外观
模板的解析
在前文中,我们将模板的编译过程概括为三个阶段:由template解析出模板AST、将模板AST转换为JavaScript AST、根据JavaScript AST生成`渲染函数。
本文我们就从第一个阶段开始,分析如何将template解析为AST,即parse过程。
template的解析过程其实就是一个状态机,它的状态转移过程和WHATWG中HTML的解析标准是相似的。
你可以直接使用@vue/compiler-dom包解析template。
html
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"compiler-dom": "https://unpkg.com/@vue/compiler-dom@3.2.37/dist/compiler-dom.esm-browser.js"
}
}
</script>
<template id="demo">
<ul :class="ulClass">
<li v-for="item in data" :key="item.id">{{ item.text }}</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script type="module">
import { parse } from 'compiler-dom'
const template = document.querySelector('#demo').innerHTML
console.log(parse(template))
</script>
parse
parse方法会调用一个baseParse方法进行解析template。
ts
export function parse(template: string, options: ParserOptions = {}): RootNode {
return baseParse(template, extend({}, parserOptions, options))
}
baseParse:
ts
export function baseParse(
content: string,
options: ParserOptions = {}
): RootNode {
// 创建上下文
const context = createParserContext(content, options)
// 获取游标
const start = getCursor(context)
// 创建根节点,同时解析content生成孩子节点
return createRoot(
parseChildren(context, TextModes.DATA, []),
// 获取需要解析的源码片段
getSelection(context, start)
)
}
在baseParse中首先使用createParserContext创建一个上下文对象。
ts
function createParserContext(
content: string,
rawOptions: ParserOptions
): ParserContext {
const options = extend({}, defaultParserOptions)
let key: keyof ParserOptions
// 如果rawOptions[key]为undefined,则应用defaultParserOptions[key]
for (key in rawOptions) {
options[key] =
rawOptions[key] === undefined
? defaultParserOptions[key]
: rawOptions[key]
}
return {
options, // 解析options
column: 1, // 当前列
line: 1, // 当前行
offset: 0, // 当前偏移量
originalSource: content, // 原始template
source: content, // 随着不断解析,不断进行更换
inPre: false, // 是否为<pre>标签,在<pre>标签内的内容,会保留空格和换行
inVPre: false, // 是否存在v-pre指令,拥有v-pre指令的元素及其子元素,会跳过他们的编译
onWarn: options.onWarn
}
}
getCursor方法在解析template中是个常用的方法,它可以获取某一时刻上下文中的位置信息。
ts
function getCursor(context: ParserContext): Position {
const { column, line, offset } = context
return { column, line, offset }
}
最后使用createRoot方法创建一个AST根节点。在创建根节点前,会先使用parseChildren解析子节点。
TextModes
模板的解析本质是个状态机,其状态迁移流程和HTML的解析过程十分类似。在不同状态下,解析器的解析行为是不同的。例如在<textarea>中的标签并不会被作为标签被解析,而是将其解析为文本,在<div>中的标签会被作为标签解析。
以下是一些特殊的状态:
ts
export const enum TextModes {
// | Elements | Entities | End sign | Inside of
DATA, // | ✔ | ✔ | End tags of ancestors |
RCDATA, // | ✘ | ✔ | End tag of the parent | <textarea>
RAWTEXT, // | ✘ | ✘ | End tag of the parent | <style>,<script>
CDATA,
ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
}
DATA状态下,解析器可以解析标签和字符实体。WHATWG DATA stateRCDATA状态下,解析器不可以解析标签,但可以解析字符实体。WHATWG RCDATA stateRAWTEXT状态下,解析器既不可以解析标签,也不可以解析字符实体。WHATWG RAWTEXT stateCDATA状态下,和RAWTEXT类似,解析器既不可以解析标签,也不可以解析字符实体,解析器会把任何字符都当做普通字符处理。WHATWG CDATA stateATTRIBUTE_VALUE
parseChildren
parseChildren函数是整个解析过程的核心函数,它接收三个参数:context上下文(包含解析过程中的一些状态)、mode当前所处的状态、ancestors一个父节点栈。
parseChildren源码
ts
function parseChildren(
context: ParserContext,
mode: TextModes,
ancestors: ElementNode[]
): TemplateChildNode[] {
// 获取父节点
const parent = last(ancestors)
const ns = parent ? parent.ns : Namespaces.HTML
const nodes: TemplateChildNode[] = []
while (!isEnd(context, mode, ancestors)) {
__TEST__ && assert(context.source.length > 0)
const s = context.source
let node: TemplateChildNode | TemplateChildNode[] | undefined = undefined
if (mode === TextModes.DATA || mode === TextModes.RCDATA) {
// 不在v-pre指令中,并且s以{{开头
// 处理插值
if (!context.inVPre && startsWith(s, context.options.delimiters[0])) {
// '{{'
node = parseInterpolation(context, mode)
}
// mode为TextModes.DATA,并且s以<开头
else if (mode === TextModes.DATA && s[0] === '<') {
// https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/parsing.html#tag-open-state
// 如果长度为1,解析错误
if (s.length === 1) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.EOF_BEFORE_TAG_NAME, 1)
} else if (s[1] === '!') { // 如果以<!开头
if (startsWith(s, '<!--')) { // 以<!--开头,按照注释进进行解析
node = parseComment(context)
} else if (startsWith(s, '<!DOCTYPE')) { // 以<!DOCTYPE开头,会按照注释进行解析
node = parseBogusComment(context)
} else if (startsWith(s, '<![CDATA[')) { // 以<![CDATA[开头
// ns不为Namespaces.HTML,按照CDATA进行解析,否则按照注释进行解析
if (ns !== Namespaces.HTML) {
node = parseCDATA(context, ancestors)
} else {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.CDATA_IN_HTML_CONTENT)
node = parseBogusComment(context)
}
} else { // 其他情况,按照注释进行解析
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.INCORRECTLY_OPENED_COMMENT)
node = parseBogusComment(context)
}
} else if (s[1] === '/') { // 以</开头
// https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/parsing.html#end-tag-open-state
// 如果长度为2,解析错误
if (s.length === 2) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.EOF_BEFORE_TAG_NAME, 2)
} else if (s[2] === '>') { // 以</>开头,解析错误
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.MISSING_END_TAG_NAME, 2)
advanceBy(context, 3)
continue
} else if (/[a-z]/i.test(s[2])) { // 以</[a-z]开头,解析错误
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.X_INVALID_END_TAG)
parseTag(context, TagType.End, parent)
continue
} else {
emitError(
context,
ErrorCodes.INVALID_FIRST_CHARACTER_OF_TAG_NAME,
2
)
node = parseBogusComment(context)
}
} else if (/[a-z]/i.test(s[1])) { // 以<[a-z]开头,按照标签节点进行解析
node = parseElement(context, ancestors)
// 2.x <template> with no directive compat
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_NATIVE_TEMPLATE,
context
) &&
node &&
node.tag === 'template' &&
!node.props.some(
p =>
p.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE &&
isSpecialTemplateDirective(p.name)
)
) {
__DEV__ &&
warnDeprecation(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_NATIVE_TEMPLATE,
context,
node.loc
)
node = node.children
}
} else if (s[1] === '?') { // 以<?开头,解析错误
emitError(
context,
ErrorCodes.UNEXPECTED_QUESTION_MARK_INSTEAD_OF_TAG_NAME,
1
)
node = parseBogusComment(context)
} else {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.INVALID_FIRST_CHARACTER_OF_TAG_NAME, 1)
}
}
}
// 如果node不存在,说明mode不为DATA或RCDATA
// 这时按文本进行解析
if (!node) {
node = parseText(context, mode)
}
// 将node放入nodes中
if (isArray(node)) {
for (let i = 0; i < node.length; i++) {
pushNode(nodes, node[i])
}
} else {
pushNode(nodes, node)
}
}
// 处理空格
let removedWhitespace = false
if (mode !== TextModes.RAWTEXT && mode !== TextModes.RCDATA) {
const shouldCondense = context.options.whitespace !== 'preserve'
for (let i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++) {
const node = nodes[i]
if (!context.inPre && node.type === NodeTypes.TEXT) {
if (!/[^\t\r\n\f ]/.test(node.content)) {
const prev = nodes[i - 1]
const next = nodes[i + 1]
// Remove if:
// - the whitespace is the first or last node, or:
// - (condense mode) the whitespace is adjacent to a comment, or:
// - (condense mode) the whitespace is between two elements AND contains newline
if (
!prev ||
!next ||
(shouldCondense &&
(prev.type === NodeTypes.COMMENT ||
next.type === NodeTypes.COMMENT ||
(prev.type === NodeTypes.ELEMENT &&
next.type === NodeTypes.ELEMENT &&
/[\r\n]/.test(node.content))))
) {
removedWhitespace = true
nodes[i] = null as any
} else {
// Otherwise, the whitespace is condensed into a single space
node.content = ' '
}
} else if (shouldCondense) {
// in condense mode, consecutive whitespaces in text are condensed
// down to a single space.
node.content = node.content.replace(/[\t\r\n\f ]+/g, ' ')
}
}
// Remove comment nodes if desired by configuration.
else if (node.type === NodeTypes.COMMENT && !context.options.comments) {
removedWhitespace = true
nodes[i] = null as any
}
}
if (context.inPre && parent && context.options.isPreTag(parent.tag)) {
// remove leading newline per html spec
// https://html.spec.whatwg.org/multipage/grouping-content.html#the-pre-element
const first = nodes[0]
if (first && first.type === NodeTypes.TEXT) {
first.content = first.content.replace(/^\r?\n/, '')
}
}
}
return removedWhitespace ? nodes.filter(Boolean) : nodes
}
parseChildren的过程就是一个状态机,其状态迁移过程可以简单表示如下:
- 如果字符串以
{{开头,则表示它是个插值节点,调用parseInterpolation解析插值节点。 - 如果遇到
<。- 如果字符串长度为1,抛出错误(错误信息为
Unexpected EOF in tag)。 - 如果下一个字符为
!。- 如果字符串以
<!--开头,则表示它是一个注释节点,调用parseComment解析注释节点。 - 如果字符串以
<!DOCTYPE开头,则会按照注释进行处理<!与>之间的内容。 - 如果字符串以
<![CDATA[开头。如果命名空间为HTML,抛出错误(错误信息为CDATA section is allowed only in XML context);否则调用parseCDATA函数按CDATA节点处理。 - 其他情况,抛出错误(错误信息为
Incorrectly opened comment)。
- 如果字符串以
- 如果下一个字符为
/。- 如果字符串长度为2,抛出错误(错误信息为
Unexpected EOF in tag)。 - 如果下一个字符为
>,抛出错误(错误信息为End tag name was expected)。 - 如果下一个字符匹配
/[a-z]/i,抛出错误(错误信息为Invalid end tag)。为什么这里抛出错误?因为每解析到一个开始标签,就会消费一个对应的闭合标签,所以如果在此处碰到闭合标签,说明缺少对应的开始标签。 - 其他情况,抛出错误(错误信息为
Illegal tag name. Use '<' to print '<'.)。
- 如果字符串长度为2,抛出错误(错误信息为
- 如果下一个字符匹配
/[a-z]/i,则表示它是个标签节点,调用parseElement解析标签。 - 如果下一个字符为
?,抛出错误(错误信息为'<?' is allowed only in XML context)。 - 其他情况,抛出错误(错误信息为
Illegal tag name. Use '<' to print '<'.)。
- 如果字符串长度为1,抛出错误(错误信息为
下图示praseChildren的状态转移过程,其中xxx state引用的是WHATWG中的定义的状态
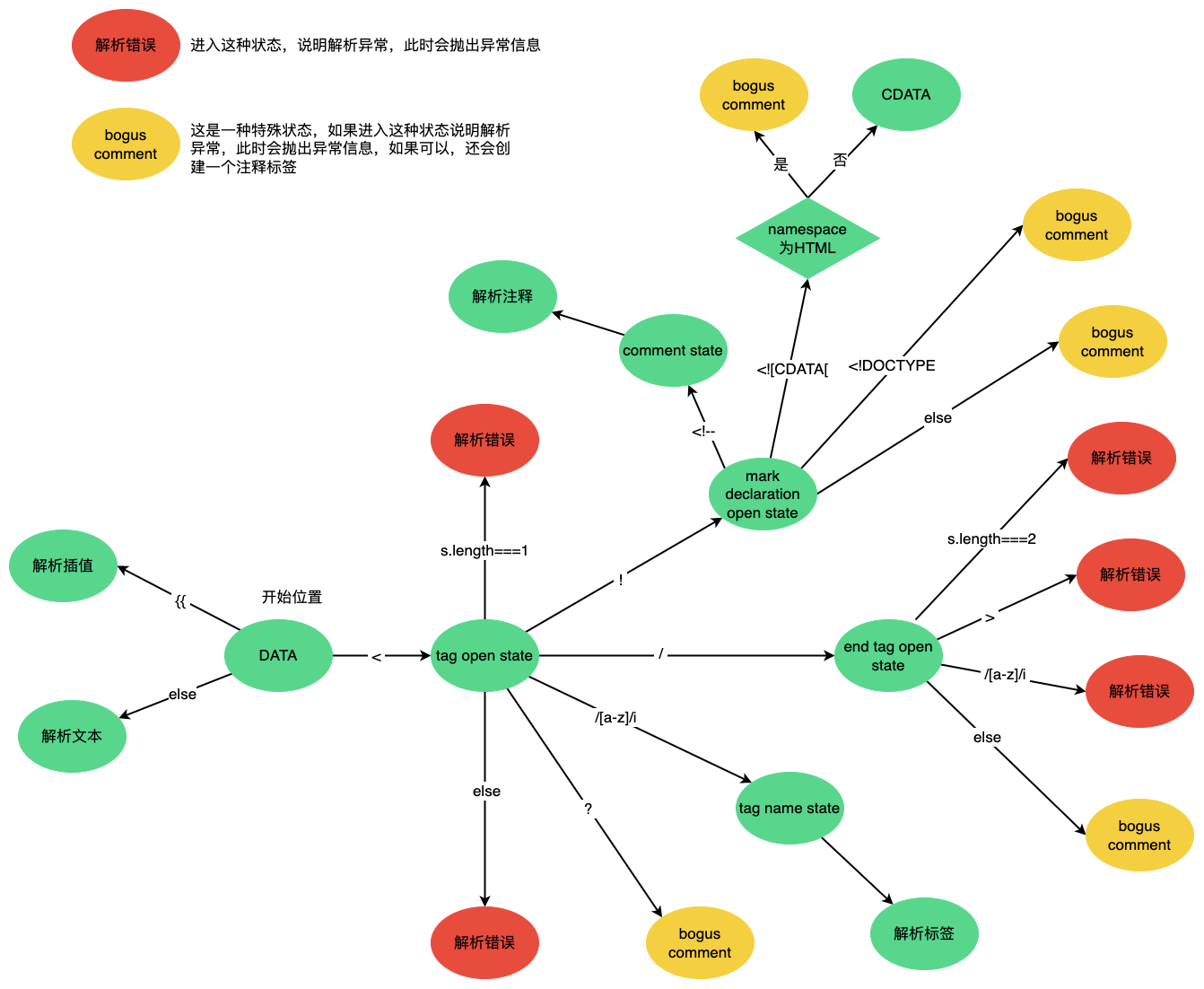
状态机何时结束?
在while循环过程中,通过一个isEnd函数来判断状态机是否应该停止。
ts
function isEnd(
context: ParserContext,
mode: TextModes,
ancestors: ElementNode[]
): boolean {
const s = context.source
switch (mode) {
// DATA模式下,支持解析标签
// 所以只要父节点栈中存在与source中的标签名一致的节点,则本轮解析完毕
// 为什么需要从父节点栈中从栈顶向栈底寻找?
// 这是因为如果标签是错乱的,也需要尽可能找到开始标签。
// 如<div><p></div></p>,此时会解析出div标签,p标签在parseElement过程中,由于未匹配闭合标签,所以抛出错误
case TextModes.DATA:
if (startsWith(s, '</')) {
// 如果source以</开头,并且父节点栈中存在对应的开始标签,则本轮解析完毕
for (let i = ancestors.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (startsWithEndTagOpen(s, ancestors[i].tag)) {
return true
}
}
}
break
// 由于RCDATA和RAWTEXT不支持解析标签
// 所以只要判断父节点栈中的最后一个节点标签名与此时source中的标签名是否一致即可
case TextModes.RCDATA:
case TextModes.RAWTEXT: {
const parent = last(ancestors)
// 存在父节点,并且source中的标签名与父节点标签名一致
if (parent && startsWithEndTagOpen(s, parent.tag)) {
return true
}
break
}
case TextModes.CDATA:
// source以]]>开头,则本轮解析完毕
if (startsWith(s, ']]>')) {
return true
}
break
}
// source消耗完毕,则解析完毕
return !s
}
parseInterpolation解析插值
ts
function parseInterpolation(
context: ParserContext,
mode: TextModes
): InterpolationNode | undefined {
// 获取插值分隔符,默认"{{"、"}}"
const [open, close] = context.options.delimiters
__TEST__ && assert(startsWith(context.source, open))
// 获取关闭插值分隔符的索引
const closeIndex = context.source.indexOf(close, open.length)
// 如果没有关闭插值分隔符,说明插值分隔符未关闭
if (closeIndex === -1) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.X_MISSING_INTERPOLATION_END)
return undefined
}
// 获取开始的游标
const start = getCursor(context)
// 将开始的插值分隔符消费掉,并更新context.source/offset/line/column
advanceBy(context, open.length)
// 插值开始位置
const innerStart = getCursor(context)
// 插值结束位置
const innerEnd = getCursor(context)
// 插值的长度
const rawContentLength = closeIndex - open.length
// 获取插值内容,"{{"与"}}"中间的内容
const rawContent = context.source.slice(0, rawContentLength)
// 解析插值内容
const preTrimContent = parseTextData(context, rawContentLength, mode)
// 删除两端空格
const content = preTrimContent.trim()
// 如果插值中存在前置空格,需要更新start位置
const startOffset = preTrimContent.indexOf(content)
if (startOffset > 0) {
advancePositionWithMutation(innerStart, rawContent, startOffset)
}
// 更新结束位置
const endOffset =
rawContentLength - (preTrimContent.length - content.length - startOffset)
advancePositionWithMutation(innerEnd, rawContent, endOffset)
// 消费关闭的插值分隔符
advanceBy(context, close.length)
// 生成节点并返回
return {
type: NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION,
content: {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION,
isStatic: false,
constType: ConstantTypes.NOT_CONSTANT,
// 去除空格后的插值
content,
// 使用getSelection获取innerStart-innerEnd之间的内容
loc: getSelection(context, innerStart, innerEnd)
},
// 包含插值分隔符的内容
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
解析插值时,首先进行插值分隔符是否完整,如果缺失关闭分隔符(默认}}),则抛出错误。如果插值完整,则会解析出不包含前后空格的插值表达式,并生成节点返回。
这里有几个比较重要的方法advanceBy、advancePositionWithMutation。advanceBy方法会消费上下文中source指定的长度,即将source从头开始删除指定长度的字符,并进行重新赋值。advancePositionWithMutation方法可以更新传入位置对象中的游标信息。
ts
function advanceBy(context: ParserContext, numberOfCharacters: number): void {
const { source } = context
__TEST__ && assert(numberOfCharacters <= source.length)
// 将context中的游标信息,向后移动numberOfCharacters步
advancePositionWithMutation(context, source, numberOfCharacters)
// 删除source的前numberOfCharacters个字符并重新赋值
context.source = source.slice(numberOfCharacters)
}
export function advancePositionWithMutation(
pos: Position,
source: string,
numberOfCharacters: number = source.length
): Position {
// 行数
let linesCount = 0
// 最后一行的位置
let lastNewLinePos = -1
for (let i = 0; i < numberOfCharacters; i++) {
// 如果第i个字符是换行符,行数+1,更新lastNewLinePos为i
if (source.charCodeAt(i) === 10 /* newline char code */) {
linesCount++
lastNewLinePos = i
}
}
// 更新偏移量,直接+numberOfCharacters即可
pos.offset += numberOfCharacters
// 更新行数
pos.line += linesCount
// 更新列数
// 如果lastNewLinePos为-1,说明未发生换行,column = column + numberOfCharacters
// 否则列数为numberOfCharacters - lastNewLinePos,因为是新行,所以列数就等于需要偏移的字符数 - 发生最后一次换行的字符索引
// 如偏移字符数为4,索引2处发生最后一次换行,那么此时列数其实就是索引2后面的字符数,即4 - 2
pos.column =
lastNewLinePos === -1
? pos.column + numberOfCharacters
: numberOfCharacters - lastNewLinePos
return pos
}
parseTextData
在解析插值表达式时,并不是直接将去除前后空格之后的内容作为插值表达式,而是调用了一个parseTextData方法。
ts
function parseTextData(
context: ParserContext,
length: number,
mode: TextModes
): string {
// 获取原始内容
const rawText = context.source.slice(0, length)
// 消费length数量的字符
advanceBy(context, length)
// 如果mode为RAWTEXT或CDATA,或rawText中不包含&,直接返回rawText
if (
mode === TextModes.RAWTEXT ||
mode === TextModes.CDATA ||
!rawText.includes('&')
) {
return rawText
} else { // 否则会调用context.options.decodeEntities方法进行解析
// DATA or RCDATA containing "&"". Entity decoding required.
return context.options.decodeEntities(
rawText,
mode === TextModes.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
)
}
}
parseTextData中会首先调用advanceBy消费掉指定数量的字符,然后判断mode是否为RAWTEXT或CDATA或文本中不包含&字符,如果符合条件,直接返回原始文本,否则调用context.options.decodeEntities进行解码。
这是因为RAWTEXT或CDATA模式下,不支持字符实体的解析,所以可以直接返回原始文本;而DATA或RCDATA模式下,是可以解析字符实体的,所以调用context.options.decodeEntities进行解码。
parseText解析文本
ts
function parseText(context: ParserContext, mode: TextModes): TextNode {
__TEST__ && assert(context.source.length > 0)
// 如果在CDATA模式下,遇到]]>后,解析结束
// 否则遇到<或开始的插值分隔符,解析结束
const endTokens =
mode === TextModes.CDATA ? [']]>'] : ['<', context.options.delimiters[0]]
// 获取结束解析索引
let endIndex = context.source.length
for (let i = 0; i < endTokens.length; i++) {
// context.source中的结束标识符的索引
// 这里从索引1处开始查找,因为索引0处的字符决定了需要解析文本,所以索引0处的字符不可能是结束表示符
// 如果同时存在<和开始的插值分隔符,则取靠左的结束索引
const index = context.source.indexOf(endTokens[i], 1)
if (index !== -1 && endIndex > index) {
endIndex = index
}
}
__TEST__ && assert(endIndex > 0)
// 获取开始的游标
const start = getCursor(context)
// 调用parseTextData解析文本
const content = parseTextData(context, endIndex, mode)
return {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT,
content,
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
在解析文本过程中,如果在CDATA模式下,遇到]]>结束解析,否则遇到<或开始插值分隔符(默认{{)结束解析。
parseComment解析注释
ts
function parseComment(context: ParserContext): CommentNode {
__TEST__ && assert(startsWith(context.source, '<!--'))
const start = getCursor(context)
let content: string
// 使用正则匹配注释的结束标识符
const match = /--(\!)?>/.exec(context.source)
// 如果没有结束标识符,说明注释节点没有被正确关闭,此时抛出错误
if (!match) {
content = context.source.slice(4)
advanceBy(context, context.source.length)
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.EOF_IN_COMMENT)
} else {
// 如果结束标识符索引小于等于3,说明注释节点不合法
// 因为进入parseComment方法时,说明注释节点至少存在"<!--",如果束标识符索引小于等于3,说明注释节点时不合法的,如<!--->
if (match.index <= 3) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.ABRUPT_CLOSING_OF_EMPTY_COMMENT)
}
// <!-- xx --!>,不合法
if (match[1]) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.INCORRECTLY_CLOSED_COMMENT)
}
// 注释的内容
content = context.source.slice(4, match.index)
// 注释中如果存在"<!--",抛出错误
const s = context.source.slice(0, match.index)
let prevIndex = 1,
nestedIndex = 0
while ((nestedIndex = s.indexOf('<!--', prevIndex)) !== -1) {
// 消费掉"<!--"
advanceBy(context, nestedIndex - prevIndex + 1)
// 如果"<!--"的索引位置+4小于s的长度,说明注释中存在嵌套<!--。
if (nestedIndex + 4 < s.length) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.NESTED_COMMENT)
}
prevIndex = nestedIndex + 1
}
// 消费完整的注释节点
advanceBy(context, match.index + match[0].length - prevIndex + 1)
}
return {
type: NodeTypes.COMMENT,
content,
loc: getSelection(context, start)
}
}
对于注释节点的解析,首先利用正则表达式/--(\!)?>/进行字符串匹配,如果没有匹配到结果,说明注释节点未关闭。如果存在匹配结果,但匹配到的开始索引小于等于3,说明注释是不合法的,因为注释节点的开始部分<!--的最大索引为3,如果结束部分的索引小等于3,说明-字符不足4个,如<!--->、<!-->;如果正则匹配到了!的话,注释节点也是不合法的;如果注释节点中存在<!--字符,也会抛出错误。
parseElement解析标签
parseElement源码
ts
function parseElement(
context: ParserContext,
ancestors: ElementNode[]
): ElementNode | undefined {
__TEST__ && assert(/^<[a-z]/i.test(context.source))
// 是否为pre标签
const wasInPre = context.inPre
// 是否在v-pre中
const wasInVPre = context.inVPre
// 父节点
const parent = last(ancestors)
// 解析tag
const element = parseTag(context, TagType.Start, parent)
// element是否为pre边界
const isPreBoundary = context.inPre && !wasInPre
// element是否为v-pre的边界
const isVPreBoundary = context.inVPre && !wasInVPre
// 如果标签是自闭和标签或是void标签(area,base,br,col,embed,hr,img,input,link,meta,param,source,track,wbr)
if (element.isSelfClosing || context.options.isVoidTag(element.tag)) {
if (isPreBoundary) {
context.inPre = false
}
if (isVPreBoundary) {
context.inVPre = false
}
return element
}
// Children.
ancestors.push(element)
// 获取此时的mode
const mode = context.options.getTextMode(element, parent)
// 递归解析子节点
const children = parseChildren(context, mode, ancestors)
// 弹出element
ancestors.pop()
// 2.x inline-template compat
if (__COMPAT__) {
const inlineTemplateProp = element.props.find(
p => p.type === NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE && p.name === 'inline-template'
) as AttributeNode
if (
inlineTemplateProp &&
checkCompatEnabled(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_INLINE_TEMPLATE,
context,
inlineTemplateProp.loc
)
) {
const loc = getSelection(context, element.loc.end)
inlineTemplateProp.value = {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT,
content: loc.source,
loc
}
}
}
// 设置子节点
element.children = children
// 解析结束标签
if (startsWithEndTagOpen(context.source, element.tag)) {
parseTag(context, TagType.End, parent)
} else {
// 结束标签丢失
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.X_MISSING_END_TAG, 0, element.loc.start)
if (context.source.length === 0 && element.tag.toLowerCase() === 'script') {
const first = children[0]
if (first && startsWith(first.loc.source, '<!--')) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.EOF_IN_SCRIPT_HTML_COMMENT_LIKE_TEXT)
}
}
}
element.loc = getSelection(context, element.loc.start)
if (isPreBoundary) {
context.inPre = false
}
if (isVPreBoundary) {
context.inVPre = false
}
return element
}
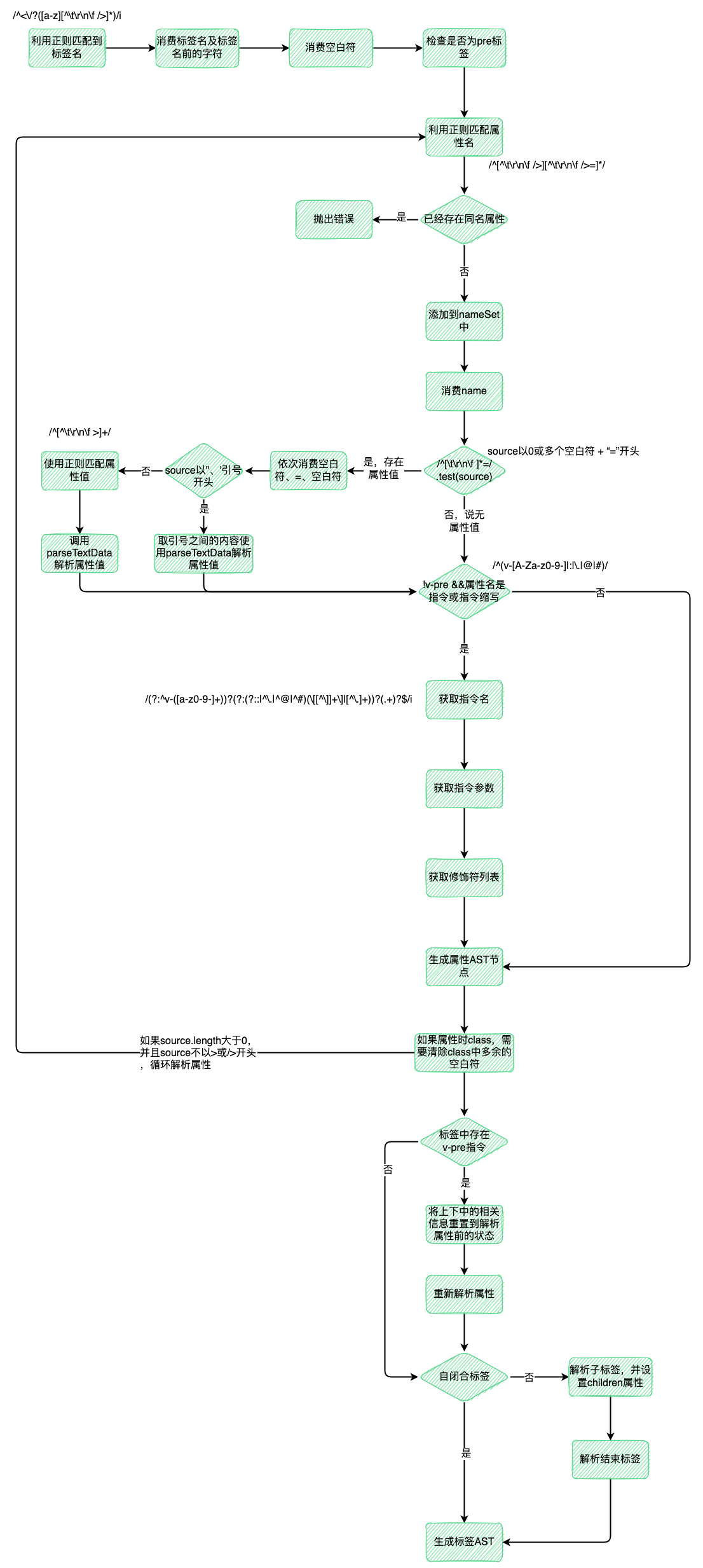
标签的解析主要分为四个步骤:
- 解析标签名
- 解析属性
- 解析子节点
- 解析闭合标签
如果节点是自闭合标签或void标签(包括area、base、br、col、embed、hr、img、input,link、meta、param、source、track、wbr),3、4步是不需要进行的。
parseTag
parseTag源码
ts
function parseTag(
context: ParserContext,
type: TagType,
parent: ElementNode | undefined
): ElementNode | undefined {
__TEST__ && assert(/^<\/?[a-z]/i.test(context.source))
__TEST__ &&
assert(
type === (startsWith(context.source, '</') ? TagType.End : TagType.Start)
)
// Tag open.
const start = getCursor(context)
// 使用正则匹配标签
// 正则解释:
// 以"<"开头,紧跟着可以有一个"/",然后紧跟着字母,然后其后不能是空白或"/"、">"
const match = /^<\/?([a-z][^\t\r\n\f />]*)/i.exec(context.source)!
// 标签名
const tag = match[1]
// 获取命名空间
const ns = context.options.getNamespace(tag, parent)
// 消费掉标签及标签之前的字符
advanceBy(context, match[0].length)
// 消费空白符,包括制表符、换行符、回车符、换页符、空格
advanceSpaces(context)
// 如果存在v-pre属性,需要借助这两个状态重新解析属性
const cursor = getCursor(context)
const currentSource = context.source
// 检查是否为pre标签
if (context.options.isPreTag(tag)) {
context.inPre = true
}
// 解析属性
let props = parseAttributes(context, type)
// 如果存在v-pre指令需要重新解析属性
if (
type === TagType.Start &&
!context.inVPre &&
props.some(p => p.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE && p.name === 'pre')
) {
context.inVPre = true
// 重置context中的source及游标信息到解析属性之前的状态
extend(context, cursor)
context.source = currentSource
// 重新解析属性并过滤v-pre属性
props = parseAttributes(context, type).filter(p => p.name !== 'v-pre')
}
// Tag close.
let isSelfClosing = false
// 如果此时source长度为0,说明标签未关闭
if (context.source.length === 0) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.EOF_IN_TAG)
} else {
// 是否为自闭合标签
isSelfClosing = startsWith(context.source, '/>')
// 如果现在解析的闭合标签,但是标签又为自闭和标签,name标签是不合法的
if (type === TagType.End && isSelfClosing) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.END_TAG_WITH_TRAILING_SOLIDUS)
}
// 消费闭合字符,如果是自闭合标签,消费"/>",否则消费">"
advanceBy(context, isSelfClosing ? 2 : 1)
}
// 如果解析的是闭合标签,此时可以return了
if (type === TagType.End) {
return
}
// 2.x deprecation checks
// v-if与v-for优先级发生变化,进行提示
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
__DEV__ &&
isCompatEnabled(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_V_IF_V_FOR_PRECEDENCE,
context
)
) {
let hasIf = false
let hasFor = false
for (let i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
const p = props[i]
if (p.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE) {
if (p.name === 'if') {
hasIf = true
} else if (p.name === 'for') {
hasFor = true
}
}
if (hasIf && hasFor) {
warnDeprecation(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_V_IF_V_FOR_PRECEDENCE,
context,
getSelection(context, start)
)
break
}
}
}
// 确定标签类型,默认ElementTypes.ELEMENT
// 如果没有v-pre指令
// - 标签名为slot,那么标签类型则为 ElementTypes.SLOT
// - 标签名为template,并且标签属性中存在if,else,else-if,for,slot中的任意一个或多个,那么标签类型为ElementTypes.TEMPLATE
// - 标签名为组件,那么标签类型为ElementTypes.COMPONENT
let tagType = ElementTypes.ELEMENT
if (!context.inVPre) {
if (tag === 'slot') {
tagType = ElementTypes.SLOT
} else if (tag === 'template') {
if (
props.some(
p =>
p.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE && isSpecialTemplateDirective(p.name)
)
) {
tagType = ElementTypes.TEMPLATE
}
} else if (isComponent(tag, props, context)) {
tagType = ElementTypes.COMPONENT
}
}
return {
type: NodeTypes.ELEMENT,
ns,
tag,
tagType,
props,
isSelfClosing,
children: [],
loc: getSelection(context, start),
codegenNode: undefined // to be created during transform phase
}
}
parseAttributes源码
ts
function parseAttributes(
context: ParserContext,
type: TagType
): (AttributeNode | DirectiveNode)[] {
const props = []
const attributeNames = new Set<string>()
// 循环解析属性
// 循环条件为:source长度大于0且不以">"和"/>"开头
while (
context.source.length > 0 &&
!startsWith(context.source, '>') &&
!startsWith(context.source, '/>')
) {
// 如果source以"/"开头,抛出错误
if (startsWith(context.source, '/')) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.UNEXPECTED_SOLIDUS_IN_TAG)
advanceBy(context, 1)
advanceSpaces(context)
continue
}
// 如果现在是在解析闭合标签,抛出错误
if (type === TagType.End) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.END_TAG_WITH_ATTRIBUTES)
}
// 解析属性
const attr = parseAttribute(context, attributeNames)
// 去除class属性的多余空白符
// 包括去除首尾空格,减少class之间的空格
// 可以减小css的大小
if (
attr.type === NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE &&
attr.value &&
attr.name === 'class'
) {
attr.value.content = attr.value.content.replace(/\s+/g, ' ').trim()
}
// 将解析好的属性放入props中
if (type === TagType.Start) {
props.push(attr)
}
// 如果此时的source开头不存在任何空白符,那么抛出错误。
// 属性之间必须要有空白符
if (/^[^\t\r\n\f />]/.test(context.source)) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.MISSING_WHITESPACE_BETWEEN_ATTRIBUTES)
}
advanceSpaces(context)
}
return props
}
parseAttribute源码:
ts
function parseAttribute(
context: ParserContext,
nameSet: Set<string>
): AttributeNode | DirectiveNode {
__TEST__ && assert(/^[^\t\r\n\f />]/.test(context.source))
// Name.
const start = getCursor(context)
// 匹配属性名
// 正则解释
// ^[^\t\r\n\f />]:不能以空白字符,或"/"、">"字符开头
// [^\t\r\n\f />=]*:匹配0或多个非空白、"/"、">"、"="字符
const match = /^[^\t\r\n\f />][^\t\r\n\f />=]*/.exec(context.source)!
// 属性名
const name = match[0]
// 已经存在重复的属性名,抛出错误
if (nameSet.has(name)) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.DUPLICATE_ATTRIBUTE)
}
// 添加到set中
nameSet.add(name)
// 如果属性名以"="开头,抛出错误
if (name[0] === '=') {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.UNEXPECTED_EQUALS_SIGN_BEFORE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME)
}
// 如果name中存在"、'、<字符,抛出错误
{
const pattern = /["'<]/g
let m: RegExpExecArray | null
while ((m = pattern.exec(name))) {
emitError(
context,
ErrorCodes.UNEXPECTED_CHARACTER_IN_ATTRIBUTE_NAME,
m.index
)
}
}
// 消费name
advanceBy(context, name.length)
// Value
let value: AttributeValue = undefined
// 检查此时source是否以(0或多个空白符 + "=")开头
if (/^[\t\r\n\f ]*=/.test(context.source)) {
// 消费空白符
advanceSpaces(context)
// 消费=
advanceBy(context, 1)
// 消费空白符
advanceSpaces(context)
// 解析属性值
value = parseAttributeValue(context)
// 如果未解析出属性值,抛出错误
if (!value) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.MISSING_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
}
}
const loc = getSelection(context, start)
// 如果不在v-pre指令中且name是指令或指令缩写
// 以v-xxx、v--、:、.、@、#开头
if (!context.inVPre && /^(v-[A-Za-z0-9-]|:|\.|@|#)/.test(name)) {
const match =
/(?:^v-([a-z0-9-]+))?(?:(?::|^\.|^@|^#)(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+))?(.+)?$/i.exec(
name
)!
let isPropShorthand = startsWith(name, '.')
// 指令名
// 如果存在match[1],取match[1]
// 否则,如果name以":"或"."开头,则为bind;如果以"@"开头,则为on;其他情况(以"#"开头)为slot
let dirName =
match[1] ||
(isPropShorthand || startsWith(name, ':')
? 'bind'
: startsWith(name, '@')
? 'on'
: 'slot')
let arg: ExpressionNode | undefined
// 存在match[2],(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+)部分匹配到的内容
// 例如
// v-model:value,match[2]为value
// @click,match[2]为click
// v-html,match[2]为undefined
if (match[2]) {
const isSlot = dirName === 'slot'
const startOffset = name.lastIndexOf(match[2])
// 获取参数名在原始source中的位置信息及对应的原始字符串
const loc = getSelection(
context,
getNewPosition(context, start, startOffset),
getNewPosition(
context,
start,
startOffset + match[2].length + ((isSlot && match[3]) || '').length
)
)
let content = match[2]
// 是否为静态属性
let isStatic = true
// 如果content以"["开头,说明是动态属性
if (content.startsWith('[')) {
isStatic = false
// 如果content没有以"]"结束,抛出错误
if (!content.endsWith(']')) {
emitError(
context,
ErrorCodes.X_MISSING_DYNAMIC_DIRECTIVE_ARGUMENT_END
)
content = content.slice(1)
} else {
// 获取动态属性
content = content.slice(1, content.length - 1)
}
} else if (isSlot) {
// v-slot与vue2保持一致,允许v-slot:item.name="xxx"
content += match[3] || ''
}
arg = {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION,
content,
isStatic,
constType: isStatic
? ConstantTypes.CAN_STRINGIFY
: ConstantTypes.NOT_CONSTANT,
loc
}
}
// value以"或'开头,需要修改value.loc的中的位置信息(去除前后引号)
if (value && value.isQuoted) {
const valueLoc = value.loc
valueLoc.start.offset++
valueLoc.start.column++
valueLoc.end = advancePositionWithClone(valueLoc.start, value.content)
valueLoc.source = valueLoc.source.slice(1, -1)
}
// 修饰符列表
const modifiers = match[3] ? match[3].slice(1).split('.') : []
if (isPropShorthand) modifiers.push('prop')
// 2.x compat v-bind:foo.sync -> v-model:foo
if (__COMPAT__ && dirName === 'bind' && arg) {
if (
modifiers.includes('sync') &&
checkCompatEnabled(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_V_BIND_SYNC,
context,
loc,
arg.loc.source
)
) {
dirName = 'model'
modifiers.splice(modifiers.indexOf('sync'), 1)
}
if (__DEV__ && modifiers.includes('prop')) {
checkCompatEnabled(
CompilerDeprecationTypes.COMPILER_V_BIND_PROP,
context,
loc
)
}
}
return {
type: NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE,
name: dirName,
exp: value && {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION,
content: value.content,
isStatic: false,
constType: ConstantTypes.NOT_CONSTANT,
loc: value.loc
},
arg,
modifiers,
loc
}
}
// 缺少指令名或非法指令名,抛出错误
if (!context.inVPre && startsWith(name, 'v-')) {
emitError(context, ErrorCodes.X_MISSING_DIRECTIVE_NAME)
}
return {
type: NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE,
name,
value: value && {
type: NodeTypes.TEXT,
content: value.content,
loc: value.loc
},
loc
}
}
parseAttributeValue源码
ts
function parseAttributeValue(context: ParserContext): AttributeValue {
const start = getCursor(context)
let content: string
const quote = context.source[0]
const isQuoted = quote === `"` || quote === `'`
// source以"或'开头
if (isQuoted) {
// 消费引号
advanceBy(context, 1)
// 末尾引号索引
const endIndex = context.source.indexOf(quote)
// 如果不存在,直接解析context.source.length个字符
// 否则解析0-endIndex个字符,即endIndex个字符,然后消费最后一个引号
if (endIndex === -1) {
content = parseTextData(
context,
context.source.length,
TextModes.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE
)
} else {
content = parseTextData(context, endIndex, TextModes.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
advanceBy(context, 1)
}
} else {
// 不以引号开头
// 以非空白符、非">"字符开头的1-n个字符
const match = /^[^\t\r\n\f >]+/.exec(context.source)
// 不存在value
if (!match) {
return undefined
}
// 如果匹配到的value存在"'<=`中的任意字符,抛出错误
const unexpectedChars = /["'<=`]/g
let m: RegExpExecArray | null
while ((m = unexpectedChars.exec(match[0]))) {
emitError(
context,
ErrorCodes.UNEXPECTED_CHARACTER_IN_UNQUOTED_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE,
m.index
)
}
// 解析value
content = parseTextData(context, match[0].length, TextModes.ATTRIBUTE_VALUE)
}
return { content, isQuoted, loc: getSelection(context, start) }
}
标签解析流程图:
几个关键正则的解释:
标签名:
/^<\/?([a-z][^\t\r\n\f />]*)/i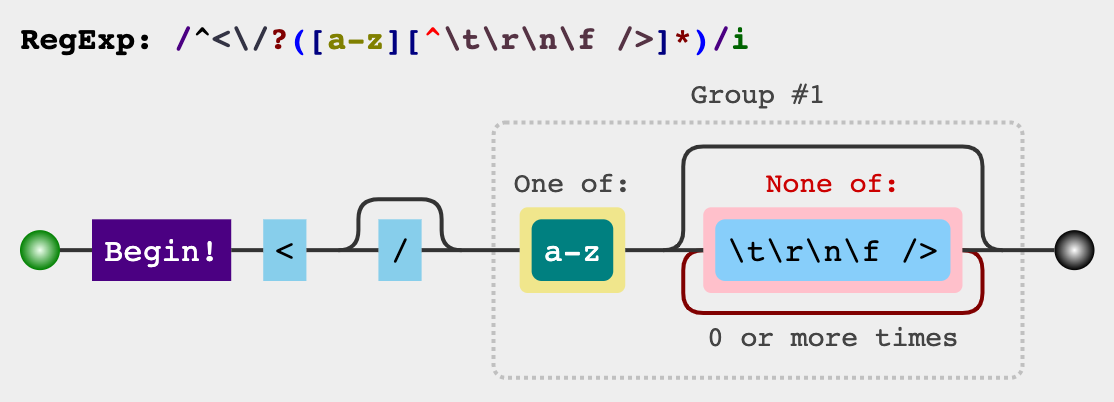 必须以
必须以<开头,后面紧跟0至1个/,然后紧跟一个字母,其后是0至多个非空白符、非/字符、非>字符。Group #1中匹配到的就是标签名。属性名:
/^[^\t\r\n\f />][^\t\r\n\f />=]*/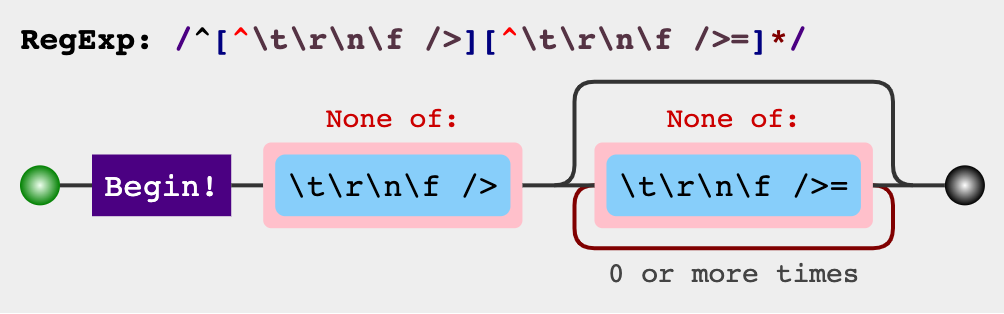 以非空白符、非
以非空白符、非/字符、非>字符开头,其后紧跟0至多个非空白符、非/字符、非>字符、非=字符。字符串能够匹配该正则,就作为属性名。是否存在属性值:
/^[\t\r\n\f ]*=/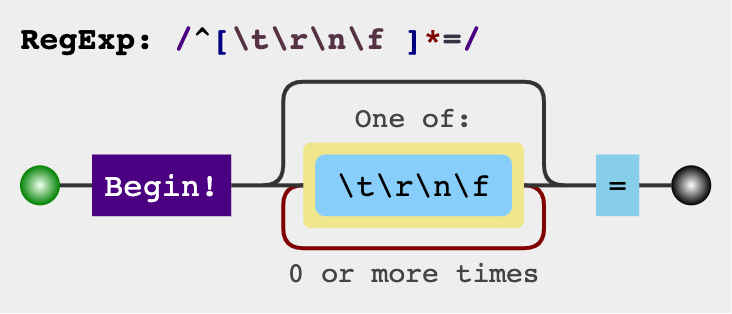 以0至多个非空白符开头,后面紧跟一个
以0至多个非空白符开头,后面紧跟一个=字符。如果字符串可以匹配该正则,那么=后可能存在属性值。属性值:
/^[^\t\r\n\f >]+/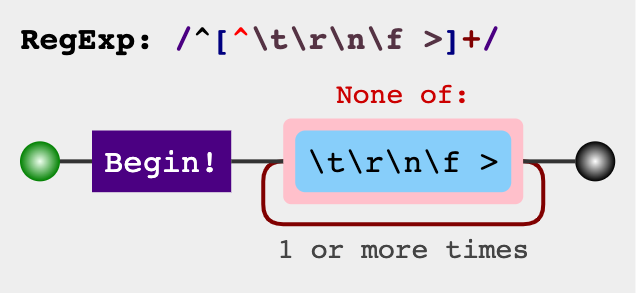 以1至多个非空白符、非
以1至多个非空白符、非>符开头。如果字符串能够匹配该正则,那么字符串可以被作为属性值。是否为指令或指令缩写:
/^(v-[A-Za-z0-9-]|:|\.|@|#)/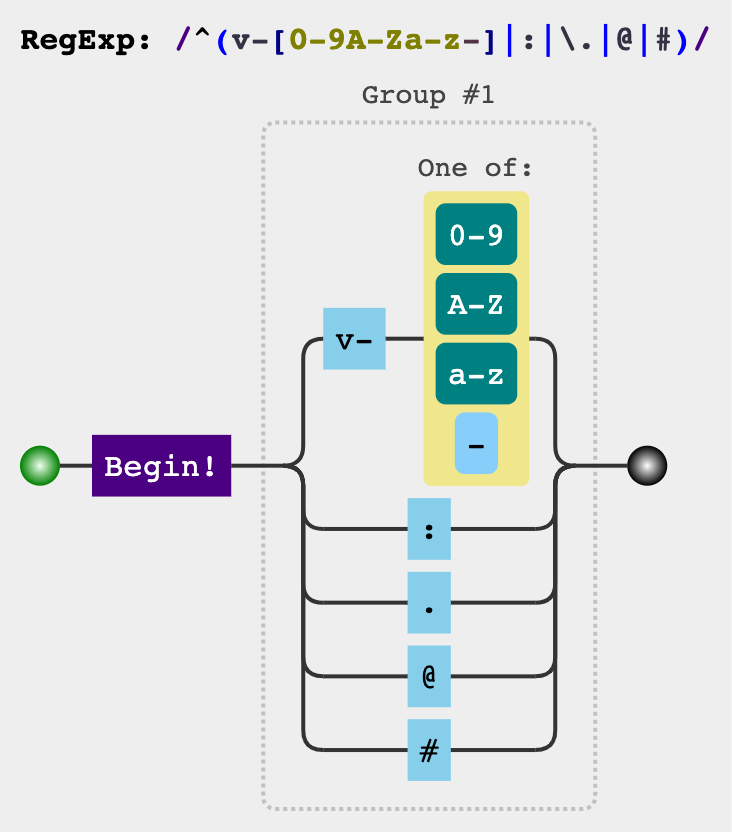 以
以v-(大写、小写)字母、v-数字、v--、:、.、@、#开头。如果属性名能够匹配该正则,那么属性名可以被作为指令。指令名及指令参数名、修饰符:
/(?:^v-([a-z0-9-]+))?(?:(?::|^\.|^@|^#)(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+))?(.+)?$/i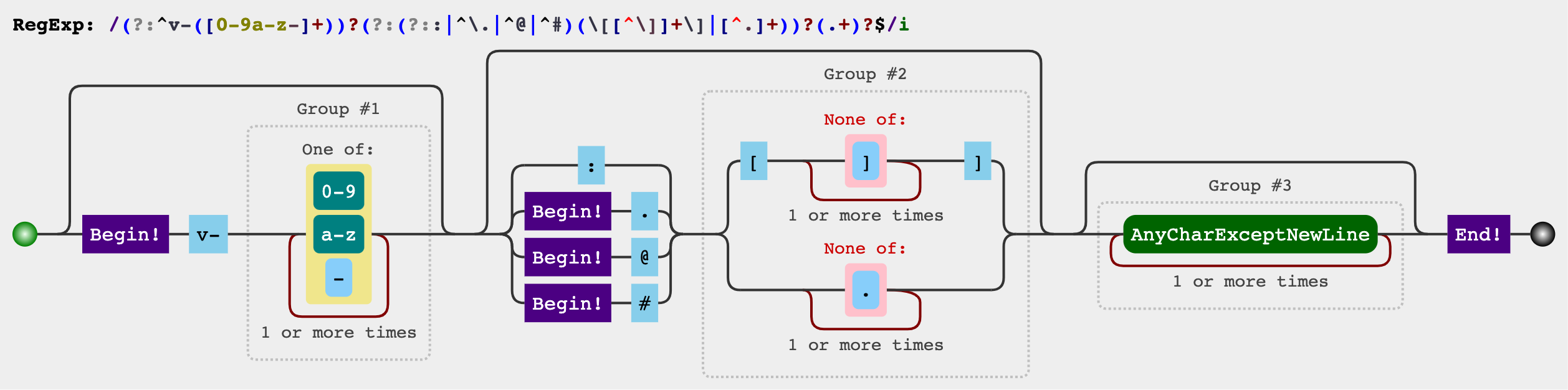 将正则分三个部分:
将正则分三个部分:(^v-([a-z0-9-]+))?、((:|^\.|^@|^#)(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+))?、(.+)?$(?:pattern)表示匹配结果不会作为结果输出,所以我们可以只关心pattern部分。第一部分:以
"v-" + 1至多个字母或数字或"-"字符开头,后面的?表示匹配0至1次第二部分:第一部分之后匹配一个
:字符,或以.、@、#字符开头。然后紧跟着"["字符 + 1至多个非"]"字符 + "]"字符格式的字符或1至多个非.字符第三部分:匹配1至多个任意字符(除了
\n、\r、\u2028、\u2029),并至此字符串结束。第三部分匹配到的字符,被作为修饰符。其中指令名为
([a-z0-9-]+)部分匹配到的字符串,即Group #1部分。指令参数为(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+)部分匹配到的字符串,即Group #2部分,其中\[[^\]]+\]匹配的是动态参数,[^\.]+匹配到的是静态参数。例如,对于字符串
v-model:[attributeName].trim字符串,([a-z0-9-]+)匹配到model,为指令名;(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+)匹配到[attributeName],attributeName被作为动态参数;(.+)?$匹配到.trim,trim被作为修饰符。
总结
template解析为AST的过程本质是个状态机,在template的解析过程中不断更新状态,完成解析,对于某些部分,会利用正则表达式进行匹配,以减少代码量。