
} else {
// 将数据缓存至instance.ctx中
ctx[key] = injected
}
// 检查是否有重复的inject key
if (__DEV__) {
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.INJECT, key)
}
}
}
在resolveInjections中首先对injectOptions进行标准化,然后遍历injectOptions中的key,调用inect函数获取key对应值。然后将获取到的值保存到instance.ctx中,最后检查是否存在重复的inject key。整个过程关键就是调用inject函数来获取对应的值,这个值应该从哪里去找呢?我们看下inject函数的实现。
inject方法可以接受三个参数:key、defaultValue(默认值)、treatDefaultAsFactory(默认值是否作为工厂函数,如果为false且defaultValue是个函数,代表默认值是个函数)
ts
export function inject(
key: InjectionKey<any> | string,
defaultValue?: unknown,
treatDefaultAsFactory = false
) {
// fallback to `currentRenderingInstance` so that this can be called in
// a functional component
const instance = currentInstance || currentRenderingInstance
if (instance) {
// 获取provides
// 如果是根组件,会从instance.vnode.appContext中获取,instance.vnode.appContext.provides中是通过`app.provide`提供的数据
// 否则获取父组件中的provides
const provides =
instance.parent == null
? instance.vnode.appContext && instance.vnode.appContext.provides
: instance.parent.provides
// 如果key在provides中返回provides[key]
if (provides && (key as string | symbol) in provides) {
return provides[key as string]
} else if (arguments.length > 1) { // 存在默认值
// 如果defaultValue是个工厂函数,调用defaultValue,否则直接返回defaultValue
return treatDefaultAsFactory && isFunction(defaultValue)
? defaultValue.call(instance.proxy)
: defaultValue
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`injection "${String(key)}" not found.`)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`inject() can only be used inside setup() or functional components.`)
}
}
inject方法中会从instance.vnode.appContext.provides(通过app.provide提供的数据)或instance.parent.provides中获取key对应的值,如果不存在,则会应用设置的默认值(如果设置了默认值的话)。
初始化methods
methods的初始化工作主要是:将methods options中的method添加到instance.ctx中,同时绑定method中的this指向instance.proxy。
ts
if (methods) {
for (const key in methods) {
const methodHandler = (methods as MethodOptions)[key]
if (isFunction(methodHandler)) {
if (__DEV__) {
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
value: methodHandler.bind(publicThis),
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
writable: true
})
} else {
// 将method保存到instance.ctx中,并绑定其this为instance.proxy
ctx[key] = methodHandler.bind(publicThis)
}
if (__DEV__) {
// 检查重复属性
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.METHODS, key)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has type "${typeof methodHandler}" in the component definition. ` +
`Did you reference the function correctly?`
)
}
}
}
初始化data
data的初始化,主要包括:data函数的执行;data函数返回值的校验;将data返回值使用reactive处理并赋给instance.data
ts
if (dataOptions) {
// 检查dataOptions是不是function
if (__DEV__ && !isFunction(dataOptions)) {
warn(
`The data option must be a function. ` +
`Plain object usage is no longer supported.`
)
}
// 执行data
const data = dataOptions.call(publicThis, publicThis)
// data不能返回promise
if (__DEV__ && isPromise(data)) {
warn(
`data() returned a Promise - note data() cannot be async; If you ` +
`intend to perform data fetching before component renders, use ` +
`async setup() + <Suspense>.`
)
}
// data必须为Object
if (!isObject(data)) {
__DEV__ && warn(`data() should return an object.`)
} else {
// 将data转为响应式对象
instance.data = reactive(data)
if (__DEV__) {
for (const key in data) {
// 检查重复key
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.DATA, key)
// dev开发模式下,将data暴露给instance.ctx中
if (!isReservedPrefix(key[0])) {
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
configurable: true,
enumerable: true,
get: () => data[key],
set: NOOP
})
}
}
}
}
}
初始化computed
computed的初始化过程:遍历computed中的key,获取对应的get、set函数,然后使用computed创建一个计算属性。在instance.ctx中添加key属性,同时指定set、get自动脱ref。
ts
if (computedOptions) {
for (const key in computedOptions) {
const opt = (computedOptions as ComputedOptions)[key]
// 获取get函数
const get = isFunction(opt)
? opt.bind(publicThis, publicThis)
: isFunction(opt.get)
? opt.get.bind(publicThis, publicThis)
: NOOP
if (__DEV__ && get === NOOP) {
warn(`Computed property "${key}" has no getter.`)
}
// 获取set函数
const set =
!isFunction(opt) && isFunction(opt.set)
? opt.set.bind(publicThis)
: __DEV__
? () => {
warn(
`Write operation failed: computed property "${key}" is readonly.`
)
}
: NOOP
// 使用computed创建一个计算属性
const c = computed({
get,
set
})
// 在instance.ctx中添加key,同时指定set、get(自动脱ref)
Object.defineProperty(ctx, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: () => c.value,
set: v => (c.value = v)
})
if (__DEV__) {
// 检查重复key
checkDuplicateProperties!(OptionTypes.COMPUTED, key)
}
}
}
初始化watch
watch的初始化:遍历watch的key,使用createWatcher创建`watcher
ts
if (watchOptions) {
for (const key in watchOptions) {
createWatcher(watchOptions[key], ctx, publicThis, key)
}
}
createWatcher函数接收四个参数:raw(key对应的值)、ctx(instance.ctx)、publicThis(watch的handler的this指向)、key
ts
export function createWatcher(
raw: ComponentWatchOptionItem,
ctx: Data,
publicThis: ComponentPublicInstance,
key: string
) {
// 获取getter函数
// 如果key中包含. 说明是嵌套属性,此时getter函数需要递归访问对应属性
const getter = key.includes('.')
? createPathGetter(publicThis, key)
: () => (publicThis as any)[key]
// 值为字符串,根据raw到instance.ctx中获取对应的方法
if (isString(raw)) {
const handler = ctx[raw]
// 如果handler是函数,使用watch api进行监听数据变化
if (isFunction(handler)) {
watch(getter, handler as WatchCallback)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`Invalid watch handler specified by key "${raw}"`, handler)
}
} else if (isFunction(raw)) { // 值为Function,直接使用raw作为回调函数,同时绑定this
watch(getter, raw.bind(publicThis))
} else if (isObject(raw)) {
if (isArray(raw)) { // 值为数组,遍历数组创建多个watcher
raw.forEach(r => createWatcher(r, ctx, publicThis, key))
} else {
// 获取raw中的handler
// 如果raw.handler是函数,绑定this
// 否则在ctx中获取raw.handler对应的值
const handler = isFunction(raw.handler)
? raw.handler.bind(publicThis)
: (ctx[raw.handler] as WatchCallback)
// 如果handler是Function,使用watch api进行监听数据变化
if (isFunction(handler)) {
watch(getter, handler, raw)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`Invalid watch handler specified by key "${raw.handler}"`, handler)
}
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`Invalid watch option: "${key}"`, raw)
}
}
createWatcher主要是根据raw获取getter函数及handler回调函数,然后利用getter与handler通过watch api创建监听。
初始化provide
provide的初始化流程:首先如果provide是个函数的话,需要执行它。然后遍历函数的返回结果的自身属性,利用provide函数设置provides。
ts
if (provideOptions) {
// 获取provides
// 如果provide是function,则执行函数,同时绑定this指向
const provides = isFunction(provideOptions)
? provideOptions.call(publicThis)
: provideOptions
// 遍历自身属性
Reflect.ownKeys(provides).forEach(key => {
provide(key, provides[key])
})
}
provide函数中会利用当时组件实例的父实例的provides,创建一个包含父组件provides的新的对象,然后将自身的provides添加到其中。这样如果使用inject获取对应的值时,就可以直接从父实例的provides中获取值。
ts
export function provide<T>(key: InjectionKey<T> | string | number, value: T) {
if (!currentInstance) {
if (__DEV__) {
warn(`provide() can only be used inside setup().`)
}
} else {
// 获取当前实例的provides
let provides = currentInstance.provides
// 在创建组件实例时instance.provides会继承父实例的provides(如果存在parent.provides)
// 当组件自身存在provides时,会以父实例的provides为基础,创建一个新的对象
// 当使用inject获取值时,就可以直接从父实例中获取对应值
const parentProvides =
currentInstance.parent && currentInstance.parent.provides
if (parentProvides === provides) {
provides = currentInstance.provides = Object.create(parentProvides)
}
// 设置值
provides[key as string] = value
}
}
至此,已经处理完了所有与组件状态相关的options,接下来就会调用created钩子函数。
执行created函数
ts
if (created) {
callHook(created, instance, LifecycleHooks.CREATED)
}
注册生命周期钩子
ts
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeMount, beforeMount)
registerLifecycleHook(onMounted, mounted)
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUpdate, beforeUpdate)
registerLifecycleHook(onUpdated, updated)
registerLifecycleHook(onActivated, activated)
registerLifecycleHook(onDeactivated, deactivated)
registerLifecycleHook(onErrorCaptured, errorCaptured)
registerLifecycleHook(onRenderTracked, renderTracked)
registerLifecycleHook(onRenderTriggered, renderTriggered)
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUnmount, beforeUnmount)
registerLifecycleHook(onUnmounted, unmounted)
registerLifecycleHook(onServerPrefetch, serverPrefetch)
if (__COMPAT__) {
if (
beforeDestroy &&
softAssertCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.OPTIONS_BEFORE_DESTROY, instance)
) {
registerLifecycleHook(onBeforeUnmount, beforeDestroy)
}
if (
destroyed &&
softAssertCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.OPTIONS_DESTROYED, instance)
) {
registerLifecycleHook(onUnmounted, destroyed)
}
}
生命周期钩子会通过一个registerLifecycleHook函数进行注册。
registerLifecycleHook函数接收两个参数:register(一个注册钩子函数的函数)、hook(用户设置的钩子函数)
ts
function registerLifecycleHook(
register: Function,
hook?: Function | Function[]
) {
if (isArray(hook)) {
hook.forEach(_hook => register(_hook.bind(publicThis)))
} else if (hook) {
register((hook as Function).bind(publicThis))
}
}
register
register会通过createHook函数
ts
export const onBeforeMount = createHook(LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_MOUNT)
export const onMounted = createHook(LifecycleHooks.MOUNTED)
export const onBeforeUpdate = createHook(LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_UPDATE)
export const onUpdated = createHook(LifecycleHooks.UPDATED)
export const onBeforeUnmount = createHook(LifecycleHooks.BEFORE_UNMOUNT)
export const onUnmounted = createHook(LifecycleHooks.UNMOUNTED)
export const onServerPrefetch = createHook(LifecycleHooks.SERVER_PREFETCH)
export type DebuggerHook = (e: DebuggerEvent) => void
export const onRenderTriggered = createHook<DebuggerHook>(
LifecycleHooks.RENDER_TRIGGERED
)
export const onRenderTracked = createHook<DebuggerHook>(
LifecycleHooks.RENDER_TRACKED
)
createHook接收一个lifecycle参数,并返回一个函数。这个函数接收两个参数:hook、target(当前组件实例)
ts
export const createHook =
<T extends Function = () => any>(lifecycle: LifecycleHooks) =>
(hook: T, target: ComponentInternalInstance | null = currentInstance) =>
// 如果是SSR,createHook返回一个noop
(!isInSSRComponentSetup || lifecycle === LifecycleHooks.SERVER_PREFETCH) &&
injectHook(lifecycle, hook, target)
ts
export function injectHook(
type: LifecycleHooks,
hook: Function & { __weh?: Function },
target: ComponentInternalInstance | null = currentInstance,
prepend: boolean = false
): Function | undefined {
if (target) {
// 获取组件实例中对应的钩子函数,如果没有则创建一个空数组
const hooks = target[type] || (target[type] = [])
// 缓存被包裹后的钩子函数,以便scheduler可以正确删除钩子
// __weh表示钩子经过错误处理
const wrappedHook =
hook.__weh ||
(hook.__weh = (...args: unknown[]) => {
// 如果组件已经被卸载了,直接return
if (target.isUnmounted) {
return
}
// 停止依赖追踪
pauseTracking()
// 设置当前实例
setCurrentInstance(target)
// 执行钩子函数
const res = callWithAsyncErrorHandling(hook, target, type, args)
// 取消当前实例
unsetCurrentInstance()
// 恢复依赖追踪
resetTracking()
return res
})
// 将被包装后的钩子添加到hooks中
if (prepend) {
hooks.unshift(wrappedHook)
} else {
hooks.push(wrappedHook)
}
return wrappedHook
} else if (__DEV__) {
const apiName = toHandlerKey(ErrorTypeStrings[type].replace(/ hook$/, ''))
warn(
`${apiName} is called when there is no active component instance to be ` +
`associated with. ` +
`Lifecycle injection APIs can only be used during execution of setup().` +
(__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__
? ` If you are using async setup(), make sure to register lifecycle ` +
`hooks before the first await statement.`
: ``)
)
}
}
初始化expose
通过expose的暴露的数据,会被添加到instance.exposed中。当从instance.exposed中获取属性或设置属性,会读取、设置instance.proxy中对应的属性。
ts
if (isArray(expose)) {
if (expose.length) {
const exposed = instance.exposed || (instance.exposed = {})
expose.forEach(key => {
Object.defineProperty(exposed, key, {
get: () => publicThis[key],
set: val => (publicThis[key] = val)
})
})
} else if (!instance.exposed) {
instance.exposed = {}
}
}
初始化render
如果存在render options,并且instance.render是在创建实例时的NOOP,才会进行赋值。如果setup执行过程中设置了render,那么这里是不会生效的。
ts
if (render && instance.render === NOOP) {
instance.render = render as InternalRenderFunction
}
if (inheritAttrs != null) {
instance.inheritAttrs = inheritAttrs
}
初始化components、directives、filters
ts
if (components) instance.components = components as any
if (directives) instance.directives = directives
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
filters &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.FILTERS, instance)
) {
instance.filters = filters
}
总结
组件实例的创建流程: