外观
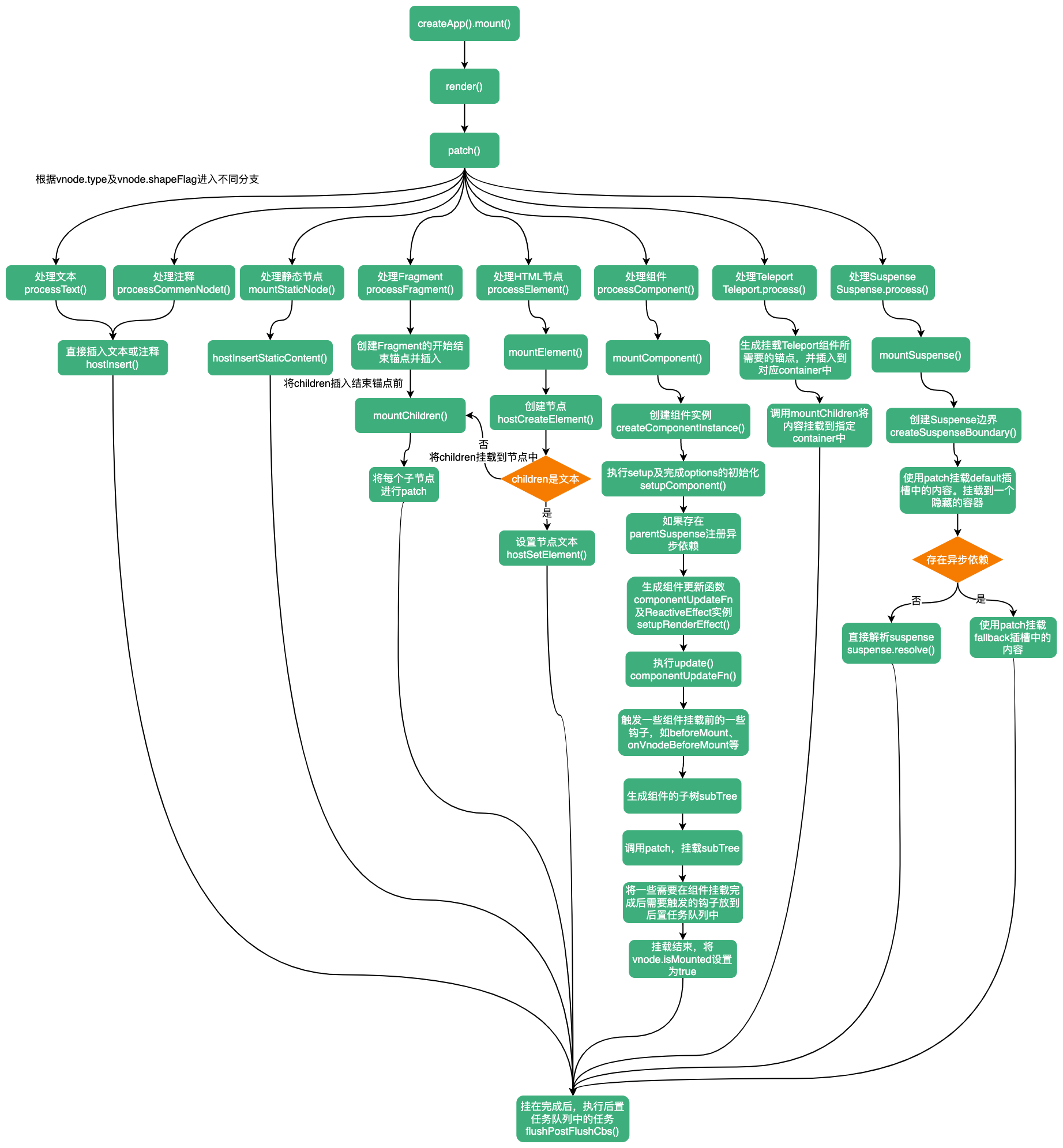
应用的挂载
在
vue项目的入口文件,我们都需要使用createApp创建一个或多个应用实例,并调用应用实例的mount方法挂载到指定的DOM元素中。
创建实例
使用createApp创建一个应用实例。它可以接受两个参数:rootComponent(根组件)、rootProps(根组件所需的props)
ts
export type CreateAppFunction<HostElement> = (
rootComponent: Component,
rootProps?: Data | null
) => App<HostElement>
源码位置:packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts
ts
export const createApp = ((...args) => {
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)
if (__DEV__) {
injectNativeTagCheck(app)
injectCompilerOptionsCheck(app)
}
const { mount } = app
app.mount = (containerOrSelector: Element | ShadowRoot | string): any => {
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
if (!container) return
const component = app._component
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
component.template = container.innerHTML
if (__COMPAT__ && __DEV__) {
for (let i = 0; i < container.attributes.length; i++) {
const attr = container.attributes[i]
if (attr.name !== 'v-cloak' && /^(v-|:|@)/.test(attr.name)) {
compatUtils.warnDeprecation(
DeprecationTypes.GLOBAL_MOUNT_CONTAINER,
null
)
break
}
}
}
}
container.innerHTML = ''
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)
if (container instanceof Element) {
container.removeAttribute('v-cloak')
container.setAttribute('data-v-app', '')
}
return proxy
}
return app
}) as CreateAppFunction<Element>
在前面文章中介绍渲染器时,我们知道在createApp中,首先会创建渲染器,并调用渲染器的createApp方法创建一个实例。接下来我们继续看createApp后续的处理。
在开发环境下,会调用injectNativeTagCheck、injectCompilerOptionsCheck两个方法。
ts
if (__DEV__) {
injectNativeTagCheck(app)
injectCompilerOptionsCheck(app)
}
其中injectNativeTagCheck方法会修改app.config.isNativeTag,一个判断tag是否为原生标签,会被用于验证组件的名称。
ts
function injectNativeTagCheck(app: App) {
Object.defineProperty(app.config, 'isNativeTag', {
value: (tag: string) => isHTMLTag(tag) || isSVGTag(tag),
writable: false
})
}
injectCompilerOptionsCheck方法主要检查编译参数的设置是否设置正确,检查的前提是isRuntimeOnly(),只在运行时时期进行检查,即不存在将模板转为渲染函数的函数compiler
ts
function injectCompilerOptionsCheck(app: App) {
if (isRuntimeOnly()) {
const isCustomElement = app.config.isCustomElement
Object.defineProperty(app.config, 'isCustomElement', {
get() {
return isCustomElement
},
set() {
warn(
`The \`isCustomElement\` config option is deprecated. Use ` +
`\`compilerOptions.isCustomElement\` instead.`
)
}
})
const compilerOptions = app.config.compilerOptions
const msg =
`The \`compilerOptions\` config option is only respected when using ` +
`a build of Vue.js that includes the runtime compiler (aka "full build"). ` +
`Since you are using the runtime-only build, \`compilerOptions\` ` +
`must be passed to \`@vue/compiler-dom\` in the build setup instead.\n` +
`- For vue-loader: pass it via vue-loader's \`compilerOptions\` loader option.\n` +
`- For vue-cli: see https://cli.vuejs.org/guide/webpack.html#modifying-options-of-a-loader\n` +
`- For vite: pass it via @vitejs/plugin-vue options. See https://github.com/vitejs/vite/tree/main/packages/plugin-vue#example-for-passing-options-to-vuecompiler-dom`
Object.defineProperty(app.config, 'compilerOptions', {
get() {
warn(msg)
return compilerOptions
},
set() {
warn(msg)
}
})
}
}
然后对app的mount方法进行了重写,并返回了app。可见我们调用createApp的mount方法就是此处的mount。接下来我们看应用是如何进行挂载的
应用的挂载
mount函数接收一个参数:containerOrSelector(一个容器,它可以是选择器、ShadowDom,也可以是个DOM节点)。
ts
app.mount = (containerOrSelector: Element | ShadowRoot | string): any => {
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
if (!container) return
const component = app._component
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
component.template = container.innerHTML
if (__COMPAT__ && __DEV__) {
for (let i = 0; i < container.attributes.length; i++) {
const attr = container.attributes[i]
if (attr.name !== 'v-cloak' && /^(v-|:|@)/.test(attr.name)) {
compatUtils.warnDeprecation(
DeprecationTypes.GLOBAL_MOUNT_CONTAINER,
null
)
break
}
}
}
}
container.innerHTML = ''
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)
if (container instanceof Element) {
container.removeAttribute('v-cloak')
container.setAttribute('data-v-app', '')
}
return proxy
}
因为containerOrSelector可能是的类型可能是字符串、ELement、ShadowRoot,所以调用normalizeContainer方法对参数进行标准化处理。
ts
function normalizeContainer(
container: Element | ShadowRoot | string
): Element | null {
if (isString(container)) {
const res = document.querySelector(container)
if (__DEV__ && !res) {
warn(
`Failed to mount app: mount target selector "${container}" returned null.`
)
}
return res
}
if (
__DEV__ &&
window.ShadowRoot &&
container instanceof window.ShadowRoot &&
container.mode === 'closed'
) {
warn(
`mounting on a ShadowRoot with \`{mode: "closed"}\` may lead to unpredictable bugs`
)
}
return container as any
}
如果没有找到对应的container直接return。
然后获取app的根组件app._component。如果根组件不是个function,也没有对应的render、tempalte属性,会将container.innerHTML作为根组件的template属性。
ts
const component = app._component
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
// 将container.innerHTML作为根组件的template属性
component.template = container.innerHTML
// 2.x兼容
if (__COMPAT__ && __DEV__) {
for (let i = 0; i < container.attributes.length; i++) {
const attr = container.attributes[i]
if (attr.name !== 'v-cloak' && /^(v-|:|@)/.test(attr.name)) {
compatUtils.warnDeprecation(
DeprecationTypes.GLOBAL_MOUNT_CONTAINER,
null
)
break
}
}
}
}
紧接着,将container中的内容设置为空,并调用mount方法生成一个proxy。如果container是个Element,会移除其v-cloak属性,并添加一个值为空的data-v-app属性,最后返回proxy。
ts
container.innerHTML = ''
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)
if (container instanceof Element) {
container.removeAttribute('v-cloak')
container.setAttribute('data-v-app', '')
}
return proxy
v-clock主要用于DOM内模板,在模板未编译完成之间,用户可能先看到原始双大括号标签,直到挂载的组件将它们替换为渲染的内容。所以通过添加v-cloak配合[v-cloak] { display: none }CSS将其暂时隐藏起来,等到实例挂载完成后,再将v-cloak移除。
mount
mount方法可以接收三个参数:rootContainer(根容器)、isHydrate(是否注水)、isSVG(根容器是否为SVG)
ts
mount(
rootContainer: HostElement,
isHydrate?: boolean,
isSVG?: boolean
): any {
if (!isMounted) {
if (__DEV__ && (rootContainer as any).__vue_app__) {
warn(
`There is already an app instance mounted on the host container.\n` +
` If you want to mount another app on the same host container,` +
` you need to unmount the previous app by calling \`app.unmount()\` first.`
)
}
const vnode = createVNode(
rootComponent as ConcreteComponent,
rootProps
)
vnode.appContext = context
if (__DEV__) {
context.reload = () => {
render(cloneVNode(vnode), rootContainer, isSVG)
}
}
if (isHydrate && hydrate) {
hydrate(vnode as VNode<Node, Element>, rootContainer as any)
} else {
render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG)
}
isMounted = true
app._container = rootContainer
;(rootContainer as any).__vue_app__ = app
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
app._instance = vnode.component
devtoolsInitApp(app, version)
}
return getExposeProxy(vnode.component!) || vnode.component!.proxy
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(
`App has already been mounted.\n` +
`If you want to remount the same app, move your app creation logic ` +
`into a factory function and create fresh app instances for each ` +
`mount - e.g. \`const createMyApp = () => createApp(App)\``
)
}
}
在mount中首先会判断是否已经挂载,如果没过载过,则进行挂载。
在挂载过程中,会先检查rootContainer.__vue_app__属性,如果存在rootContainer.__vue_app__,说明rootContainer已经挂载一个实例了,此时会进行一个提示。
ts
if (__DEV__ && (rootContainer as any).__vue_app__) {
warn(
`There is already an app instance mounted on the host container.\n` +
` If you want to mount another app on the same host container,` +
` you need to unmount the previous app by calling \`app.unmount()\` first.`
)
}
紧接着创建根组件的vnode,并将上下文对象保存到设置vnode的appContext。这里的rootComponent就是createApp时传入的rootComponent。
ts
const vnode = createVNode(
rootComponent as ConcreteComponent,
rootProps
)
vnode.appContext = context
然后渲染vnode,如果是同构渲染使用hydrate,否在调用render进行渲染,渲染完成后,将isMounted设置为true,表示已经挂载完毕,同时将rootContainer保存到app实例的_container中,并将app实例保存在rootContainer的__vue_app__属性中。
ts
if (isHydrate && hydrate) {
hydrate(vnode as VNode<Node, Element>, rootContainer as any)
} else {
render(vnode, rootContainer, isSVG)
}
isMounted = true
app._container = rootContainer
;(rootContainer as any).__vue_app__ = app
最后返回组件所暴露的一些属性或方法。vnode.component.proxy是组件实例this的代理对象
ts
return getExposeProxy(vnode.component!) || vnode.component!.proxy
getExposeProxy方法会返回instance.exposeProxy
ts
export function getExposeProxy(instance: ComponentInternalInstance) {
if (instance.exposed) {
return (
instance.exposeProxy ||
(instance.exposeProxy = new Proxy(proxyRefs(markRaw(instance.exposed)), {
get(target, key: string) {
if (key in target) {
return target[key]
} else if (key in publicPropertiesMap) {
return publicPropertiesMap[key](instance)
}
}
}))
)
}
}
render
挂载过程调用了一个render方法或hydrate进行渲染。此处我们继续看下render函数如何将vnode渲染为真实DOM的。
在介绍渲染器时,我们知道渲染器中有个createApp方法,这个方法会在创建app实例时被首先调用。createApp方法通过一个createAppAPI函数生成,这个函数接收两个参数:render、hydrate,这里的render就是在挂载过程中调用的渲染函数。
ts
function baseCreateRenderer(
options: RendererOptions,
createHydrationFns?: typeof createHydrationFunctions
): any {
// ...
return {
render,
hydrate,
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate)
}
}
来看下render函数的实现:
ts
const render: RootRenderFunction = (vnode, container, isSVG) => {
if (vnode == null) {
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true)
}
} else {
patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container, null, null, null, isSVG)
}
flushPostFlushCbs()
container._vnode = vnode
}
render函数接收三个参数::vnode(需要挂载的虚拟DOM)、container(需要渲染到的容器)、isSVG(被渲染到的容器是否为SVG)
当被传入的vnode为null时,说明什么都不渲染,这时会检查container中是否存在_vnode,如果存在调用unmount卸载函数。如果传入的vnode不为null,会调用patch函数进行更新,也可以称为打补丁。最后执行flushPostFlushCbs()(如果此时有等待中的前置任务和后置任务,需要执行这些任务,如通过watchEffect、watchPostEffect添加的effect,还有mounted等钩子),并将vnode添加到container._vnode中。
由于在挂载过程中,会向render传入根组件的vnode,所以继续调用patch方法。
patch
patch函数可以接收9个参数:
n1:旧的vnoden2:新的vnodecontainer:需要更新的容器anchor:锚点parentComponent:父组件parentSuspense:父SuspenceisSVG:容器是否为SVGslotScopeIdsoptimized:是否开启优化模式
patch完整代码
ts
const patch: PatchFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = __DEV__ && isHmrUpdating ? false : !!n2.dynamicChildren
) => {
if (n1 === n2) {
return
}
// patching & not same type, unmount old tree
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
anchor = getNextHostNode(n1)
unmount(n1, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
n1 = null
}
if (n2.patchFlag === PatchFlags.BAIL) {
optimized = false
n2.dynamicChildren = null
}
const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
switch (type) {
case Text:
processText(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Comment:
processCommentNode(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Static:
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG)
} else if (__DEV__) {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG)
}
break
case Fragment:
processFragment(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
break
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
processElement(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
;(type as typeof TeleportImpl).process(
n1 as TeleportVNode,
n2 as TeleportVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
internals
)
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
;(type as typeof SuspenseImpl).process(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
internals
)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn('Invalid VNode type:', type, `(${typeof type})`)
}
}
// set ref
if (ref != null && parentComponent) {
setRef(ref, n1 && n1.ref, parentSuspense, n2 || n1, !n2)
}
}
首先比较n1与n2,如果n1与n2相同,代表着新节点没有发生更新,所以直接return。在第一次挂载过程中,由于旧vnode是空的,所以会继续进行下面的操作。
ts
if (n1 === n2) {
return
}
如果旧节点不为空,而且新旧节点的节点类型不同,则需要卸载旧节点。
ts
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
// 获取锚点
anchor = getNextHostNode(n1)
// 卸载旧节点
unmount(n1, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
// 将旧节点置为空
n1 = null
}
判断两个节点类型是否一样
比较两个节点的type和key是否一致。
ts
export function isSameVNodeType(n1: VNode, n2: VNode): boolean {
if (
__DEV__ &&
n2.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT &&
hmrDirtyComponents.has(n2.type as ConcreteComponent)
) {
// HMR only: if the component has been hot-updated, force a reload.
return false
}
return n1.type === n2.type && n1.key === n2.key
}
如果新节点的patchFlag为PatchFlags.BAIL,意味着diff过程退出优化模式,这时会将optimized设置为false,并将新节点的dynamicChildren设置为null
ts
if (n2.patchFlag === PatchFlags.BAIL) {
optimized = false
n2.dynamicChildren = null
}
接着就是根据新节点的type及shapeFlag属性进行不同的分支:
ts
const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
switch (type) {
case Text: // 处理文本节点
processText(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Comment: // 处理注释节点
processCommentNode(n1, n2, container, anchor)
break
case Static: // 处理静态节点
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG)
} else if (__DEV__) {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG)
}
break
case Fragment: // 处理片段
processFragment(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
break
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) { // 处理HTML节点
processElement(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) { // 处理组件,包括有状态组件及函数式组件
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) { // 处理teleport
;(type as typeof TeleportImpl).process(
n1 as TeleportVNode,
n2 as TeleportVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
internals
)
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) { // 处理suspense
;(type as typeof SuspenseImpl).process(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
internals
)
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn('Invalid VNode type:', type, `(${typeof type})`)
}
}
在应用挂载时,这里可能进入不同分支。我们这里以createApp(ComponentXXX)为例。
在render过程中,创建根vnode时,由于其type是Object,所以vnode.shapeFlag属性为ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT(ShapeFlags.COMPONENT = ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT | ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT),所以第一次patch,会执行processComponent。
processComponent
processComponent函数接收与patch相同的参数
ts
const processComponent = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
n2.slotScopeIds = slotScopeIds
if (n1 == null) {
if (n2.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE) {
;(parentComponent!.ctx as KeepAliveContext).activate(
n2,
container,
anchor,
isSVG,
optimized
)
} else {
mountComponent(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
}
} else {
updateComponent(n1, n2, optimized)
}
}
可以看到当旧节点为空时,如果新节点对应的组件已经被keep-alive了,则调用parentComponent.ctx.activate方法进行激活组件,否则调用mountComponent方法挂载组件;如果旧节点不为空,则会调用updateComponent方法更新组件。因为应用挂载时,第一次patch过程旧节点是空的,组件也没有被keep-alive,所以会继续执行mountComponent方法。
mountComponent
mountComponent接收参数和processComponent类似,只不过mountComponent参数中没有旧节点,只有initialVNode待被初始化的节点,即新节点。
mountComponent完整代码
ts
const mountComponent: MountComponentFn = (
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
const compatMountInstance =
__COMPAT__ && initialVNode.isCompatRoot && initialVNode.component
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance =
compatMountInstance ||
(initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense
))
if (__DEV__ && instance.type.__hmrId) {
registerHMR(instance)
}
if (__DEV__) {
pushWarningContext(initialVNode)
startMeasure(instance, `mount`)
}
if (isKeepAlive(initialVNode)) {
;(instance.ctx as KeepAliveContext).renderer = internals
}
// resolve props and slots for setup context
if (!(__COMPAT__ && compatMountInstance)) {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `init`)
}
setupComponent(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `init`)
}
}
// setup() is async. This component relies on async logic to be resolved
// before proceeding
if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && instance.asyncDep) {
parentSuspense && parentSuspense.registerDep(instance, setupRenderEffect)
// Give it a placeholder if this is not hydration
// TODO handle self-defined fallback
if (!initialVNode.el) {
const placeholder = (instance.subTree = createVNode(Comment))
processCommentNode(null, placeholder, container!, anchor)
}
return
}
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
if (__DEV__) {
popWarningContext()
endMeasure(instance, `mount`)
}
}
在挂载组件过程中,第一步就是创建组件实例:
ts
const compatMountInstance =
__COMPAT__ && initialVNode.isCompatRoot && initialVNode.component
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance =
compatMountInstance ||
(initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense
))
创建完组件实例后,会针对KeepAlive的vnode进行一些特殊化处理,即为instance.ctx添加一个renderer。这里忽略一些仅在开发环境下生效的代码。
ts
if (isKeepAlive(initialVNode)) {
;(instance.ctx as KeepAliveContext).renderer = internals
}
然后会调用一个setupComponent关键函数,该函数作用是在做一些组件初始化的工作,包括props、slots等的初始化、执行setup函数、options的初始化。
ts
if (!(__COMPAT__ && compatMountInstance)) {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `init`)
}
setupComponent(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `init`)
}
}
关于组件实例的创建过程及setupComponent的执行可以参考:组件实例的创建过程
接着,会处理Suspense。如果存在parentSuspense,异步setup的返回值会作为依赖注册到parentSuspense中。
ts
if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && instance.asyncDep) {
parentSuspense && parentSuspense.registerDep(instance, setupRenderEffect)
// 如果initialVNode.el不为空创建一个占位符
// TODO handle self-defined fallback
if (!initialVNode.el) {
const placeholder = (instance.subTree = createVNode(Comment))
processCommentNode(null, placeholder, container!, anchor)
}
return
}
然后调用一个setupRenderEffect函数。
ts
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
)
setupRenderEffect
setupRenderEffect完整代码
ts
const setupRenderEffect: SetupRenderEffectFn = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | null | undefined
const { el, props } = initialVNode
const { bm, m, parent } = instance
const isAsyncWrapperVNode = isAsyncWrapper(initialVNode)
toggleRecurse(instance, false)
// beforeMount hook
if (bm) {
invokeArrayFns(bm)
}
// onVnodeBeforeMount
if (
!isAsyncWrapperVNode &&
(vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeBeforeMount)
) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parent, initialVNode)
}
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
instance.emit('hook:beforeMount')
}
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
if (el && hydrateNode) {
// vnode has adopted host node - perform hydration instead of mount.
const hydrateSubTree = () => {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `hydrate`)
}
hydrateNode!(
el as Node,
instance.subTree,
instance,
parentSuspense,
null
)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `hydrate`)
}
}
if (isAsyncWrapperVNode) {
;(initialVNode.type as ComponentOptions).__asyncLoader!().then(
// note: we are moving the render call into an async callback,
// which means it won't track dependencies - but it's ok because
// a server-rendered async wrapper is already in resolved state
// and it will never need to change.
() => !instance.isUnmounted && hydrateSubTree()
)
} else {
hydrateSubTree()
}
} else {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
patch(
null,
subTree,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
initialVNode.el = subTree.el
}
// mounted hook
if (m) {
queuePostRenderEffect(m, parentSuspense)
}
// onVnodeMounted
if (
!isAsyncWrapperVNode &&
(vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeMounted)
) {
const scopedInitialVNode = initialVNode
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook!, parent, scopedInitialVNode),
parentSuspense
)
}
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => instance.emit('hook:mounted'),
parentSuspense
)
}
// activated hook for keep-alive roots.
// #1742 activated hook must be accessed after first render
// since the hook may be injected by a child keep-alive
if (
initialVNode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE ||
(parent &&
isAsyncWrapper(parent.vnode) &&
parent.vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_SHOULD_KEEP_ALIVE)
) {
instance.a && queuePostRenderEffect(instance.a, parentSuspense)
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => instance.emit('hook:activated'),
parentSuspense
)
}
}
instance.isMounted = true
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
devtoolsComponentAdded(instance)
}
// #2458: deference mount-only object parameters to prevent memleaks
initialVNode = container = anchor = null as any
} else {
// updateComponent
// This is triggered by mutation of component's own state (next: null)
// OR parent calling processComponent (next: VNode)
let { next, bu, u, parent, vnode } = instance
let originNext = next
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | null | undefined
if (__DEV__) {
pushWarningContext(next || instance.vnode)
}
// Disallow component effect recursion during pre-lifecycle hooks.
toggleRecurse(instance, false)
if (next) {
next.el = vnode.el
updateComponentPreRender(instance, next, optimized)
} else {
next = vnode
}
// beforeUpdate hook
if (bu) {
invokeArrayFns(bu)
}
// onVnodeBeforeUpdate
if ((vnodeHook = next.props && next.props.onVnodeBeforeUpdate)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parent, next, vnode)
}
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
instance.emit('hook:beforeUpdate')
}
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
// render
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
const nextTree = renderComponentRoot(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
const prevTree = instance.subTree
instance.subTree = nextTree
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
patch(
prevTree,
nextTree,
// parent may have changed if it's in a teleport
hostParentNode(prevTree.el!)!,
// anchor may have changed if it's in a fragment
getNextHostNode(prevTree),
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
next.el = nextTree.el
if (originNext === null) {
// self-triggered update. In case of HOC, update parent component
// vnode el. HOC is indicated by parent instance's subTree pointing
// to child component's vnode
updateHOCHostEl(instance, nextTree.el)
}
// updated hook
if (u) {
queuePostRenderEffect(u, parentSuspense)
}
// onVnodeUpdated
if ((vnodeHook = next.props && next.props.onVnodeUpdated)) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook!, parent, next!, vnode),
parentSuspense
)
}
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
queuePostRenderEffect(
() => instance.emit('hook:updated'),
parentSuspense
)
}
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
devtoolsComponentUpdated(instance)
}
if (__DEV__) {
popWarningContext()
}
}
}
// create reactive effect for rendering
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(
componentUpdateFn,
() => queueJob(update),
instance.scope // track it in component's effect scope
))
const update: SchedulerJob = (instance.update = () => effect.run())
update.id = instance.uid
// allowRecurse
// #1801, #2043 component render effects should allow recursive updates
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
if (__DEV__) {
effect.onTrack = instance.rtc
? e => invokeArrayFns(instance.rtc!, e)
: void 0
effect.onTrigger = instance.rtg
? e => invokeArrayFns(instance.rtg!, e)
: void 0
update.ownerInstance = instance
}
update()
}
setupRenderEffect看似很长,但将componentUpdateFn折叠起来,逻辑就清晰多了。
ts
const setupRenderEffect: SetupRenderEffectFn = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
// 组件更新的副作用函数
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
// ...
}
// 创建一个关于渲染的ReactiveEffect
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(
componentUpdateFn,
() => queueJob(update), // 一个调度器,依赖被触发时会执行(将updata加入到queue队列中)
instance.scope // 在组件作用域内进行依赖追踪
))
// 一个更新函数,这个更新函数中会执行effect.run方法
const update: SchedulerJob = (instance.update = () => effect.run())
update.id = instance.uid
// 组件渲染允许递归更新
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
if (__DEV__) {
effect.onTrack = instance.rtc
? e => invokeArrayFns(instance.rtc!, e)
: void 0
effect.onTrigger = instance.rtg
? e => invokeArrayFns(instance.rtg!, e)
: void 0
update.ownerInstance = instance
}
// 手动执行更新函数
update()
}
setupRenderEffect主要,使用组件更新函数创建一个ReactiveEffect对象,然后声明一个update函数,并手动调用update函数。
由于update函数中执行了effect.run(),我们知道ReactiveEffect的实例方法run最终会调用副作用函数,以进行依赖的收集。所以继续执行componentUpdateFn函数。
componentUpdateFn
在componentUpdateFn中分了两个分支:instance未挂载及instance已经挂载。
因为此时instance还未挂载,所以进入instance未挂载分支,进行挂载组件。
接下来,我们详细看下组件时如何进行挂载的。
首先声明一些变量:
ts
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | null | undefined
const { el, props } = initialVNode
// bm:beforeMount钩子
// m:mounted钩子
// parent父组件实例
const { bm, m, parent } = instance
// 是否为AsyncComponentWrapper,通过defineAsyncComponent定义的组件会被AsyncComponentWrapper包裹
const isAsyncWrapperVNode = isAsyncWrapper(initialVNode)
toggleRecurse(instance, false)
然后执行beforeMount及onVnodeBeforeMount钩子:
ts
// beforeMount钩子
if (bm) {
invokeArrayFns(bm)
}
// onVnodeBeforeMount钩子
if (
!isAsyncWrapperVNode &&
(vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeBeforeMount)
) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parent, initialVNode)
}
// vue2中以hook:beforeMount方式添加的钩子函数
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_EVENT_HOOKS, instance)
) {
instance.emit('hook:beforeMount')
}
toggleRecurse(instance, true)
接着会执行renderComponentRoot函数,获取当前组件的子虚拟dom树,并挂载子树。
ts
if (el && hydrateNode) {
// ...
} else {
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
// 获取实例的子节点
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance))
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `render`)
}
if (__DEV__) {
startMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
// 递归挂载subTree
patch(
null,
subTree,
container,
anchor,
instance,
parentSuspense,
isSVG
)
if (__DEV__) {
endMeasure(instance, `patch`)
}
initialVNode.el = subTree.el
}
renderComponentRoot完整代码
ts
export function renderComponentRoot(
instance: ComponentInternalInstance
): VNode {
const {
type: Component,
vnode,
proxy,
withProxy,
props,
propsOptions: [propsOptions],
slots,
attrs,
emit,
render,
renderCache,
data,
setupState,
ctx,
inheritAttrs
} = instance
let result
let fallthroughAttrs
// 设置当前正在渲染的实例
const prev = setCurrentRenderingInstance(instance)
if (__DEV__) {
accessedAttrs = false
}
// 执行render函数
try {
if (vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) { // 有状态组件
const proxyToUse = withProxy || proxy
// 执行render函数
result = normalizeVNode(
render!.call(
proxyToUse,
proxyToUse!,
renderCache,
props,
setupState,
data,
ctx
)
)
fallthroughAttrs = attrs
} else { // 函数式组件
const render = Component as FunctionalComponent
// in dev, mark attrs accessed if optional props (attrs === props)
if (__DEV__ && attrs === props) {
markAttrsAccessed()
}
// 执行render函数
result = normalizeVNode(
render.length > 1
? render(
props,
__DEV__
? {
get attrs() {
markAttrsAccessed()
return attrs
},
slots,
emit
}
: { attrs, slots, emit }
)
: render(props, null as any /* we know it doesn't need it */)
)
// 如果函数式组件定义了props,fallthroughAttrs就是attrs,否则fallthroughAttrs中只包含class、style及on开头的属性
fallthroughAttrs = Component.props
? attrs
: getFunctionalFallthrough(attrs)
}
} catch (err) {
blockStack.length = 0
handleError(err, instance, ErrorCodes.RENDER_FUNCTION)
result = createVNode(Comment)
}
// 合并attr
// in dev mode, comments are preserved, and it's possible for a template
// to have comments along side the root element which makes it a fragment
let root = result
let setRoot: SetRootFn = undefined
if (
__DEV__ &&
result.patchFlag > 0 &&
result.patchFlag & PatchFlags.DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT
) {
;[root, setRoot] = getChildRoot(result)
}
// 允许透传attr
if (fallthroughAttrs && inheritAttrs !== false) {
const keys = Object.keys(fallthroughAttrs)
const { shapeFlag } = root
if (keys.length) {
if (shapeFlag & (ShapeFlags.ELEMENT | ShapeFlags.COMPONENT)) { // root是普通HTML元素或组件
if (propsOptions && keys.some(isModelListener)) { // keys中存在onUpdate:开头的属性
// 该操作会保留fallthroughAttrs中非onUpdate:开头的属性及以onUpdate:开头但不在propsOptions中的属性
fallthroughAttrs = filterModelListeners(
fallthroughAttrs,
propsOptions
)
}
// 复制root,目的是合并root.props与fallthroughAttrs
root = cloneVNode(root, fallthroughAttrs)
} else if (__DEV__ && !accessedAttrs && root.type !== Comment) { // 其他情况,如果root不是注释,attrs不会被继承
const allAttrs = Object.keys(attrs)
const eventAttrs: string[] = []
const extraAttrs: string[] = []
for (let i = 0, l = allAttrs.length; i < l; i++) {
const key = allAttrs[i]
if (isOn(key)) {
// ignore v-model handlers when they fail to fallthrough
if (!isModelListener(key)) {
// remove `on`, lowercase first letter to reflect event casing
// accurately
eventAttrs.push(key[2].toLowerCase() + key.slice(3))
}
} else {
extraAttrs.push(key)
}
}
if (extraAttrs.length) {
warn(
`Extraneous non-props attributes (` +
`${extraAttrs.join(', ')}) ` +
`were passed to component but could not be automatically inherited ` +
`because component renders fragment or text root nodes.`
)
}
if (eventAttrs.length) {
warn(
`Extraneous non-emits event listeners (` +
`${eventAttrs.join(', ')}) ` +
`were passed to component but could not be automatically inherited ` +
`because component renders fragment or text root nodes. ` +
`If the listener is intended to be a component custom event listener only, ` +
`declare it using the "emits" option.`
)
}
}
}
}
// 兼容模式下开启INSTANCE_ATTRS_CLASS_STYLE,会将style与class添加到root.props中
if (
__COMPAT__ &&
isCompatEnabled(DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_ATTRS_CLASS_STYLE, instance) &&
vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT &&
root.shapeFlag & (ShapeFlags.ELEMENT | ShapeFlags.COMPONENT)
) {
const { class: cls, style } = vnode.props || {}
if (cls || style) {
if (__DEV__ && inheritAttrs === false) {
warnDeprecation(
DeprecationTypes.INSTANCE_ATTRS_CLASS_STYLE,
instance,
getComponentName(instance.type)
)
}
// 将class与style添加到root.props中
root = cloneVNode(root, {
class: cls,
style: style
})
}
}
// 继承指令
if (vnode.dirs) {
if (__DEV__ && !isElementRoot(root)) {
warn(
`Runtime directive used on component with non-element root node. ` +
`The directives will not function as intended.`
)
}
// 克隆root,因为root可能是个提升的节点
root = cloneVNode(root)
// 添加指令
root.dirs = root.dirs ? root.dirs.concat(vnode.dirs) : vnode.dirs
}
// 继承transition
if (vnode.transition) {
if (__DEV__ && !isElementRoot(root)) {
warn(
`Component inside <Transition> renders non-element root node ` +
`that cannot be animated.`
)
}
root.transition = vnode.transition
}
if (__DEV__ && setRoot) {
setRoot(root)
} else {
result = root
}
// 设置当前渲染中的实例
setCurrentRenderingInstance(prev)
// 返回根节点
return result
}
renderComponentRoot函数中最重要的就是执行instance的render方法,生成instance的子vnode树。这个过程还会处理透传 Attribute。
示例
下面我们以一个例子来理解应用挂载的流程:
html
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"vue": "https://unpkg.com/vue@3.2.37/dist/vue.esm-browser.prod.js"
}
}
</script>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="module">
import { createApp, h, defineComponent, ref } from 'vue'
const ComA = defineComponent({
setup() {
return () => h('span', 'ComA')
}
})
createApp({
setup() {
return () => h('div', [ 'parent text', h(ComA) ])
}
}).mount('#app')
</script>
首先使用
createApp创建app示例,并调用其mount方法进行加载。在
app.mount方法中,因为此时app还未进行加载,所以调用render函数进行渲染。在调用render函数前会先生成根vnode。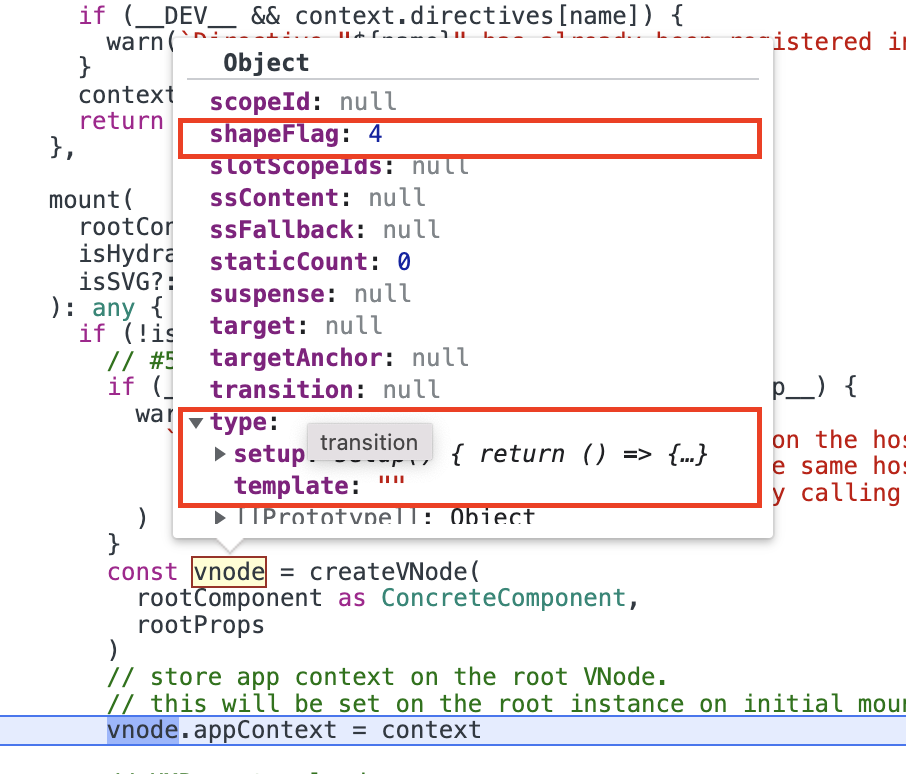
注意此时根
vnode的type为Object,及它的shapeFlag为4(即ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT),这决定了在patch过程进入哪个分支。创建完
vnode后,执行render方法,在render方法中会执行patch方法。在
patch方法中,根据vnode.type及vnode.shapeFlag属性,进入shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT分支,执行processComponent方法。在
processComponent中,由于n1为null,继续进入mountComponent方法。进入
mountComponent方法中就是组件正式挂载的流程了。其中首先就是根据vnode创建组件实例,然后调用setupComponent函数执行setup函数及options的初始化等操作。执行完
setupComponent函数后,会执行setupRenderEffect。在setupRenderEffect声明组件的渲染函数componentUpdateFn,并创建一个ReactiveEffect实例和一个update更新函数。紧跟着调用update函数,在update函数中执行effect.run,在effect.run中会执行副作用函数(即组件渲染函数),继续调用组件渲染函数componentUpdateFn。在
componentUpdateFn中进入!instance.isMounted分支,调用renderComponentRoot函数生成当前组件实例的子vnode树。在
renderComponentRoot中执行render函数,生成vnode树。注意此时vnode的type为div,shapFlag为17(ShapeFlag.ELEMENT | ShapeFlag.ARRAY_CHILDREN)。此时没有透传attr需要处理,所以透传attr过程就跳过了。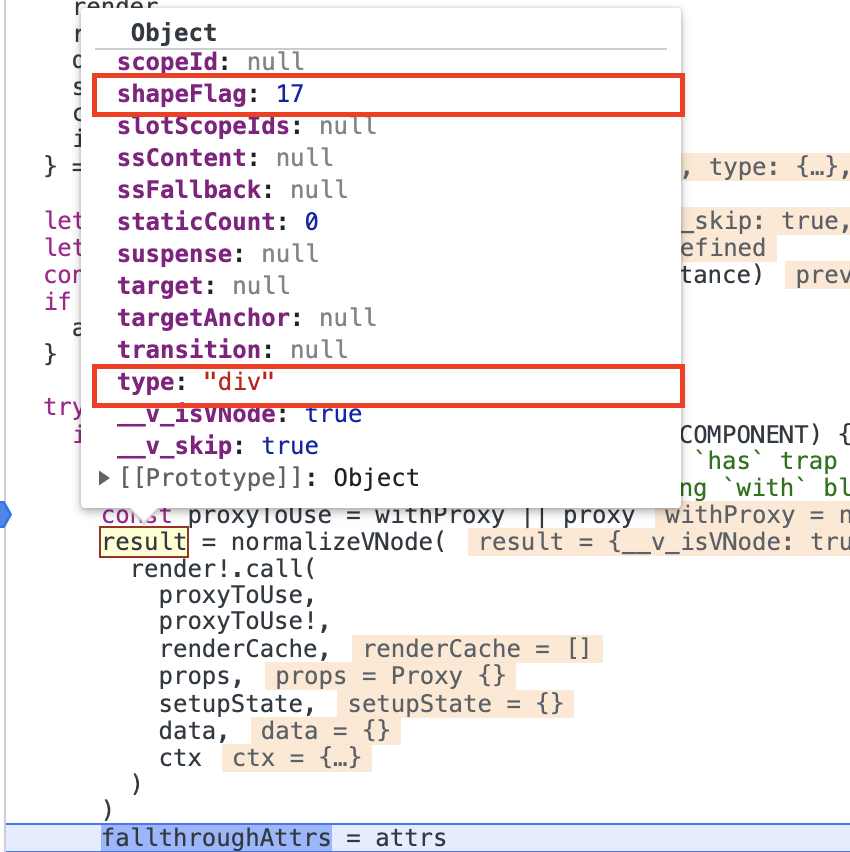
此时根组件的子
vdom树subTree已经生成,接着调用patch方法挂载subTree。这次进入
patch,根据vnode的type及shapeFlag属性,进入shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT分支,执行processElement。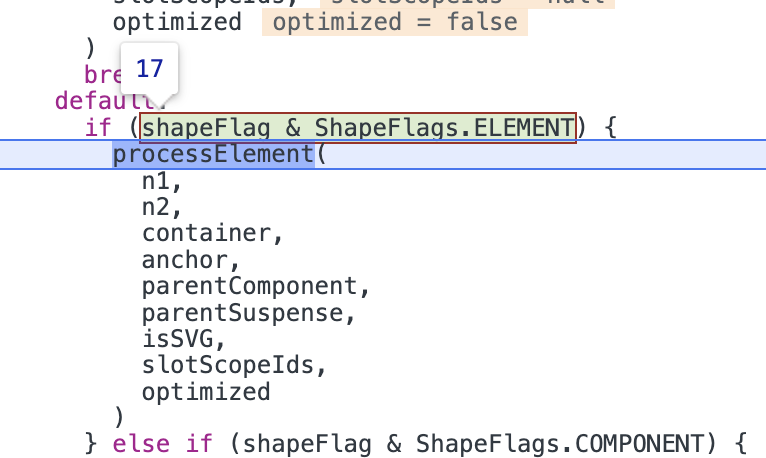
在
processElement中,由于n1为null,所以执行mountElement。进入
mountElement中,vnode.el为null,执行hostCreateElement函数创建DOM(div)。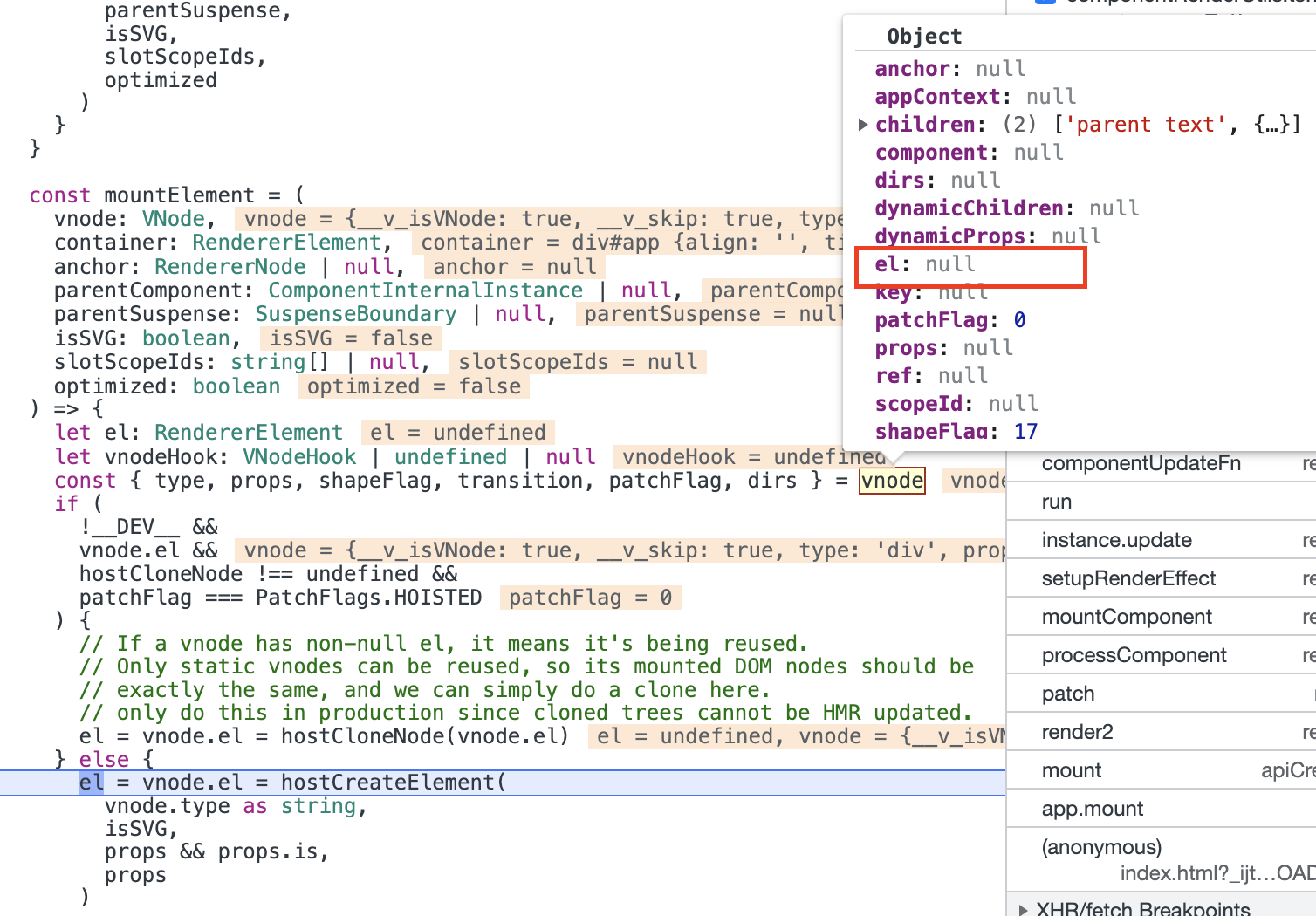
接着,因为
vnode.shapeFlag为17,17 & 16 !== 0(shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN),所以会继续执行mountChildren方法挂载子节点。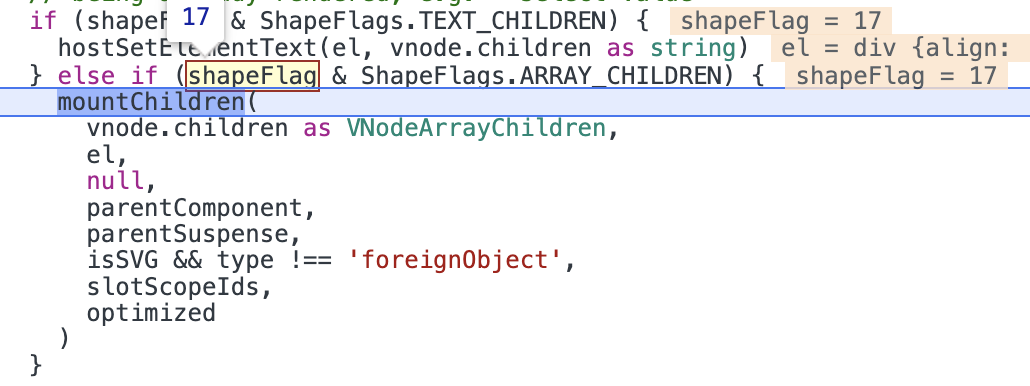
mountChildren方法会遍历children,并对每个孩子节点执行patch方法。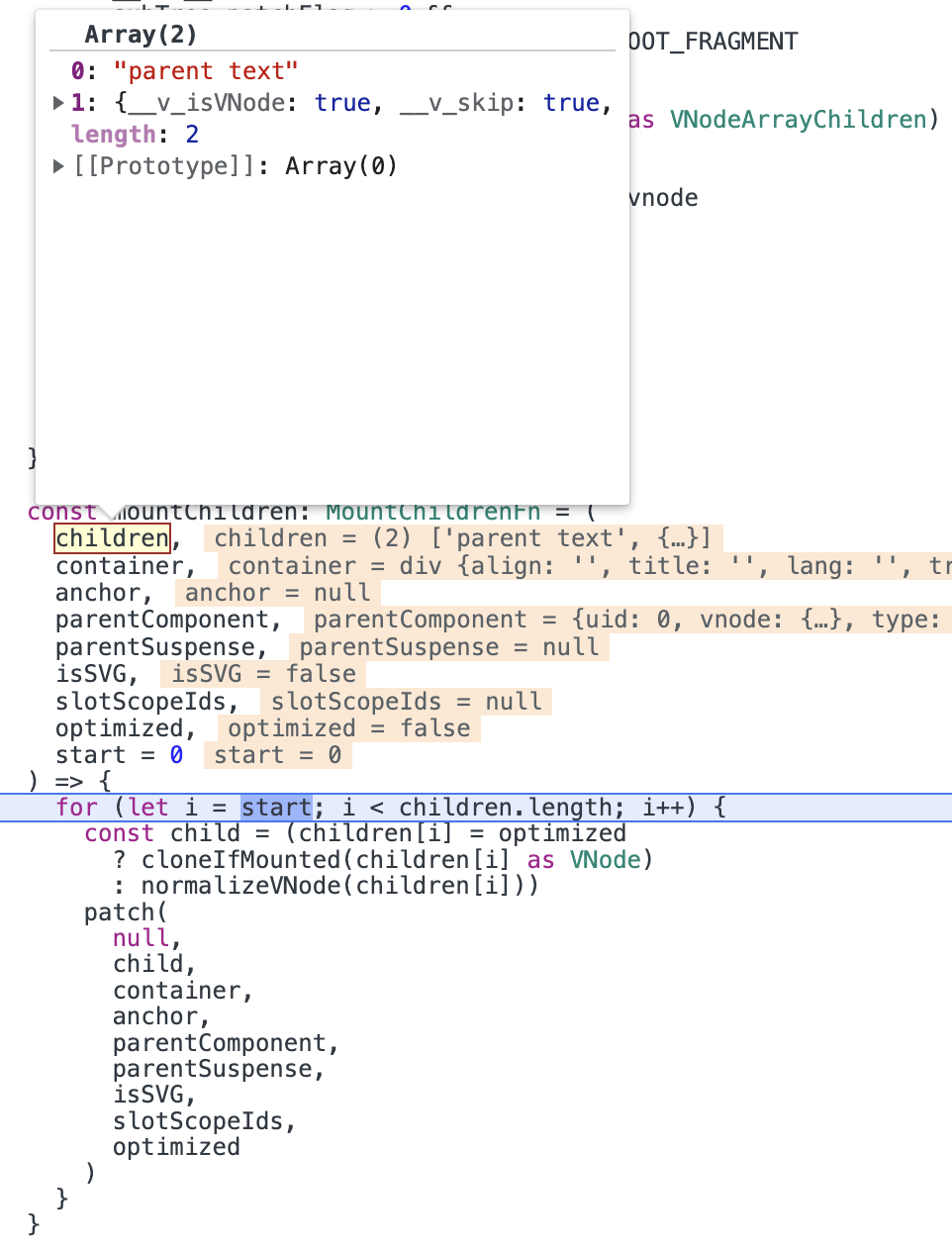
此时
children中有两个节点。第一个节点为一个type为Text的vnode(在mountChildren中调用patch前会对vnode进行标准化。在标准化的过程中会将字符串转为type为Text的vnode),在patch过程中会调用processText,最终将字符串插入到div中;第二个节点为一个type为Object的vnode,它的挂载过程和根组件挂载过程类似,这里就不详细说明了,其最终结果就是渲染出的span标签插入到div标签中。执行
hostInsert将div插入div#app中。
render执行完毕, 调用flushPostFlushCbs,执行一些mounted钩子或watch等操作。
processText
processText方法用来处理静态文本节点。该类节点对应vdom的type为Text(一个Symbol对象)。
例如以下模板经过编译后,text所对应的vdom的type就是Text。那么它在patch的过程就会进入processText中。SFC Playground
vue
<template>
<Component>text</Component>
</template>
processText源码:
ts
const processText: ProcessTextOrCommentFn = (n1, n2, container, anchor) => {
if (n1 == null) { // n1为null,意味着这是个挂载操作
// 在浏览器环境中hostInsert利用insertBefore方法进行添加子节点
hostInsert(
(n2.el = hostCreateText(n2.children as string)),
container,
anchor // 锚点,新创建的text节点被添加到该节点的前面
)
} else { // n1不为null,代表这是个更新操作
const el = (n2.el = n1.el!)
if (n2.children !== n1.children) { // 新旧节点的chidren不同时才会更新
hostSetText(el, n2.children as string)
}
}
}
processCommentNode
processCommentNode方法用来处理注释节点。该类节点对应vdom的type为Comment(一个Symbol对象)。使用createCommentVNode方法可以创建一个注释节点。
以下模板经过编译后,会使用createCommentVNode创建一个注释节点。SFC Playground
vue
<template>
<!-- Comment -->
</template>
processCommentNode源码:
ts
const processCommentNode: ProcessTextOrCommentFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor
) => {
if (n1 == null) { // 挂载注释节点
hostInsert(
(n2.el = hostCreateComment((n2.children as string) || '')),
container,
anchor
)
} else {
// 不支持动态注释
n2.el = n1.el
}
}
Static类型的vnode处理
Static类型的vnode所代表的并不一定是一个DOM节点,而是表示一个至多个连续静态DOM节点。对于Static类型的vnode,会直接进行批量插入。
vue
<template>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>7</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
</template>
上方模板经过编译后,你会发现ul中的li会使用createStaticVNode创建一个Static类型的vnode。SFC Playground
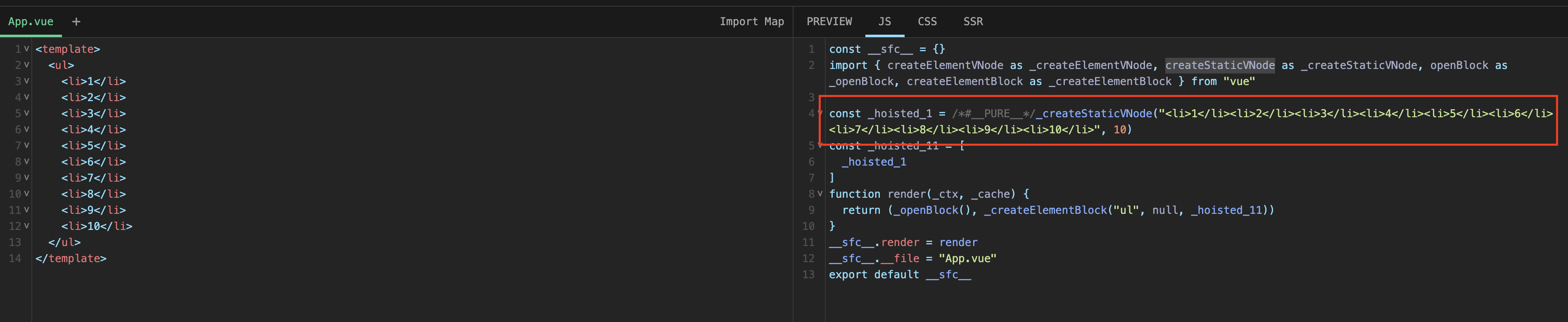
在patch中对于Static类型的vnode的处理:
ts
if (n1 == null) {
mountStaticNode(n2, container, anchor, isSVG)
} else if (__DEV__) {
patchStaticNode(n1, n2, container, isSVG)
}
挂载Static类型vnode:
ts
const mountStaticNode = (
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
isSVG: boolean
) => {
// static nodes are only present when used with compiler-dom/runtime-dom
// which guarantees presence of hostInsertStaticContent.
;[n2.el, n2.anchor] = hostInsertStaticContent!(
n2.children as string,
container,
anchor,
isSVG,
n2.el,
n2.anchor
)
}
processFragment
processFragment用来处理Fragment类型的vnode。vue3的template支持多个根组件,对于这多个根组件会使用一个Fragment类型的vnode进行表示。
如下面模板经过编译后,组件的根组件就是个Fragment类型的vnode。SFC Playground
ts
<template>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
</template>
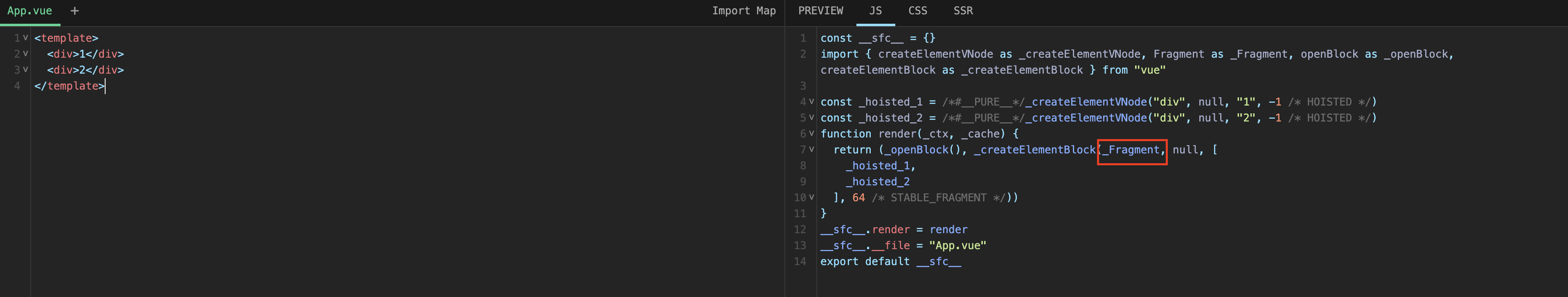
Fragment类型vnode的处理:
ts
const processFragment = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
// fragment的开始结束锚点
const fragmentStartAnchor = (n2.el = n1 ? n1.el : hostCreateText(''))!
const fragmentEndAnchor = (n2.anchor = n1 ? n1.anchor : hostCreateText(''))!
let { patchFlag, dynamicChildren, slotScopeIds: fragmentSlotScopeIds } = n2
if (
__DEV__ &&
// #5523 dev root fragment may inherit directives
(isHmrUpdating || patchFlag & PatchFlags.DEV_ROOT_FRAGMENT)
) {
// HMR updated / Dev root fragment (w/ comments), force full diff
patchFlag = 0
optimized = false
dynamicChildren = null
}
// check if this is a slot fragment with :slotted scope ids
if (fragmentSlotScopeIds) {
slotScopeIds = slotScopeIds
? slotScopeIds.concat(fragmentSlotScopeIds)
: fragmentSlotScopeIds
}
if (n1 == null) { // 挂载
// 插入fragment的开始结束锚点
hostInsert(fragmentStartAnchor, container, anchor)
hostInsert(fragmentEndAnchor, container, anchor)
// 挂载子节点
mountChildren(
n2.children as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
fragmentEndAnchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// ...
}
}
processElement
processElement用来处理原生HTML节点。
ts
const processElement = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
isSVG = isSVG || (n2.type as string) === 'svg'
if (n1 == null) {
mountElement(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
patchElement(
n1,
n2,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
}
mountElement源码:
ts
const mountElement = (
vnode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
let el: RendererElement
let vnodeHook: VNodeHook | undefined | null
const { type, props, shapeFlag, transition, patchFlag, dirs } = vnode
if (
!__DEV__ &&
vnode.el &&
hostCloneNode !== undefined &&
patchFlag === PatchFlags.HOISTED
) {
// 如果vnode存在el属性,意味着vnode被重用了。
// 如果vnode是静态节点,我们可以通过拷贝vnode.el,重用vnode.el
el = vnode.el = hostCloneNode(vnode.el)
} else { // 否则根据vnode创建DOM,并将DOM添加到vnode.el中
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(
vnode.type as string,
isSVG,
props && props.is,
props
)
// 先挂载children,因为某些props可能依赖孩子节点,如<select value>
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) { // 子节点是文本,直接创建文本DOM
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children as string)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) { // 自己节点是数组,调用mountChildren挂载子节点
mountChildren(
vnode.children as VNodeArrayChildren,
el,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG && type !== 'foreignObject',
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
// 执行vnode中的所有指令的created钩子
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'created')
}
// 为DOM添加props
if (props) {
for (const key in props) {
if (key !== 'value' && !isReservedProp(key)) { // key不是value,也不是vue中保留的props,如空字符串、ref、key等
hostPatchProp(
el,
key,
null,
props[key],
isSVG,
vnode.children as VNode[],
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
unmountChildren
)
}
}
// 一些属性应该在value之前被设置,如min/max
if ('value' in props) {
hostPatchProp(el, 'value', null, props.value)
}
// vnode挂载前钩子
if ((vnodeHook = props.onVnodeBeforeMount)) {
invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, vnode)
}
}
// scopeId
setScopeId(el, vnode, vnode.scopeId, slotScopeIds, parentComponent)
}
if (__DEV__ || __FEATURE_PROD_DEVTOOLS__) {
Object.defineProperty(el, '__vnode', {
value: vnode,
enumerable: false
})
Object.defineProperty(el, '__vueParentComponent', {
value: parentComponent,
enumerable: false
})
}
// 执行vnode中的所有指令的beforeMount钩子
if (dirs) {
invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'beforeMount')
}
// #1583 For inside suspense + suspense not resolved case, enter hook should call when suspense resolved
// #1689 For inside suspense + suspense resolved case, just call it
// 执行transition的beforeEnter钩子
const needCallTransitionHooks =
(!parentSuspense || (parentSuspense && !parentSuspense.pendingBranch)) &&
transition &&
!transition.persisted
if (needCallTransitionHooks) {
transition!.beforeEnter(el)
}
// 插入el
hostInsert(el, container, anchor)
// 有需要执行的vnodeMounted钩子或transition.enter钩子或指令的mounted钩子时
// 将这些钩子的执行放入pendingPostFlushCbs队列中,等到DOM更新后执行
if (
(vnodeHook = props && props.onVnodeMounted) ||
needCallTransitionHooks ||
dirs
) {
queuePostRenderEffect(() => {
vnodeHook && invokeVNodeHook(vnodeHook, parentComponent, vnode)
needCallTransitionHooks && transition!.enter(el)
dirs && invokeDirectiveHook(vnode, null, parentComponent, 'mounted')
}, parentSuspense)
}
}
挂载Teleport
Teleport组件在被转为vnode后,其shapeFlag为ShapeFlags.TELEPORT。对于Teleport的挂载,处理如下:
ts
export const TeleportImpl = {
__isTeleport: true,
process(
n1: TeleportVNode | null,
n2: TeleportVNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
internals: RendererInternals
) {
const {
mc: mountChildren,
pc: patchChildren,
pbc: patchBlockChildren,
o: { insert, querySelector, createText, createComment }
} = internals
// 是否禁用Teleport
const disabled = isTeleportDisabled(n2.props)
let { shapeFlag, children, dynamicChildren } = n2
if (__DEV__ && isHmrUpdating) {
optimized = false
dynamicChildren = null
}
if (n1 == null) { // 挂载Teleport
// teleport DOM位置(行内位置):
// <div>placeholder | teleport | mainAnchor</div>
// target中的位置
// <target>teleport | targetAnchor</target>
// teleport开始的位置
const placeholder = (n2.el = __DEV__
? createComment('teleport start')
: createText(''))
// teleport结束的位置
const mainAnchor = (n2.anchor = __DEV__
? createComment('teleport end')
: createText(''))
// 将placeholder、mainAnchor先后插入到container中
insert(placeholder, container, anchor)
insert(mainAnchor, container, anchor)
// 需要挂载的到的目标
const target = (n2.target = resolveTarget(n2.props, querySelector))
// 挂载目标的锚点,被挂载的内容会被挂载在锚点前面
const targetAnchor = (n2.targetAnchor = createText(''))
if (target) {
// 向目标中插入锚点
insert(targetAnchor, target)
// #2652 we could be teleporting from a non-SVG tree into an SVG tree
isSVG = isSVG || isTargetSVG(target)
} else if (__DEV__ && !disabled) {
warn('Invalid Teleport target on mount:', target, `(${typeof target})`)
}
const mount = (container: RendererElement, anchor: RendererNode) => {
// Teleport总是具有数组孩子,所有调用mountChildren进行挂载
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(
children as VNodeArrayChildren,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
}
// 如果禁用了teleport,内容会被挂载到container中
// 否则挂载到target中
if (disabled) {
mount(container, mainAnchor)
} else if (target) {
mount(target, targetAnchor)
}
} else {
// ...
}
},
// ...
}
挂载Suspence
Suspense组件在被转为vnode后,其shapeFlag为ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE。对于Suspense的挂载,处理如下:
ts
export const SuspenseImpl = {
name: 'Suspense',
__isSuspense: true,
process(
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
// platform-specific impl passed from renderer
rendererInternals: RendererInternals
) {
if (n1 == null) {
mountSuspense(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals
)
} else {
patchSuspense(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals
)
}
},
// ...
}
Suspence的挂载通过mountSuspense函数进行:
ts
function mountSuspense(
vnode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
rendererInternals: RendererInternals
) {
const {
p: patch,
o: { createElement }
} = rendererInternals
// 一个暂时存放suspense内容的div
const hiddenContainer = createElement('div')
// 创建suspense的边界
const suspense = (vnode.suspense = createSuspenseBoundary(
vnode,
parentSuspense,
parentComponent,
container,
hiddenContainer,
anchor,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals
))
// 挂载suspense中default插槽对应的vnode。注意这里挂载到的是hiddenContainer
patch(
null,
(suspense.pendingBranch = vnode.ssContent!),
hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds
)
// suspense存在异步依赖
if (suspense.deps > 0) {
// 触发pending、fallback事件
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onPending')
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onFallback')
// 挂载 fallback vnode,这里直接挂载到container上了
patch(
null,
vnode.ssFallback!,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
isSVG,
slotScopeIds
)
// 设置suspense中当前被激活的分支
setActiveBranch(suspense, vnode.ssFallback!)
} else {
// Suspense没有异步依赖,只需要解析即可
suspense.resolve()
}
}
function setActiveBranch(suspense: SuspenseBoundary, branch: VNode) {
// 指定当前被激活的分支
suspense.activeBranch = branch
const { vnode, parentComponent } = suspense
// suspense对应vnode的el指向当前激活分支对应的el
const el = (vnode.el = branch.el)
// 如果suspense是组件的根节点,递归更新HOC el
if (parentComponent && parentComponent.subTree === vnode) {
parentComponent.vnode.el = el
updateHOCHostEl(parentComponent, el)
}
}
总结
应用实例的挂载流程: